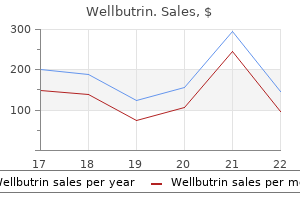
Wellbutrin 300 mg cheap with visa
Antibiotics are covered in additional element in the chapters on anti-infective remedy (see Chapter 30) mood disorder in teens 300 mg wellbutrin purchase otc. It additionally exhibits anti-inflammatory activity anxiety vs fear cheap wellbutrin 300 mg free shipping, inhibits the division and differentiation of keratinocytes, and reveals comedolytic exercise. It is out there as a cream and a gel, and the most important antagonistic results are mild and transient pruritus, burning, stinging and tingling. The main adverse effects are dry pores and skin, irritation, and bleaching of bedding and clothes. Dapsone is out there as a topical gel with the most common antagonistic results being transient oiliness, dryness, and erythema, which can be a minimal of partly as a result of the nondrug a half of the formulation. Retinoids Retinoids are vitamin A derivatives that interact with retinoid receptors to regulate gene expression in a fashion that normalizes keratinocyte differentiation and reduces hyperproliferation (giving them comedolytic activity). These numerous effects make retinoids helpful for zits, as properly as a selection of different conditions, together with psoriasis and severe rosacea. Adverse results of the topical retinoids embody erythema, desquamation, burning, and stinging. Other potential antagonistic results embody dry mucous membranes and photosensitivity. Though their systemic absorption is generally restricted, use should be prevented during being pregnant, particularly topical tazarotene, which is the most teratogenic of the three topical retinoids for pimples. Oral isotretinoin, used in severe acne, has probably critical opposed effects including psychiatric results and birth defects. The drug has mild antiinflammatory exercise and is keratolytic at larger concentrations. Salicylic acid is used as a treatment for gentle acne and is out there in plenty of over-the-counter facial washes and medicated therapy pads. The product is on the market as cleanser, cream, foam, gel, lotion, pads, suspension, and a wash. The commonest antagonistic effects embody contact dermatitis, erythema, pruritus, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and xeroderma. Agents for Superficial Bacterial Infections Several gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria may cause varied superficial pores and skin infections, corresponding to folliculitis and impetigo, in addition to deeper infections, similar to erysipelas and cellulitis. In extra severe cases, these infections can result in ulceration and systemic infections. This section covers topical antibacterial brokers that can be utilized for the remedy and prevention of certain superficial pores and skin infections. Bacitracin is generally used for the prevention of pores and skin infections after burns or minor scrapes. It is frequently found in combination merchandise with neomycin and/or polymyxin (see below). This agent is commonly used in mixture with other agents to treat skin infections brought on by gram-negative organisms. This agent is commonly formulated with different topical anti-infectives, corresponding to bacitracin and polymyxin to deal with skin infections. Common opposed effects related to the combination agents embody contact dermatitis, erythema, rash, and urticaria. The solely out there dosage form is an ointment, and the most typical adverse effects are pruritus and skin irritation. Agents Used for Rosacea Rosacea is a common inflammatory disorder affecting the central portion of facial skin. Common clinical options embody facial erythema (flushing) and inflammatory lesions which are just like acne lesions. It is out there as a gel and its main opposed effects are burning, localized heat feeling, and flushing. It is on the market as a capsule and pill, and its main adverse results include diarrhea, nausea, dyspepsia, and nasopharyngitis. It is believed to work in rosacea through anti-inflammatory or immunosuppressive effects, somewhat than via its antibacterial effects. It is available as a cream, gel, and lotion, and its main adverse results are burning, erythema, skin irritation, xeroderma, and zits vulgaris. It is out there as a cream, and its main adverse results are utility website dermatitis, worsening inflammatory lesions, site pruritus, site erythema, and a burning sensation. It is on the market as a cream, and its major opposed effects are burning, irritation, pruritus, and erythema. Agents for Pigmentation Disorders the colour of pores and skin is derived from melanin produced by melanocytes in the basal layer of the epidermis. When the melanocytes are broken, the melanin ranges are affected, which ultimately leads to pigmentation disorders. Pigmentation disorders can be widespread and have an result on many areas of the skin or they can be localized. It is commonly utilized in combination with topical retinoids to deal with the indicators of photoaging. The mechanism of action of hydroquinone is thru inhibition of the tyrosinase, an enzyme required for melanin synthesis. Hydroquinone lightens the pores and skin briefly and is commonly used as a 4% preparation. Topical methoxsalen may be used for small patches of vitiligo, and oral therapy is used for more widespread disease. Tazarotene Tazarotene is a topical retinoid, which decreases hyperpigmentation, and is typically used to treat the indicators of photoaging. The commonest opposed effects embrace itching, burning, erythema, rash, and dryness. Agents for Psoriasis Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune pores and skin illness that manifests as epidermal hyperplasia and dermal irritation, which may range from delicate to disabling. It is a condition that has important genetic associations and it tends to wax and wane, with flare-ups that might be triggered by a quantity of environmental components including stress and skin trauma. There are several forms of psoriasis, with the commonest type being plaque psoriasis. Therapies might target inflammation and the abnormal immune response, as well as epidermal hyperproliferation. It works by inhibiting phosphodiesterase-4, which ultimately leads to decreased production of a quantity of inflammatory mediators in psoriasis. Biologic agents Biologics are agents isolated from natural sources, including people, animals, and microorganisms. They could be composed of sugars, proteins, or nucleic acids or complicated combos of those substances. They are used for moderate-to-severe psoriasis and their mechanism of action results from their interplay with particular cytokines that induce or mediate T-cell effector perform, which is essential in autoimmune illnesses corresponding to psoriasis. Though each agent has specific potential risks and antagonistic results, among the antagonistic results that they share include injection or infusion reactions and elevated danger of infections because of their suppression of the immune system. Keratolytic agents Keratolytic brokers such as coal tar and salicylic acid are efficient in localized psoriasis, particularly on the scalp. Coal tar inhibits extreme pores and skin cell proliferation and may have antiinflammatory effects.
