Rumalaya gel 30 gr purchase without a prescription
The gracilis muscle is an extended muscle relaxant rx buy 30 gr rumalaya gel free shipping, skinny muscle that receives its blood supply from the adductor artery muscle relaxant sciatica 30 gr rumalaya gel cheap with mastercard, a department of the profunda femoris. The vascular pedicle enters the muscle at the junction of its upper third and decrease two thirds (8 to 10 cm inferior to the pubic tubercle). The nerve provide is from the anterior branch of the obturator nerve, which enters the muscle 2 to 3 cm cephalad to the entry level of the vascular pedicle. The muscle is usually sutured between the temporalis fascia and the orbicularis oris at the nook of the mouth. The muscle is reinnervated with using a cross facial nerve graft from the contralateral facet of the face or with the utilization of the nerve to the masseter. Any portion of the jejunum could be harvested from the ligament of Treitz to the ileum. This flap can be utilized as a tube conduit for circumferential pharyngeal defects or as a patch if the antimesenteric facet of the jejunum is opened. The jejunum is exclusive in that the viability of the flap will at all times remain dependent on the vascular pedicle. The voice rehabilitation results of the jejunal free flap are conspicuously decrease than different free flaps. Although this is a reliable flap, the use of the jejunal free flap has decreased with the arrival of the tubed anterolateral thigh flap, which is related to less morbidity. Approximately 22 to 25 cm of bone may be harvested, which is sufficient for the reconstruction of the whole mandible. Because of the variation in anatomy and also because of the potential of peripheral vascular illness, preoperative imaging corresponding to angiography or magnetic resonance angiography is highly beneficial. Leaving approximately 6 cm of bone proximally and distally will maintain the stability of the knee and ankle joint and also reduces the danger of damage to the frequent peroneal nerve. The most reliable cutaneous perforators to the pores and skin of the calf are positioned around the junction of the center and lower third of the fibula. The skin perforators can run by way of the posterior septum (septal) or soleus muscle (musculocutaneous). The primary use of the fibula free flap in the head and neck is for mandibular reconstruction. Osteotomies could be safely performed in the fibula, and the bone has adequate top and bicortical strength to obtain dental implants. The fibula is the preferred technique for lengthy phase and anterior mandibular defects. All of these flaps are based on the scapular artery and vein; due to this fact multiple flap could be raised on one pedicle. Latissimus dorsi and serratus anterior flaps are based mostly on the thoracodorsal artery and are normally raised as muscle-only flaps, however they can additionally be raised as musculocutaneous and osteomusculocutaneous flaps (a rib with the serratus flap and scapula with the latissimus flap). Because of the large dimension of the latissimus muscle, this flap is an efficient choice for giant scalp defects. Donor website defects as wide as 7 cm could be closed primarily, which is probably one of the advantages of this flap. Regardless of the extent of the flap, it ought to all the time be centered over the infraspinatus fossa (the triangular house between the teres main, teres minor, and long head of the triceps). In addition, the colour match is best than with use of the anterolateral thigh flap. The scapular tip bony flap is predicated on the angular branch of the thoracodorsal artery. Up to 10 to 14 cm of bone may be harvested from the lateral border of the scapula. Because of the versatility of this system, scapula and parascapular system flaps have been used in most head and neck defects. The iliac crest offers the thickest stock of vascularized bone for oromandibular reconstruction. In addition to the bone, the interior oblique muscle and pores and skin of the groin can be harvested based mostly on the same pedicle. The extent of skin paddle can lengthen from the anterosuperior iliac spine to 9 cm posterior. The main use of the iliac crest flap is in mandibular and maxillary reconstruction. Because of the thickness of the bone, dental implants may be extra effectively