Wellbutrin 300 mg purchase without a prescription
The bone was floor to a thin part to present empty canals for blood vessels anxiety keeping me from working wellbutrin 300 mg buy with amex, lacunae for osteocytes mood disorder dsm 4 wellbutrin 300 mg cheap line, and the connecting canaliculi. The structural items of a compact bone matrix are the osteons (Haversian systems) (3, 10). Each osteon (3, 10) consists of layers of concentric lamellae (3b) organized round a central (Haversian) canal (3a). Central canals are proven in cross part (3a) and in indirect section (10, center leader). Lamellae are thin plates of bone that include osteocytes in almond-shaped spaces called lacunae (3c, 9). Canaliculi (2) penetrate the lamellae (3b, 8), anastomose with canaliculi (2) from other lacunae (3c, 9), and type a network of speaking channels with other osteocytes. Some of the canaliculi (2) open instantly into central (Haversian) canals (3a) of the osteon (3) and the marrow cavities of the bone. The small irregular areas of bone between osteons (3, 10) are the interstitial lamellae (5, 12) that characterize the remnants of eroded or transformed osteons. External circumferential lamellae (7) kind the external wall of a compact bone (beneath the periosteum) and run parallel to each other and to the long axis of the bone. The internal wall of the bone (the endosteum alongside the marrow cavity) is lined by inside circumferential lamellae (1). Osteons (3, 10) are located between the interior circumferential lamellae (1) and the exterior circumferential lamellae (7). The central canals (3a) comprise reticular connective tissue, blood vessels, and nerves. The boundary between each osteon (3, 10) is outlined by a refractile line of modified bone matrix called the cement line (4, 11). Anastomoses between central canals (3a) are called perforating (Volkmann) canals (6). Because central canals (1, 9) course longitudinally, each central canal is seen as a vertical tube that shows branching. Central canals (1, 9) are surrounded by lamellae (2, 6) with lacunae (4) and radiating canaliculi (5). The lamellae (2, 6), lacunae (4), and the osteon boundaries, the cement lines (3, 8), course parallel to the central canals (1, 9) in the compact bone. Other canals that extend in either a transverse or indirect direction are the perforating (Volkmann) canals (7). Perforating canals (7) be part of the central canals (1, 9) of osteons with the marrow cavity. Located within the center of the osteon is the dark-staining central (Haversian) canal (3) surrounded by the concentric lamellae (4). The dark, almond-shaped structures between the lamellae (4) are the lacunae (1, 7) that house osteocytes in residing bone. Tiny canaliculi (2) radiate from individual lacuna (1, 7) to adjoining lacunae and kind a system of communicating canaliculi (2) throughout the bony matrix and inside the central canal (3). In this manner, osteocytes around the osteon talk with one another and blood vessels within the central canals. Because the cartilage matrix is delicate, cartilage throughout endochondral ossification can grow in length and width by interstitial and appositional growth strategies. These cells kind ossification facilities where the mesenchyme cells differentiate into osteoblasts to form the bone. Parathyroid hormone not directly influences osteoclasts by appearing first on the osteoblasts. Calcitonin counteracts the effect of parathyroid hormone, by decreasing osteoclast exercise and calcium resorption. These muscle tissue could be recognized by their structure and function, with each muscle sort displaying morphologic and practical similarities as properly as variations. The cytoplasm of muscle cells is called sarcoplasm, and the encircling cell membrane or plasmalemma known as sarcolemma. Skeletal muscle fibers are lengthy, cylindrical, multinucleated cells, with peripheral nuclei due to the fusion of numerous mesenchymal cells known as myoblasts throughout embryonic development. Each muscle fiber is composed of smaller subunits known as myofibrils that extend the entire length of the fiber. The myofibrils, in turn, are composed of tiny myofilament models formed by the contractile thin protein actin and the thick protein myosin. In the sarcoplasm of every skeletal muscle, the arrangement of actin and myosin filaments may be very common, forming the distinct cross-striation patterns seen under a light-weight microscope as lighter-staining I bands and dark-staining A bands. Because of those cross-striations, skeletal muscle can also be referred to as striated muscle. Transmission electron microscopy illustrates the inner group of the contractile proteins in every myofibril. These high-resolution pictures show that each light I band is bisected by a dense transverse Z line (disc or band). Between the two adjacent Z strains is discovered the smallest structural and practical contractile unit of the muscle, the sarcomere. Sarcomeres are the repeating contractile units seen alongside the complete length of every myofibril and are highly attribute options of the sarcoplasm of skeletal and cardiac muscle fibers. The heart and the dark-staining a part of every sarcomere incorporates the thick (myosin) filaments, which type the A band. The peripheries and the lightstaining portion of the sarcomere comprise the light-staining, thin actin filaments. Actin and myosin filaments are precisely aligned and stabilized inside individual myofibrils and sarcomeres by accessory proteins. The skinny actin filaments are sure to the protein -actinin, which binds them to the dense Z line (band, disc). The thick myosin filaments are anchored to the Z line by the very large protein referred to as titin that positions and centers the myosin filaments on the Z line. Another massive protein, nebulin, extends the size of the skinny filaments actin, 296 anchors them to the Z line, and capabilities in regulating the length of the actin filament. Further help is offered by the protein desmin that extends from Z line of one myofibril to the adjoining myofibril, linking them together and attaching them to the sarcolemma (cell membrane). Skeletal muscles are surrounded by a dense, irregular connective tissue layer called epimysium. From the epimysium, a much less dense and thinner irregular connective tissue layer known as perimysium extends into the muscle and divides the muscle mass into smaller bundles of muscle fibers, the fascicles, and surrounds them. An even thinner layer of reticular connective tissue fibers, known as endomysium, invests particular person muscle fibers. This picture illustrates the tongue muscle fibers in both the longitudinal (upper region) and transverse (lower region) sections. Each skeletal muscle fiber (9, transverse section; 11, longitudinal section) is multinucleated.
Diseases
- Alexia (acquired dyslexia)
- Neuropathy, hereditary sensory, type I
- Urticaria pigmentosa
- Hypotelorism cleft palate hypospadias
- Neurofibromatosis type 3
- Selig Benacerraf Greene syndrome
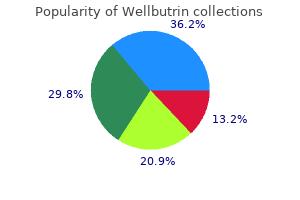
Buy discount wellbutrin 300 mg on line
Through the adept use of the spatula anxiety keeping me from sleeping wellbutrin 300 mg buy discount, some pharmacists place a curl in the heart of the floor of the ointment depression prevalence buy wellbutrin 300 mg amex. Ointments ready by fusion could also be poured while still delicate however viscous immediately into the tubes with warning to prevent stratification of the components. On a small scale, as within the extemporaneous filling of an ointment within the pharmacy, the tube could also be crammed manually. Tubes can be filled using a "caulkinggun" system the place the semisolid is filled into the chamber and the product is delivered into the tube. The tubes can then be heat-sealed using a heat-sealing crimper for a nice, skilled look. Rotary machines have 4 stations for tube feeding, cleaning, filling, and closing. Metal tubes are sealed by folding and crimping with or and not using a vinyl, latex, or lacquer sealant (5). The paper clip can then be removed and the seal shaped by the plunger is reestablished. Other dosage varieties include solutions, powders, and transdermal drug delivery methods, mentioned elsewhere on this textual content. In treating pores and skin illnesses, the drug in a medicated utility should penetrate and be retained within the skin for a while. Drug penetration into the skin is determined by a variety of elements, including the physicochemical properties of the medicinal substance, the characteristics of the pharmaceutical vehicle, and the condition of pores and skin itself. The stratum corneum is the desquamating attractive layer, a 10- to 15-m thick layer of flat, partially desiccated, lifeless epidermal cells (8, 9). On the floor is a movie of emulsified materials composed of a complex combination of sebum, sweat, and desquamating epidermal cells. The film covering the stratum corneum varies in composition, thickness, and continuity as a end result of variations in the proportion of sebum and sweat produced and the extent of their elimination through washing and sweat evaporation. The stratum corneum, being keratinized tissue, behaves as a semipermeable artificial membrane, and drug molecules can penetrate by passive diffusion. Substances with both aqueous and lipid solubility traits are good candidates for diffusion through the stratum corneum. Once through the stratum corneum, drug molecules may pass by way of the deeper epidermal tissues and into the dermis. If the drug reaches the vascularized dermal layer, it turns into obtainable for absorption into the overall circulation. Differences in emollient and occlusive results and ease of software and removing between merchandise is an element of the bottom used and product kind. As noted earlier, oleaginous bases provide higher occlusion and emollient results than do hydrophilic or water-washable bases. Pastes provide even higher occlusion and are more effective than ointments at absorbing serous discharge. Creams, usually oil-in-water emulsions, spread extra easily than ointments and are easier to remove. Unless otherwise directed, earlier than making use of a dermatologic product, the patient ought to completely clean the affected area with soap and water and dry by patting with a gentle material. Typically, about 1 to 3 mg of ointment or cream is applied per sq. centimeter of pores and skin (1). The patient must be advised if signs persist or irritation develops, use of the product should be discontinued and a physician or pharmacist consulted. It is fairly frequent for sufferers to have an allergic response, corresponding to a pores and skin rash, to a topical product on account of sensitivity to the medicinal agent or pharmaceutic ingredient. Other ophthalmic dosage types used topically include options, suspensions, and inserts, discussed elsewhere in this textual content. Systemic remedy additionally could additionally be undertaken, as in using diuretics within the adjunctive therapy of glaucoma. Petrolatum based vehicle Vehicle of water-miscible polyethylene glycols Local treatment of pores and skin infections by prone microorganisms Treatment of minor cuts, scrapes Treatment of impetigo (continued) Adrenocorticoid�Antifungal Combination Betamethasone, Lotrisone Cream (Schering) clotrimazole cream Analgesic Capsaicin cream Antiacne Tretinoin cream Zostrix Cream (Rodlen Labs) Retin-A (Ortho McNeil) 0. For medicine which are poorly absorbed by the cornea, the conjunctiva and sclera provide an alternate route (11). The cornea is a three-layered structure with a lipophilic epithelial layer, a hydrophilic stromal layer, and a less lipophilic endothelial layer on the within (11). Compared with ophthalmic options, ophthalmic ointments and gels present extended residence time on the surface of the attention, rising the duration of their floor results and bioavailability for absorption into the ocular tissues. The ointment base chosen for an ophthalmic ointment should not be irritating to the eye and must allow the diffusion of the medicinal substance throughout the secretions bathing the attention. Medicinal brokers are added to an ointment base either as an answer or as a finely micronized powder. Rendering an ophthalmic ointment sterile requires particular method and processing. For a selection of causes, the terminal sterilization of a finished ointment by standard strategies could also be problematic. Although dry heat sterilization can penetrate the ointment base, the excessive heat required could pose a risk to the stability of the drug substance and introduces the potential of separating the ointment base from the other elements (14). Rather, strict methods of aseptic processing are employed as each drug and nondrug part is rendered sterile after which aseptically weighed and incorporated in a ultimate product that meets the sterility requirement (14). These tubes have an elongated slim tip to facilitate utility of a slender band of ointment to the attention. Without touching the tip to any part of the eye, a skinny ribbon of ointment, roughly zero. Then any extra ointment ought to be wiped from the eyelids and lashes with a clear tissue. To facilitate the procedure, a affected person may sit in front of a mirror with elbows stabilized or have one other particular person administer the ointment. It is important to emphasize to the affected person that ocular products if dealt with improperly can turn into contaminated by bacteria that trigger ocular infections, which can result in severe consequences. Thus every effort should be made to keep away from touching the tip of the tube to the attention, eyelid, fingertip, or any other floor, and the ointment should be used by just one particular person. The ciliated epithelium of the nasal passage facilitates the motion of the mucous layer. The mucus accommodates lysozyme, glycoproteins, and immunoglobulins that act in opposition to bacteria and defend towards their entry into the lungs. Drugs launched into the nasal passage are primarily for local results on the mucous membranes and underlying tissues. However, drug absorption to the overall circulation does occur through the wealthy blood supply feeding the nasal lining. In addition, the nasal route holds great promise for the administration of insulin, vaccines, and a variety of other polypeptides and proteins. Ointments, creams, and gels are used for topical application to the perianal space and for insertion throughout the anal canal. They largely are used to deal with native situations of anorectal pruritus, irritation, and the pain and discomfort related to hemorrhoids. Substances applied rectally could additionally be absorbed by diffusion into the overall circulation through the network of three hemorrhoidal arteries and accompanying veins in the anal canal (16).
Safe wellbutrin 300 mg
They are characterized by small unspecified mood disorder dsm 5 buy 300 mg wellbutrin free shipping, dark-staining pyknotic nuclei and a reddish depression symptoms ehow wellbutrin 300 mg cheap otc, or eosinophilic, cytoplasm. As normoblasts (2, 23) mature, the cells lose the flexibility to divide and extrude their densely staining pyknotic nuclei to turn into erythrocytes (3). The early granulocytes initially exhibit quite a few major, or azurophilic, granules in their cytoplasm. As a end result, the immature types of neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils are morphologically indistinguishable and become recognizable only in the myelocyte stage, when specific granules seem in recognizable quantities in their cytoplasm that can be stained for recognition. In neutrophilic cells, the specific granules are solely faintly stained, and the cytoplasm appears clear or impartial. Basophilic granulocytes are hardly ever observed within the bone marrow due to their small numbers. The cytoplasm of mature basophils exhibits a bilobed nucleus and dense blue, or basophilic, granules. The granulocytic myelocytes (13, 19) exhibit a large spherical nucleus and a cytoplasm with many azurophilic granules. The myelocytes (13, 19) give rise to metamyelocytes (4, eleven, 20), whose nuclei are bean or horseshoe formed. The neutrophilic metamyelocytes (17) exhibit a deeply indented nuclei and cytoplasm with azurophilic granules and faintly stained particular granules. In contrast, a cell with bright-staining red (eosinophilic) granules within the cytoplasm is an eosinophilic myelocyte (18). The stroma of the reticular connective tissue within the bone marrow is almost obscured by hematopoietic cells. In less dense areas, the reticular connective tissue with the elongated reticular cells (16) is visible. Also, numerous thinwalled sinusoids (1, 12) and various varieties of blood vessels (14, 15) containing erythrocytes and leukocytes are present in the bone marrow. Also conspicuous 221 are the large adipose cells (5) with giant vacuoles (because of fats removal throughout part preparation) and a small, peripheral cytoplasm that surrounds the nucleus (5). Other identifiable cells in the bone marrow are the very giant megakaryocytes (9, 10) with various nuclear lobulation. One of those megakaryocytes (10) is located adjoining to a blood sinusoid, into which the fragments from its cytoplasmic extensions separate and discharged as platelets. Selected blood cells from the pink bone marrow are illustrated on the following page at the next magnification. In the erythrocytic series, the precursor cell proerythroblast (3) displays a thin rim of basophilic cytoplasm and a large, oval nucleus that 222 occupies most of the cell. Azurophilic granules are absent from the cytoplasm in all cells of the erythrocytic sequence. The proerythroblasts (3) divide to form the smaller basophilic erythroblasts (8, 16). Basophilic erythroblasts (8, 16) are characterized by a rim of basophilic cytoplasm and a decreased cell and nuclear size. The nuclear chromatin is coarse and reveals the attribute "checkerboard" pattern. Basophilic erythroblasts (8, 16) give rise to the polychromatophilic erythroblasts (12), which are comparable in size to basophilic erythroblasts (8, 16). The cytoplasm of the polychromatophilic erythroblast (12) turns into progressively less basophilic and more acidophilic as a outcome of increased hemoglobin accumulation. The nuclei of polychromatophilic erythroblasts (12) are smaller and exhibit a coarse checkerboard pattern. When the polychromatophilic cells (12) acquire a extra eosinophilic (pink) cytoplasm because of increased hemoglobin accumulation, their dimension decreases and so they turn out to be orthochromatophilic erythroblasts (late normoblasts) (1). Initially, the nucleus of orthochromatophilic erythroblasts (1) reveals a concentrated checkerboard chromatin pattern. Eventually, the nucleus decreases in size, becomes pyknotic, and is extruded from the cytoplasm, forming a biconcave-shaped cell with a bluish pink cytoplasm called a reticulocyte or young erythrocyte. With special supravital staining, a fragile reticulum is seen within the reticulocyte cytoplasm because of the remaining polyribosomes. After polyribosomes are lost from the cytoplasm, the cells turn out to be mature erythrocytes (9) and enter the systemic circulation by way of the quite a few blood channels. Erythrocytes (9) are small cells with a homogeneous eosinophilic, or pink, cytoplasm. Also seen in the bone marrow smear are different types of myelocytes and metamyelocytes of the granulocytic cell line. Myelocytes exhibit an eccentric nucleus with condensed chromatin and a less basophilic cytoplasm with few azurophilic granules. More mature myelocytes, similar to neutrophilic myelocytes (14), an eosinophilic myelocyte (15), and a uncommon basophilic myelocyte (11), show an abundance of specific granules of their barely acidophilic cytoplasm. The myelocyte is the last cell of the granulocytic line able to mitosis, after which they mature into metamyelocytes. The form of the nucleus in the neutrophilic line adjustments from oval to one with indentation, as seen in neutrophilic metamyelocytes (4). Before full 223 maturation and segmentation of the nucleus into distinct lobes, the neutrophils pass by way of a band cell (10) stage, during which the nucleus assumes a virtually uniform curved rod or band form. Mature neutrophils (13) with segmented nuclei are additionally present in the bone marrow smear, in addition to a mature eosinophil (7) with specific pink granules filling its cytoplasm. These cells measure roughly 50 to a hundred m in diameter and have a big, slightly acidophilic cytoplasm crammed with fantastic azurophilic granules. A frequent stem cell offers rise to different hematopoietic cell strains, from which arise erythrocytes, granulocytes, lymphocytes, and megakaryocytes. Because of its capacity to differentiate into all blood cells, this cell is called the pluripotential hematopoietic stem cell. The proerythroblast (1) divides to produce a smaller cell called a basophilic erythroblast (2) with a rim of basophilic cytoplasm and a more condensed nucleus without visible nucleoli. In the next stage, a smaller cell referred to as the polychromatophilic erythroblast (3) is produced. These cells present a decrease in basophilic ribosomes and an increase in the acidophilic hemoglobin content material of their cytoplasm. At this stage, the cell is known as an orthochromatophilic erythroblast (normoblast) (4). After extruding its nucleus, the orthochromatophilic erythroblast (4) becomes a reticulocyte (5) because a small variety of ribosomes could be stained in its cytoplasm. After dropping the ribosomes, 225 the reticulocyte turns into a mature erythrocyte (6). The myeloblast (7) is a small cell with a big nucleus, dispersed chromatin, three or more nucleoli, and a basophilic cytoplasm rim that lacks particular granules. As improvement progresses, the cell enlarges, acquires azurophilic granules, and turns into a promyelocyte (8, 9).