positioned in this flap than in all different bony flaps. A downside of anastomosing all branches of the facial nerve to the primary trunk is the event of synkinesis. In the zonal strategy to facial rehabilitation, the upper face is rehabilitated with a forehead carry for the frontal department and a gold weight or lateral tarsorraphy for the palpebral department. For the midface, static slings, a temporalis tendon transfer, and a gracilis dynamic free flap can be utilized. For reinnervation of the gracilis flap, either a cross-facial nerve graft from the contralateral facial nerve or anastomosis to the nerve to the masseter can be utilized. The main ideas are using color- and texture-matched skin, restoration of the contour of the nostril with cartilage and bone grafts, and restoration of the inside lining with an epithelial surface. Incisions for native flaps are best placed within the borders of aesthetic items somewhat than in the center of one. A variety of local and regional flaps can be used with a mix of cartilage grafts from auricular or septal cartilages. Alar defects are best restored with cartilage grafts or composite skincartilage grafts from the ear. For a total rhinectomy defect, an osteocutaneous free flap or sometimes a full prosthesis will obtain passable results. Local tissues are strongly most well-liked as a result of they supply a better colour match, better operate, and superior cosmetic results. For small superficial defects, main closure or mucosal development flaps will suffice. Full-thickness defects, depending on the situation and extent, can be repaired by a wide range of techniques. Full-thickness defects as much as one third of the lower lip could be reconstructed by wedge resection and first closure. The benefit of this flap is that it preserves neurovascular bundles to the flap, thus reaching superior functional results. Abbe flap reconstruction is completed in a single stage, however Estlander flap reconstruction has to be carried out in two stages as a end result of the pedicle should be preserved for two to 3 weeks. When the Abbe and Estlander flaps are designed, the size of the flap is measured as half of the defect for lower lip reconstruction and the same measurement because the defect for upper lip reconstruction. The incisions are finest positioned at the borders of each subunit or, if not possible, parallel to the relaxed pressure skin lines.
30 gr rumalaya gel trusted
Urethral injuries are unusual in girls due to spasms hamstring buy rumalaya gel 30 gr visa the protective configuration of the female pelvic ground and shorter urethral size muscle relaxant injection for back pain 30 gr rumalaya gel generic mastercard. Approximately 10% of sufferers with major pelvic fractures will maintain a urethral injury, usually involving the posterior (proximal) portion. In males, blood on the urethral meatus, lack of ability to void, elevation of the prostate gland on rectal examination, or perineal swelling or hematoma should raise the suspicion for this injury. In ladies with urethral harm, pelvic fractures, the presence of vaginal bleeding, labial edema, dysuria, blood on the urethral orifice, hematuria, or urine leak through the rectum have all been described. Anteroposterior pelvic radiography will nearly at all times demonstrate pubic symphysis diastasis in a affected person with a urethral harm. Imaging assessment of the urethra ought to precede cystography however ought to be delayed till after pelvic arteriography. A retrograde urethrogram is performed using 30 mL of 60% contrast medium via a Foley balloon catheter positioned within the distal urethra and inflated with 2 mL of saline. Urethrography outcomes can be utilized to classify the injury using the Goldman system Table 11-13), which helps in remedy planning. Anterior (distal) urethral damage is extra generally attributable to iatrogenic or penetrating rather than blunt trauma. The injury may be restricted to the corporal bodies if the Buck fascia stays intact or, if disrupted, might spread all through the scrotum, perineum, and anterior belly wall. Differentiating testicular hematoma, rupture, or torsion is exceeding difficult by medical examination. Rapid and accurate evaluation is important as a outcome of a ruptured testis may be salvaged in 90% of sufferers if repaired inside 