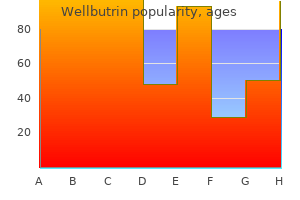
300 mg wellbutrin purchase mastercard
If the specified plasma concentration of digoxin for optimum therapeutic exercise in heart failure is 1 azor 025mg anxiety wellbutrin 300 mg cheap with visa. The extra dosage of digoxin wanted to obtain the desired plasma concentration can be calculated utilizing the equation Vd (C2 � C1) angle of depression definition english 300 mg wellbutrin purchase with amex. Most medicine exert results, each helpful and dangerous, by interacting with specialized target macromolecules referred to as receptors, that are present on or within the cell. A drug is termed an "agonist" if it binds to a site on a receptor protein and prompts it to initiate a sequence of reactions that finally result in a selected intracellular response. The drug�receptor advanced Cells have many several types of receptors, every of which is particular for a particular agonist and produces a singular response. Cardiac cell membranes, for instance, include -adrenergic receptors that bind and reply to epinephrine or norepinephrine. Cardiac cells additionally contain muscarinic receptors that bind and reply to acetylcholine. The magnitude of the mobile response is proportional to the variety of drug�receptor complexes. This idea is conceptually similar to the formation of complexes between enzyme and substrate and shares many frequent features, such as specificity of the receptor for a given agonist. Although much of this chapter centers on the interaction of medicine with specific receptors, it is important to know that not all medication exert effects by interacting with a receptor. Antacids, for instance, chemically neutralize extra gastric acid, thereby lowering stomach upset. Receptor states Receptors exist in no less than two states, inactive (R) and active (R*), which would possibly be in reversible equilibrium with one another, usually favoring the inactive state. Binding of agonists causes the equilibrium to shift from R to R* to produce a biologic impact. Some medication (partial agonists) shift the equilibrium from R to R*, however the fraction of R* is lower than that caused by an agonist. In summary, agonists, antagonists, and partial agonists are examples of molecules or ligands that bind to the activation site on the receptor and might affect the fraction of R*. Major receptor families A receptor is outlined as any biologic molecule to which a drug binds and produces a measurable response. However, the richest sources of receptors are membrane-bound proteins that transduce extracellular signals into intracellular responses. Transmembrane ligand-gated ion channels the extracellular portion of ligand-gated ion channels contains the drug-binding website. The channel is often closed till the receptor is activated by an agonist, which opens the channel for a couple of milliseconds. Depending on the ion carried out by way of these channels, these receptors mediate numerous capabilities, including neurotransmission and muscle contraction. For instance, stimulation of the nicotinic receptor by acetylcholine opens a channel that allows sodium influx and potassium outflux throughout the cell membranes of neurons or muscle cells. This change in ionic concentrations throughout the membrane generates an action potential in a neuron and contraction in skeletal and cardiac muscle. For example, local anesthetics bind to the voltage-gated sodium channel, inhibiting sodium influx and reducing neuronal conduction. There are many kinds of G proteins (for example, Gs, Gi, and Gq), however every kind are composed of three protein subunits. The and subunits are then free to work together with particular mobile effectors, normally an enzyme or an ion channel, that cause further actions throughout the cell. Often, the activated effectors produce "second messenger" molecules that further activate different effectors in the cell, inflicting a sign cascade impact. The most typical enzymelinked receptors (for instance, growth elements and insulin) possess tyrosine kinase activity. For instance, the phosphorylated insulin receptor in flip phosphorylates other proteins that now become lively. Thus, enzyme-linked receptors usually trigger a signal cascade impact like that caused by G protein�coupled receptors. The major targets of activated intracellular receptors are transcription components in the cell nucleus that regulate gene expression. The impact of drugs or endogenous ligands that activate intracellular receptors takes hours to days to occur. For example, tubulin is the target of antineoplastic agents similar to paclitaxel (see Chapter 35), the enzyme dihydrofolate reductase is the target of antimicrobials corresponding to trimethoprim (see Chapter 31), and the 50S subunit of the bacterial ribosome is the target of macrolide antibiotics such as erythromycin (see Chapter 30). Characteristics of sign transduction Signal transduction has two essential features: 1) the flexibility to amplify small indicators and 2) mechanisms to defend the cell from excessive stimulation. Signal amplification A attribute of G protein�linked and enzyme-linked receptors is the flexibility to amplify sign intensity and duration by way of the sign cascade effect. Additionally, activated G proteins persist for an extended duration than does the unique agonist�receptor complex. The binding of albuterol, for instance, might only exist for a few milliseconds, however the subsequent activated G proteins may final for lots of of milliseconds. Because of this amplification, only a fraction of the entire receptors for a particular ligand could have to be occupied to elicit a maximal response. About 99% of insulin receptors are "spare," offering an immense useful reserve that ensures that adequate amounts of glucose enter the cell. On the other hand, solely about 5% to 10% of the whole -adrenoceptors within the coronary heart are spare. Therefore, little useful reserve exists in the failing heart, as a result of most receptors must be occupied to get hold of maximum contractility. Desensitization and down-regulation of receptors Repeated or continuous administration of an agonist or antagonist typically leads to modifications within the responsiveness of the receptor. This phenomenon, known as tachyphylaxis, is often because of phosphorylation that renders receptors unresponsive to the agonist. In addition, receptors may be internalized inside the cell, making them unavailable for further agonist interaction (down-regulation). Some receptors, significantly ion channels, require a finite time following stimulation before they can be activated once more. Up-regulation of receptors could make cells extra delicate to agonists and/or extra proof against results of the antagonist. Dose�Response Relationships Agonist medication mimic the motion of the endogenous ligand for the receptor (for instance, isoproterenol mimics norepinephrine on 1 receptors of the heart). Graded dose�response relationship As the focus of a drug increases, its pharmacologic impact also gradually increases till all the receptors are occupied (the most effect). Two necessary drug traits, potency and efficacy, could be decided by graded dose�response curves. Potency Potency is a measure of the amount of drug necessary to produce an effect. For example, candesartan and irbesartan are angiotensin receptor blockers used to treat hypertension. The therapeutic dose vary for candesartan is four to 32 mg, as in comparability with 75 to 300 mg for irbesartan.
Wellbutrin 300 mg order fast delivery
Activating nicotinic receptors Inhibiting the discharge of acetylcholine Inhibiting cholinesterase enzyme Blocking muscarinic receptors Correct answer = C depression connect test discount wellbutrin 300 mg mastercard. Activation of muscarinic receptors in the detrusor muscle of the urinary bladder can promote urination in sufferers the place the tone of detrusor muscle is low depression test australia order wellbutrin 300 mg free shipping. Inhibiting cholinesterase enzyme will increase the degrees of acetylcholine, and acetylcholine can improve the tone of the detrusor muscle. Inhibiting the discharge of acetylcholine or blocking muscarinic receptors worsens urinary retention. Muscarinic agonists and drugs that increase acetylcholine ranges cause constriction of bronchial clean muscle tissue and could exacerbate asthma signs. Bethanechol and pilocarpine are muscarinic agonists, and pyridostigmine is a cholinesterase inhibitor that increases ranges of acetylcholine. Theoretically, it should relieve symptoms of asthma (not used clinically for this purpose). Muscarinic receptor activator (agonist) Muscarinic receptor inhibitor (antagonist) Pilocarpine Neostigmine Correct reply = B. Muscarinic agonists (for instance, pilocarpine) contract the round smooth muscles within the iris sphincter and constrict the pupil (miosis). Muscarinic antagonists, then again, chill out the circular smooth muscular tissues within the iris sphincter and trigger dilation of the pupil (mydriasis). Theoretically, which technique is beneficial in treating symptoms of Alzheimer illness Inhibiting cholinergic receptors in the mind Inhibiting the release of acetylcholine in the mind Inhibiting the acetylcholinesterase enzyme within the mind Activating the acetylcholinesterase enzyme in the mind Correct reply = C. She offered with diarrhea, frequent urination, convulsions, breathing difficulties, constricted pupils (miosis), and excessive salivation. Since the aged female lives on a farm and the signs are in keeping with a cholinergic disaster (usually attributable to cholinesterase inhibitors), it might be assumed that she has consumed an organophosphate pesticide (irreversible cholinesterase inhibitor). Neuromuscular blockers act by blocking nicotinic receptors on the skeletal muscle tissue. Her salivary secretion was reduced as a end result of radiation and she or he suffers from dry mouth (xerostomia). Salivary secretion could also be enhanced by activating muscarinic receptors within the salivary glands. This could be achieved in theory by utilizing a muscarinic agonist or an anticholinesterase agent. The perform of nicotinic receptors in skeletal muscles is diminished in myasthenia gravis as a outcome of the development of antibodies to nicotinic receptors (autoimmune disease). Thus, edrophonium, a reversible cholinesterase inhibitor with a brief length of action can quickly enhance skeletal muscle weak point in myasthenia gravis, serving as a diagnostic tool. Which of the following medicine or classes of medicine shall be most useful in treating poisoning with belladonna Malathion Physostigmine Muscarinic antagonists Nicotinic antagonists 179 Correct answer = B. Atropine is a aggressive muscarinic receptor antagonist that causes anticholinergic effects. Thus, anticholinesterases similar to malathion and physostigmine can counteract the consequences of atropine, in theory. The most clinically useful of those brokers are selective blockers of muscarinic receptors. The results of parasympathetic innervation are thus, interrupted by these agents, and the actions of sympathetic innervation are left unopposed. A second group of medication, the ganglionic blockers, exhibits a choice for nicotinic receptors of the sympathetic and parasympathetic ganglia. A third household of compounds, the neuromuscular blocking brokers (mostly nicotinic antagonists), intervene with transmission of efferent impulses to skeletal muscular tissues. These medicine are used as skeletal muscle relaxants in surgical anesthesia and as agents to facilitate intubation in surgical and significant care patients. Atropine Atropine [A-troe-peen] is a tertiary amine extracted from belladonna alkaloid. General actions final about 4 hours; nonetheless, effects of topical administration within the eye may persist for days. The greatest inhibitory results are seen in bronchial tissue, salivary and sweat glands, and the guts. Eye Atropine blocks muscarinic exercise in the eye, resulting in mydriasis (dilation of the pupil), unresponsiveness to mild, and cycloplegia (inability to focus for near vision). In sufferers with angle-closure glaucoma, intraocular stress might rise dangerously. Atropine and scopolamine (discussed below) are most likely essentially the most potent antispasmodic medicine available. Doses of atropine that cut back spasms also cut back saliva secretion, ocular lodging, and urination. Higher doses of atropine cause a progressive increase in heart rate by blocking M2 receptors on the sinoatrial node. Secretions Atropine blocks muscarinic receptors in the salivary glands, producing dryness of the mouth (xerostomia). Ophthalmic Topical atropine exerts both mydriatic and cycloplegic results, and it permits the measurement of refractive errors with out interference by the accommodative capability of the attention. Cardiovascular Injectable atropine is used to deal with bradycardia of varying etiologies. Antisecretory Atropine is typically used as an antisecretory agent to block secretions in the respiratory tract previous to surgery. Antidote for cholinergic agonists 186 Atropine is used for the treatment of organophosphate (insecticides, nerve gases) poisoning, of overdose of clinically used anticholinesterases corresponding to physostigmine, and in some forms of mushroom poisoning (certain mushrooms contain cholinergic substances that block cholinesterases). Massive doses of injectable atropine could also be required over a long period to counteract the poisons. Pharmacokinetics Atropine is readily absorbed, partially metabolized by the liver, and eliminated primarily in urine. Adverse effects Depending on the dose, atropine may cause dry mouth, blurred imaginative and prescient, "sandy eyes," tachycardia, urinary retention, and constipation. In distinction to atropine, scopolamine produces sedation, but at greater doses, it could produce excitement. Therapeutic uses Scopolamine is used for the prevention of motion illness and postoperative nausea and vomiting. Pharmacokinetics and opposed effects these elements are much like these of atropine, aside from longer half-life. Ipratropium and tiotropium are also used within the acute management of bronchospasm in asthma and chronic administration of asthma, respectively (see Chapter 39). Benztropine and trihexyphenidyl Benztropine and trihexyphenidyl are helpful as adjuncts with other antiparkinson agents to deal with Parkinson disease (see Chapter 8) and different forms of parkinsonian syndromes, including antipsychotic-induced extrapyramidal signs. Actions By competitively blocking muscarinic (M3) receptors within the bladder, intravesical pressure is lowered, bladder capability is elevated, and the frequency of bladder contractions is decreased. Darifenacin and solifenacin are relatively more selective M3 muscarinic receptor antagonists; nonetheless, the other medication are mainly nonselective muscarinic antagonists, and binding to different muscarinic receptor subtypes might contribute to adverse effects.
Rosary Pea (Precatory Bean). Wellbutrin.
- Dosing considerations for Precatory Bean.
- How does Precatory Bean work?
- Are there safety concerns?
- Quickening labor, inducing abortion, preventing pregnancy, pain in terminally ill patients, and eye inflammation.