72 hours, but salvage drops to 55% with growing time since damage. Ultrasound examination has 100% sensitivity and 65% specificity in detecting testicular rupture. Testicular rupture signifies tearing of the tunica albuginea with extrusion of the testis into the scrotal sac. Acute hematomas are typically isoechoic to normal testicular parenchyma and could be difficult to establish. Although a hematoma will usually be managed conservatively, follow-up to resolution is recommended due to the danger for infection and necrosis, which can require orchiectomy. Dislocation is mostly seen in a patient involved in a bike collision with impaction of the scrotum against the fuel tank. Prompt analysis is crucial as a result of a missed dislocation places the affected person at risk for improvement of intratesticular cellular modifications which will predispose to malignant degeneration. The "fracture" is actual rupture of the tunica albuginea, usually accompanied by a cracking sound from the erect penis, with pain and detumescence. Corporal laceration may be seen with direct trauma corresponding to a kick to the flaccid penis. Color Doppler might present blood flush by way of the tunica defect upon squeezing of the penile shaft. Ovarian and adnexal torsion: spectrum of sonographic findings with pathologic correlation. Potential errors within the analysis of pericardial effusion on trauma ultrasound for penetrating accidents. Sonography in a medical algorithm for early evaluation of 1671 patients with blunt belly trauma. Diagnosis and preliminary management of blunt pancreatic trauma: guidelines from a multiinstitutional review. Importance of evaluating organ parenchyma throughout screening abdominal ultrasonography after blunt trauma. Revision of present American Association for the Surgery of Trauma renal damage grading system. Chapter eleven Blunt Abdominal and Retroperitoneal Trauma Catalano O, Aiani L, Barozzi L, et al. Sexually transmitted diseases remedy pointers, 2010: pelvic inflammatory illness. What are the particular computed tomography scan standards that may predict or exclude the need for renal angioembolization after high-grade renal trauma in a conservative management strategy? Computed tomography grading methods poorly predict the need for intervention after spleen and liver injuries. Classification and treatment of pooling of distinction materials on computed tomographic scan of blunt hepatic trauma. The standing of ultrasonography coaching and use generally surgery residency applications. Abdominal ultrasound is an unreliable modality for the detection of hemoperitoneum in patients with pelvic fracture. Blunt trauma of the pancreas and biliary tract: a multimodality imaging method to analysis. Diagnosis and classification of pancreatic and duodenal accidents in emergency radiology. Institutional and particular person learning curves for centered abdominal ultrasound for trauma: cumulative sum evaluation. Appearance of solid organ damage with contrast-enhanced sonography in blunt belly trauma: preliminary expertise. Radiographic predictors of need for angiographic embolization after traumatic renal damage. Endoscopic treatment for suprapancreatic biliary stricture following blunt stomach trauma. Focused assessment with sonography for trauma: strategies, accuracy, and indications. Blunt belly trauma sufferers: can organ damage be excluded without performing computed tomography? Blunt belly trauma: does the usage of a second-generation sonographic distinction agent help to detect stable organ injuries? Disconnection of the pancreatic duct: an necessary but ignored complication of severe pancreatitis. Focused stomach sonogram for trauma: the training curve of nonradiologist clinicians in detecting hemoperitoneum. Impact of a defined administration algorithm on end result after traumatic pancreatic damage. Nonoperative management of blunt hepatic harm: an Eastern Association for the Surgery of Trauma apply management guideline. Selective nonoperative administration of blunt splenic injury: an Eastern Association for the Surgery of Trauma follow administration guideline. Blunt stomach trauma: emergency contrast-enhanced sonography for detection of strong organ accidents. Scalea Firearm-related harm is the second leading reason for demise following motorcar collision.