- What is Precatory Bean?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96811
Cheap wellbutrin 300 mg on line
Like different brokers that intervene with bacterial protein synthesis depression symptoms lack of empathy buy wellbutrin 300 mg low cost, linezolid and tedizolid are bacteriostatic; nonetheless depression suicidal wellbutrin 300 mg cheap amex, linezolid has bactericidal activity in opposition to streptococci. Pharmacokinetics Linezolid and tedizolid are well absorbed after oral administration. Tedizolid is metabolized by sulfation, and the vast majority of elimination happens through the liver, and drug is mainly excreted within the feces. No dose adjustments are required for either agent for renal or hepatic dysfunction. Adverse effects the most typical opposed effects are gastrointestinal upset, nausea, diarrhea, headache, and rash. Thrombocytopenia has been reported, usually in sufferers taking the drug for longer than 10 days. Linezolid and tedizolid possess nonselective monoamine oxidase exercise and may lead to serotonin syndrome if given concomitantly with large portions of tyramine-containing meals, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, or monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Irreversible peripheral neuropathies and optic neuritis inflicting blindness have been associated with larger than 28 days of use, limiting utility for extended-duration remedies. Bind the 30S ribosomal subunit, interfering with meeting of the practical ribosomal equipment. Bind irreversibly to a web site on the 50S subunit of the bacterial ribosome, inhibiting translocation steps of protein synthesis. Tetracyclines enter vulnerable organisms by way of passive diffusion and likewise by an energydependent transport protein mechanism unique to the bacterial inner cytoplasmic membrane. B is the mechanism for aminoglycosides, C is the mechanism for macrolides, and D is the mechanism for oxazolidinones. Bacteremia caused by Staphylococcus aureus Urinary tract an infection attributable to Escherichia coli Pneumonia brought on by drug-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae Diabetic foot an infection caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa Correct answer = C. Which of the next organisms would you be involved about as the causative pathogen of diarrhea Escherichia coli Bacteroides fragilis Staphylococcus aureus Clostridium difficile Correct answer = D. Clindamycin use has been related to Clostridium difficile�associated diarrhea. This infection must be thought of in a patient who presents with diarrhea whereas on clindamycin. Azithromycin has higher activity towards respiratory pathogens similar to Haemophilus influenzae and Moraxella catarrhalis but much less potent exercise against staphylococci and streptococci. Erythromycin has the same activity as azithromycin against gram-positives and gram-negatives. Azithromycin has better activity towards staphylococci and streptococci compared to erythromycin. Erythromycin has higher exercise towards gram-positive organisms, so B and C are incorrect. Which of the following antibiotics is more than likely liable for this improve in serum creatinine Aminoglycosides such as tobramycin accumulate in the proximal tubular cells of the kidney and disrupt calcium-mediated transport processes. This ends in kidney injury ranging from mild, reversible renal impairment to extreme, doubtlessly irreversible acute tubular necrosis. Gentamicin crosses the placental barrier and may accumulate in fetal plasma and amniotic fluid. Gray child syndrome is an adverse impact caused by chloramphenicol in neonates because of their underdeveloped renal operate and low capacity to glucuronidate the antibiotic. Gram-positive aerobes Gram-negative aerobes Gram-positive anaerobes Gram-negative anaerobes Correct answer = B. Fluoroquinolones Discovery of quinolone antimicrobials led to the event of numerous compounds utilized in clinical follow. Following synthesis of nalidixic acid in the early Sixties, continued modification of the quinolone nucleus expanded the spectrum of exercise, improved pharmacokinetics, and stabilized compounds towards widespread mechanisms of resistance. Due to these enhancements, quinolone antimicrobials had been rapidly integrated into human and agricultural drugs. Unfortunately, overuse resulted in rising rates of resistance in gram-negative and gram-positive organisms, elevated frequency of Clostridium difficile infections, and identification of numerous untoward adverse effects. Consequently, these agents have been relegated to second-line options for varied indications. This chapter evaluations key traits of fluoroquinolones and their function in remedy. This interference increases the variety of permanent chromosomal breaks, triggering cell lysis. Modifications to the quinolone nucleus steadily improved topoisomerase inhibitory activity and facilitated bacterial cell wall penetration. These modifications enhanced exercise in opposition to a wide selection of pathogens including aerobic gram-negative and gram-positive organisms, atypical organisms (for example, Chlamydia, Legionella, and Mycoplasma spp. Based on the impact of these structural changes, fluoroquinolones are often categorized according to spectrum of exercise. First-generation compounds (for example, nalidixic acid) had been slim spectrum agents with activity against aerobic gram-negative bacilli, principally Enterobacteriaceae. Second-generation compounds (for example, ciprofloxacin) exhibit improved intracellular penetration and broadened protection, which incorporates Enterobacteriaceae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Haemophilus influenzae, Neisseria spp. Third-generation compounds (for instance, levofloxacin) maintain the bacterial spectrum of secondgeneration brokers, with improved activity against Streptococcus spp. Fourth-generation compounds (moxifloxacin, gemifloxacin, and delafloxacin) have enhanced gram-positive exercise, together with Staphylococcus and Streptococcus spp. Further, delafloxacin and moxifloxacin have exercise in opposition to Bacteroides fragilis and Prevotella spp. Lastly, these brokers maintain atypical coverage, with moxifloxacin and delafloxacin showing exercise in opposition to Mycobacteria spp. Resistance Numerous mechanisms of fluoroquinolone resistance exist in scientific pathogens. High-level fluoroquinolone resistance is primarily driven by chromosomal mutations inside topoisomerases, though decreased entry, efflux methods, and modifying enzymes play a task. Decreased accumulation Reduced intracellular concentration is linked to 1) a reduction in membrane permeability or 2) efflux pumps. Alterations in membrane permeability are mediated via a discount in outer membrane porin proteins, thus limiting drug access to topoisomerases. Fluoroquinolone degradation An aminoglycoside acetyltransferase variant can acetylate fluoroquinolones, rendering them inactive. Ingestion of fluoroquinolones with sucralfate, aluminum- or magnesium-containing antacids, or dietary supplements containing iron or zinc can reduce the absorption. Concentrations are excessive in bone, urine (except moxifloxacin), kidney, prostatic tissue (but not prostatic fluid), and lungs as in comparability with serum. Accumulation in macrophages and polymorphonuclear leukocytes ends in activity towards intracellular organisms corresponding to Listeria, Chlamydia, and Mycobacterium. Common adverse results resulting in discontinuation are nausea, vomiting, headache, and dizziness. Patients taking fluoroquinolones are in danger for phototoxicity leading to exaggerated sunburn reactions. Arthropathy is rare, however arthralgia and arthritis are reported with fluoroquinolone use in pediatric patients.
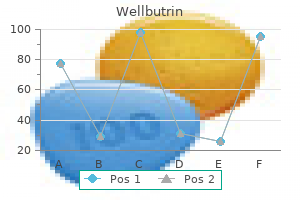
Order 300 mg wellbutrin
Therefore anxiety kit generic wellbutrin 300 mg free shipping, the nitratefree interval in sufferers with variant angina should occur within the late afternoon anxiety 10 year old daughter 300 mg wellbutrin generic otc. Nitroglycerin patches are worn for 12 hours after which eliminated for 12 hours to present the nitrate-free interval. Angina that happens more regularly or with progressively much less exercise or stress than before Angina because of spasm of coronary arteries Angina as a result of increased myocardial demand which is reproducible and relieved by relaxation or nitroglycerin Angina ache accompanied by will increase in serum biomarkers of myocardial necrosis Correct answer = C. Isosorbide dinitrate Nitroglycerin patch Nitroglycerin sublingual pill or spray Ranolazine Correct reply = C. Remove the old patch after 24 hours of use, then instantly apply the subsequent patch to stop any breakthrough angina pain. Have a nitrate-free interval of 10 to 12 hours daily to forestall growth of nitrate tolerance. Sublingual nitroglycerin should be used to treat breakthrough angina because of its fast onset of action; transdermal nitroglycerin has a delayed onset of motion. Diltiazem, amlodipine, verapamil Verapamil, diltiazem, nifedipine Nifedipine, verapamil, diltiazem Amlodipine, diltiazem, verapamil Correct answer = B. Verapamil has essentially the most unfavorable inotropic results, nifedipine is a peripheral vasodilator, and diltiazem is intermediate with actions on both myocardial and peripheral calcium channels. Crescendo angina is indicative of unstable angina that requires instant evaluation. Dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers can be utilized in sufferers with heart failure with lowered ejection fraction, however nondihydropyridine calcium channel blockers must be averted as a result of unfavorable inotropic effects. She should be recommended to take nitroglycerin earlier than physical exercise to forestall signs. Prinzmetal or vasospastic angina responds nicely to vasodilators, including the dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker felodipine. Beta-blockers could also be used with warning in sufferers with diabetes, but these medicine are less efficient options for Prinzmetal angina. Nitrates are also effective, but Prinzmetal angina is provoked by coronary artery vasospasm somewhat than bodily exercise. Overview this chapter describes drugs that are useful within the therapy of disorders of hemostasis. Thrombosis, the formation of an undesirable clot within a blood vessel, is the most common abnormality of hemostasis. Bleeding problems associated to the failure of hemostasis are much less widespread than thromboembolic issues. Thrombus Versus Embolus A clot that adheres to a vessel wall is called a "thrombus," whereas an intravascular clot that floats in the blood is termed an "embolus. Arterial thrombosis most frequently occurs in medium-sized vessels rendered thrombogenic by atherosclerosis. In contrast, venous thrombosis is triggered by blood stasis or inappropriate activation of the coagulation cascade. Platelet Response to Vascular Injury Physical trauma to the vascular system, such as a puncture or a reduce, initiates a posh sequence of interactions between platelets, endothelial cells, and the coagulation cascade. These interactions lead to hemostasis or the cessation of blood loss from a damaged blood vessel. The subsequent step involves the formation of a platelet�fibrin plug at the website of the puncture. The creation of an undesirable thrombus involves many of the same steps as regular clot formation, besides that the triggering stimulus is a pathologic situation within the vascular system, somewhat than external bodily trauma. Resting platelets Platelets act as vascular sentries, monitoring the integrity of the vascular endothelium. Chemical mediators synthesized by endothelial cells Prostacyclin is synthesized by intact endothelial cells and acts as an inhibitor of platelet aggregation. Decreased intracellular calcium prevents platelet activation and the next launch of platelet aggregation agents. Roles of thrombin, thromboxanes, and collagen the platelet membrane also incorporates receptors that can bind thrombin, thromboxanes, and uncovered collagen. In the intact, regular vessel, circulating levels of thrombin and thromboxane are low, and the intact endothelium covers collagen within the subendothelial layers. However, when occupied, each of those receptor types triggers a collection of reactions leading to the discharge into the circulation of intracellular granules by the platelets. These signaling molecules bind to receptors within the outer membrane of resting platelets circulating nearby. In flip, thrombin, a serine protease, catalyzes the hydrolysis of fibrinogen to fibrin, which is integrated into the clot. Plasmin limits the expansion of the clot and dissolves the fibrin community as wounds heal. Prostaglandin H2 is additional metabolized to thromboxane A2, which is released into plasma. Repeated administration of aspirin has a cumulative effect on the perform of platelets. Pharmacokinetics When given orally, aspirin is absorbed by passive diffusion and quickly hydrolyzed to salicylic acid within the liver. Salicylic acid is further metabolized within the liver and some is excreted unchanged in the urine. The half-life of aspirin ranges from 15 to 20 minutes and for salicylic acid is 3 to 12 hours. Adverse effects Higher doses of aspirin enhance drug-related toxicities as well as the probability that aspirin may inhibit prostacyclin manufacturing. Therefore, immediate-release aspirin must be taken no less than 60 minutes before or no much less than 8 hours after ibuprofen. All of those brokers are administered orally, with the exception of cangrelor, which is an injectable formulation. Pharmacokinetics these agents require oral loading doses for quicker antiplatelet impact, besides cangrelor that has a fast onset of 791 action with intravenous administration. Elimination of the drugs and metabolites occurs by both the renal and fecal routes. Tests are at present out there to identify poor metabolizers, and it is suggested that different antiplatelet agents (prasugrel or ticagrelor) be prescribed for these sufferers. Additionally, ticagrelor carries a black field warning for diminished effectiveness with concomitant use of aspirin doses above 100 mg. After cessation of abciximab infusion, platelet perform progressively returns to normal, with the antiplatelet effect persisting for 24 to 48 hours. Tirofiban is excreted largely unchanged by the kidney and to a lesser extent within the feces. Adverse results the major opposed effect of those agents is bleeding, especially if used with anticoagulants. The drug undergoes hepatic metabolism, mainly glucuronidation, and is excreted primarily within the feces. Blood Coagulation the coagulation course of that generates thrombin consists of two interrelated pathways, the extrinsic and the intrinsic techniques. This happens when blood comes into contact with the collagen in the damaged wall of a blood vessel.

Buy generic wellbutrin 300 mg
In the alveoli anxiety remedies safe wellbutrin 300 mg, goblet cells are absent and the lining epithelium is skinny easy squamous anxiety 7 weeks pregnant wellbutrin 300 mg buy. By examining this epithelium with both light and transmission electron microscopes, several different cell sorts are acknowledged. Ciliated columnar cells are the most abundant cells that extend the complete thickness of the epithelium. The cilia sweep the surface of the epithelium and protect the lungs by eradicating small inhaled particles. Goblet cells are numerous in the extra proximal airways and progressively decrease in number towards the distal parts of the respiratory tube. These cells include and release mucus glycoproteins to type a protecting layer on the epithelial floor. These cells function stem cells for continual substitute of other epithelial cells. Located within the superior and lateral areas in the roof of the nostril are the bony nasal cabinets known as conchae. Lining this chosen region is a highly specialized sensory pseudostratified epithelium known as the olfactory epithelium that detects and transmits odor sensations to the brain. This epithelium consists of three major cell varieties: supportive (sustentacular), basal, and olfactory (sensory). Located inferior to the epithelium within the lamina propria are the serous olfactory (Bowman) glands. In distinction to the respiratory epithelium, the olfactory epithelium lacks goblet cells or motile cilia on its cells. Olfactory cells are the sensory bipolar neurons which are distributed between the more apical supportive cells and the basal cells. The olfactory cells span the thickness of the olfactory epithelium and finish at the surface as small, round bulbs known as the olfactory vesicles. Radiating from each olfactory vesicle are lengthy, nonmotile olfactory cilia that lie parallel to the epithelial surface. The bases of the olfactory cells connect with axons that go away the epithelium through the basement membrane, converge in the lamina propria under the epithelium to kind bundle of nerve fibers that pass via the ethmoid bone of the cranium, and synapse within the olfactory bulb of the mind (olfactory, or cranial nerve I). In the olfactory epithelium are olfactory nerves, olfactory (Bowman) glands, blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and different mobile elements of the connective tissue. Olfactory (Bowman) glands produce a serous fluid that bathes 657 the olfactory cilia and serves as a solvent to dissolve the odor molecules for stimulation of the olfactory cells for odor detection. Hyaline cartilage helps and keeps the larger air passageways always patent (open). Starting with the trachea, incomplete Cshaped hyaline cartilage rings encircle the tube. Elastic and easy muscle fibers, the trachealis muscle, bridge the area between the ends of the hyaline cartilage. The ends of the C-shaped cartilage rings face posteriorly and are adjoining to the esophagus. As the trachea divides into bronchi and the bronchi enter the lungs, the Cshaped hyaline cartilage rings are replaced by irregular hyaline cartilage plates that encircle the lumen of the intrapulmonary bronchi. As the bronchi proceed to divide and reduce in measurement, the cartilage plates additionally lower in measurement and quantity. When the diameters of bronchioles lower to about 1 mm, cartilage plates disappear from conducting passageways. Terminal bronchioles represent the ultimate stable conducting passageways with the diameters starting from 0. There are between 20 and 25 generations of branching of intrapulmonary bronchi before the passageways reach the dimensions of terminal bronchioles. The larger bronchioles are lined with a tall, ciliated pseudostratified epithelium similar to trachea and bronchi. As the tubular size decreases, the epithelial peak is steadily reduced, and the epithelium becomes a simple ciliated epithelium. The number of goblet cells, nevertheless, decreases with the decreasing tubule dimension; the goblet cells are absent from the epithelium of terminal bronchioles. In place of the goblet cells, Clara cells are found mixed with the ciliated cells in the terminal and respiratory bronchioles. Clara cells are nonciliated, secretory cuboidal cells with dome-shaped apices that protrude into 658 the lumen and improve in quantity as ciliated cells lower. Terminal bronchioles department to give rise to respiratory bronchioles, that are characterized by thin-walled outpockets known as alveoli. This is the first area of the respiratory tube the place gaseous change can take place. The respiratory bronchioles symbolize the transitional zone the place air conduction and gaseous trade or respiration can take place. Respiration happens only in alveoli because the barrier between inspired air within the alveoli and the capillaries is extraordinarily skinny. Each alveolus is surrounded by capillary plexuses that bring venous blood near the impressed air inside the alveoli for gaseous exchange. Other intrapulmonary constructions where respiration happens are the alveolar ducts and alveolar sacs. The alveoli include two cell types with essentially the most plentiful cells being the squamous type I alveolar cells, or sort I pneumocytes. Lung macrophages, derived from circulating blood monocytes, are found each within the connective tissue of alveolar partitions, or interalveolar septa (alveolar macrophages), and in the alveoli (dust cells). Present in the interalveolar septa are intensive capillary networks, pulmonary arteries, pulmonary veins, lymphatic ducts, and nerves. The olfactory epithelium (2, 6) is a pseudostratified tall columnar epithelium with out goblet cells and with out motile cilia, in distinction to the respiratory epithelium. The lamina propria incorporates the branched tubuloacinar olfactory (Bowman) glands (4, 5). These glands produce a serous secretion, in distinction to the combined mucous and serous secretions produced by glands in the relaxation of the nasal cavity. Small nerves which may be located in the lamina propria are the olfactory nerves (3, 7) and symbolize the afferent axons that leave the olfactory cells, continue into the cranial cavity, and synapse within the olfactory (cranial) nerves. The olfactory epithelium (1) is a tall, pseudostratified columnar epithelium composed of three different cell varieties: supportive, basal, and neuroepithelial olfactory cells. The particular person cell outlines are troublesome to distinguish in a routine histologic preparation; nevertheless, the situation and shape of nuclei allow identification of the cell varieties. The supportive, or sustentacular cells (3), are elongated, with oval nuclei located extra apically (or superficially) in the epithelium. The olfactory cells (4) have oval or round nuclei which may be positioned between the nuclei of the supportive cells (3) and the basal cells (5). The apical surfaces of the olfactory cells (4) include slender, nonmotile microvilli that extend into the mucus (2) that covers the epithelial floor. The basal cells (5) are short cells positioned on the base of the epithelium between the supportive (3) and olfactory cells (4). The olfactory nerves (14) depart the nasal cavity and pass into the olfactory bulbs at the base of the mind.