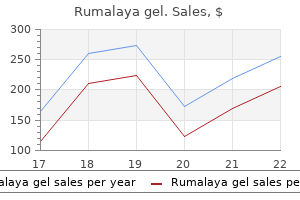
| Comparative prices of Rumalaya gel |
| # | Retailer | Average price |
| 1 | Office Depot | 716 |
| 2 | True Value | 839 |
| 3 | Walgreen | 238 |
| 4 | Raley's | 772 |
| 5 | AutoZone | 239 |
| 6 | Albertsons | 373 |
| 7 | Ingles Markets | 409 |
| 8 | Starbucks | 468 |
| 9 | Bed Bath & Beyond | 365 |
| 10 | Apple Stores / iTunes | 396 |
Purchase 30 gr rumalaya gel visa
Posterior knee dislocation is related to a vascular harm in roughly 30% of patients muscle relaxant for dogs proven 30 gr rumalaya gel, resulting in muscle relaxant effects safe 30 gr rumalaya gel amputation in up to 20% of these patients. Quadriceps and Patellar Tendon Rupture Quadriceps tendon rupture might outcome from acute trauma or sports damage or could also be as a outcome of underlying tendinosis. Quadriceps tendon rupture could additionally be inferred by lack of the tendon contour, soft tissue swelling, and a low-lying patella, referred to as patella baja. The most generally accepted goal technique for figuring out patellar place is the Insall-Salvati ratio, which is calculated by dividing the patellar tendon length by the length of the patella as measured on the lateral projection. Patellar tendon ruptures happen less regularly than tears of the quadriceps tendon. The diagnosis is sometimes recommended by patella alta, an abnormally excessive place of the patella outlined by an Insall-Salvati ratio larger than 1. A, Oblique lateral radiograph reveals severely comminuted distal femoral fracture with disruption and displace- ment of the articular surface of the medial femoral condyle. Supracondylar femoral fractures are classified as extra-articular, unicondylar, or bicondylar and should show intercondylar and intra-articular extension. Computed tomography is really helpful for evaluating complicated fractures so that the suitable operative management is performed. Subchondral Insufficiency Fracture Older, osteoporotic patients presenting with acute-onset, atraumatic knee ache may have a subchondral insufficiency fracture, most commonly involving the medial femoral condyle. This situation may be instructed when an eccentric lucency with slight flattening or irregularity involving the subchondral bone is observed. More advanced lesions may reveal peripheral sclerosis, and continual fractures present cortical impaction. The characteristic appearance 518 Section V MuSculoSkeletal eMergencieS dislocation. Accurate assessment of those fractures is important as a result of the tibial plateau is critical in maintaining knee alignment and stability. An in situ kind occurs in younger individuals, termed osteochondritis dissecans, and is likely attributable to repetitive overloading of the bone. Also observe comminuted proximal fibula in this affected person, who was involved in a high-speed motorcar collision. Tibiofibular Joint Dislocation Proximal tibiofibular joint dislocation is an uncommon harm. This injury may happen as an isolated damage from a direct influence leading to anterolateral or posteromedial displacement. Anterolateral dislocations are most typical, caused by a fall on a flexed knee with the foot in inversion and plantar flexed. Yu the tibia, fibula, and talus kind the ankle joint, which acts primarily as a hinge joint. Stability of the ankle joint is determined by the integrity of a hoop fashioned by these three bones and the ligaments that unite them. The medial malleolus consists of the anterior colliculus, onto which the superficial deltoid ligament attaches, and the posterior colliculus, which anchors the deep deltoid ligament. The posterior malleolus restrains the talus from posterior translation, and fractures involving graph reveals anterior displacement of proximal fibula (arrow) with respect to the posterior tibial plateau in a affected person with clinically apparent tibiofibular joint dislocation. Fractures of the tibial tubercle normally have an result on adolescent males who take part in athletic actions that involve jumping. Chronic stress harm at the Chapter 15 Lower Extremity (in which the talus is displaced internally, or medially), abduction (in which the talus is displaced laterally with out important rotation), adduction (in which the talus is displaced medially without vital rotation), and dorsiflexion (in which the talus is dorsiflexed on the tibia). The external rotation of the talus impacts against the lateral malleolus forcing it in the posterior direction producing the attribute abnormalities. Two or more breaks in the ring enable irregular talar movement that could be evident radiographically, but application of stress usually is required to verify the prognosis of instability. Localizing the