Discount wellbutrin 300 mg
Rare complications of remedy embrace pulmonary fibrosis mood disorder scale discount 300 mg wellbutrin with mastercard, neuropathy mood disorders 101 300 mg wellbutrin cheap amex, and autoimmune hepatitis. Levofloxacin-hyperkalemia Nitrofurantoin-pulmonary fibrosis Cotrimoxazole-hepatic encephalopathy Methenamine-nystagmus Correct answer = B. Hepatic encephalopathy may be associated to therapy with methenamine in sufferers with hepatic insufficiency. Hyperkalemia Pulmonary fibrosis Tendon rupture Blood glucose disturbances Correct answer = A. Trimethoprim acts as a potassium-sparing agent, leading to an increase in serum potassium concentrations. Tendon rupture and blood glucose 1183 disturbances are opposed effects of fluoroquinolones. The nurse famous that the patient lately took an antibiotic for community-acquired pneumonia. After reviewing her antimicrobial therapy, which actions must be taken prior to clinic discharge Continue present remedy and counsel on gastrointestinal effects of nitrofurantoin. Patients taking a fluoroquinolone should apply sunscreen and take precautions to reduce danger of phototoxicity. Due to its conversion to formaldehyde, this compound is the least doubtless compound to select for resistant isolates. This agent is just out there as an oral formulation, and it has a narrow spectrum of activity. Overview Mycobacteria are rod-shaped cardio bacilli that multiply slowly, every 18 to 24 hours in vitro. Under selective strain from inadequate remedy, especially from monotherapy, these resistant organisms can emerge as the dominant inhabitants. The first-line medicine isoniazid, rifampin, ethambutol, and pyrazinamide are most well-liked because of their excessive efficacy and acceptable incidence of toxicity. Active illness all the time requires remedy with multidrug regimens, and preferably three or more medication with proven in vitro exercise in opposition to the isolate. Patients take the medications underneath remark of a member of the health care team. Mechanism of motion Isoniazid is a prodrug activated by a mycobacterial catalase�peroxidase (KatG). The drug is especially effective in opposition to rapidly growing bacilli and can also be lively in opposition to intracellular organisms. Resistance Resistance follows chromosomal mutations, together with 1) mutation or deletion of KatG (producing mutants incapable of prodrug activation), 2) varying mutations of the acyl carrier proteins, or 3) overexpression of the target enzyme InhA. Adverse results Hepatitis is the most severe adverse impact related to isoniazid. Peripheral neuropathy, manifesting as paresthesia of the arms and ft, seems to be because of a relative pyridoxine deficiency attributable to isoniazid. Antimicrobial spectrum Rifampin is bactericidal for both intracellular and extracellular mycobacteria, together with M. It is effective towards many gram-positive and gram-negative organisms and is used prophylactically for people exposed to meningitis attributable to meningococci or Haemophilus influenzae. Unrelated to its results on cytochrome P450 enzymes, rifampin undergoes autoinduction, resulting in a shortened elimination half-life over the first 1 to 2 weeks of dosing. However, the drug should be used judiciously in older patients, alcoholics, or those with chronic liver illness. There is a modest improve in the incidence of hepatic dysfunction when rifampin is coadministered with isoniazid and pyrazinamide. When rifampin is dosed intermittently, particularly with higher doses, a flu-like syndrome can occur, with fever, chills, and myalgia, typically extending to acute renal failure, hemolytic anemia, and shock. Rifabutin is a much less potent inducer (approximately 40% less) of cytochrome P450 enzymes, thus lessening drug interactions. Rifabutin has opposed results similar to these of rifampin however can even trigger uveitis, skin hyperpigmentation, and neutropenia. Pyrazinamide have to be enzymatically hydrolyzed by pyrazinamidase to pyrazinoic acid, which is the lively form of the drug. Ethambutol inhibits arabinosyl transferase-an enzyme necessary for the synthesis of the mycobacterial cell wall. Ethambutol is utilized in combination with pyrazinamide, isoniazid, and rifampin pending culture and susceptibility data. Both the parent drug and its hepatic metabolites are primarily excreted within the urine. The most essential opposed impact is optic neuritis, which leads to diminished visible acuity and loss of capacity to discriminate between purple and green. Uric acid excretion is decreased by ethambutol, and warning should be exercised in patients with gout. In general, these brokers are much less efficient and extra poisonous than the first-line brokers. Infections due to streptomycin-resistant organisms may be handled with kanamycin or amikacin, to which these bacilli usually stay susceptible. Capreomycin it is a parenterally administered polypeptide that inhibits protein synthesis just like aminoglycosides. Careful monitoring of renal function and hearing is necessary to decrease nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity, respectively. Cycloserine Cycloserine is an orally effective, tuberculostatic drug that disrupts D-alanine incorporation into the bacterial cell wall. Ethionamide Ethionamide is a structural analog of isoniazid that also disrupts mycolic acid synthesis. Metabolism is in depth, most probably within the liver, to energetic and inactive metabolites. Fluoroquinolones the fluoroquinolones (see Chapter 31), specifically moxifloxacin and levofloxacin, have an essential place within the remedy of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. Azithromycin could additionally be preferred for sufferers at larger risk for drug interactions, since clarithromycin is each a substrate and inhibitor of cytochrome P450 enzymes. Elevations in liver enzymes have also been reported and liver operate should be monitored during therapy. The drug is properly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and is distributed all through the body, with high concentrations within the skin. Adverse reactions include hemolysis (especially in patients with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency), methemoglobinemia, and peripheral neuropathy. Its redox properties could lead to the generation of cytotoxic oxygen radicals which are toxic to the micro organism. Eosinophilic and other types of enteritis, typically requiring surgical procedure, have been reported. The affected person obtained self-administered isoniazid, rifampin, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol. Two weeks following initiation of therapy, the affected person is anxious that her urine is a "funny-looking reddish shade. Rifampin (as properly as rifabutin and rifapentine) and its metabolites may color urine, feces, saliva, sputum, sweat, and tears a brilliant red-orange.