epicenter of soft tissue swelling is essential within the identification of acute fractures. Major axial load (crush) or direct impaction typically produces fractures that are advanced and though conspicuous radiographically do require cross-sectional imaging for additional characterization. Pronation-Abduction In the pronation-abduction damage mechanism the lateral floor of the talus impacts the lateral malleolus, forcing it laterally. The second term displays the course by which the talus is displaced or rotated relative to the ankle mortise. There are 11 goal sites that symbolize weak areas the place fractures occur, includ- ing the medial (1) and lateral (2) malleoli, anterior tibial tubercle (3) and posterior tibial malleolus (4), talar dome (5), lateral talar course of (6), tubercles of the posterior talus course of (7), dorsal to the talonavicular joint (8), anterior calcaneus process (9), calcaneal insertion of the extensor digitorum brevis (10), and the base of the fifth metatarsal bone (11). A, Frontal radiograph exhibits medial subluxation of the talus and a displaced and distracted medial malleolus fracture. The deltoid ligament and distal tibiofibular syndesmosis are intact, however there could also be an indirect medial malleolar fracture. In Type B the distal fibular fracture begins at the tibiotalar joint level and courses obliquely because it extends proximally. There may be an associated deltoid ligament tear or a transverse medial malleolar fracture. Type C1 refers to a easy distal fibular fracture without interosseous membrane damage, and sort C2 refers to a fancy fibular fracture greater up in the fibula associated with interosseous membrane harm on the fracture web site. Type C3 is a proximal fibular fracture associated with rupture of the interosseous membrane inflicting instability of fibula or a Maisonneuve fracture. Injuries affecting the interosseous membrane may lead to its ossification, limiting movement. There is widening of the medial clear space between the talus and medial malleolus (curved arrow) and an oblique distal fibular fracture (arrow). Dorsiflexion on the pronated foot produces impaction of the distal tibia with the talus, usually resulting in in depth comminution of the tibia, although the medial malleolus usually maintains its relationship with the talus. Computed tomography is advocated to consider for displacement, comminution, and impaction on the articular floor. It is attributable to external rotation of the ankle with a tear of the interosseous membrane at the level of the fibular fracture. Ankle radiographs that show an isolated fracture of both the medial or posterior malleolus should be followed with tibia/fibula radiographs to search for the harm. Increased pressure inside the posterior tibiofibular ligament may cause an avulsion fracture of the posterior tibial malleolus. When small, it has the looks of an arcuate sliver of bone adjoining to the posterior tibial lip on the lateral radiograph. There are two kinds of triplane fractures relying on whether there are two (most widespread type) or three fragments. Both varieties happen as a end result of plantar flexion and external rotation and may occur with or without an associated fracture of the distal fibula. The fracture line sometimes extends horizontally along the physeal plate and then turns 90 degrees vertically to the articular surface as a result of the medial a part of the growth plate has fused while the lateral part has not. The triplane fracture is much like a juvenile Tillaux fracture, nevertheless it additionally extends into the Tibiotalar and Subtalar Dislocations the tibiotalar joint is inherently stable, so a dislocation requires high-energy trauma to produce disarticulation. The commonest ankle dislocation is a posterior dislocation with the talus disarticulating to a terminal place posterior to the tibial plafond. This dislocation happens as a result of fall from height, motor vehicle accident, or extreme twisting of the ankle.
Purchase rumalaya gel 30 gr line
For circumferential defects muscle relaxant reviews generic 30 gr rumalaya gel mastercard, jejunum muscle relaxant starting with b rumalaya gel 30 gr order, gastric pull-up, tubed anterolateral thigh, or tubed radial forearm can be used. If the level of the defect extends to the whole cervical esophagus or past the thoracic inlet, the gastric pull-up might be a greater option. The use of jejunum or gastric conduit is related to poorer quality voice rehabilitation after tracheoesophageal puncture. In contrast, most defects after transoral resection of oropharynx cancers or laryngeal cancers can be left open to granulate without the need for reconstruction. Supraclavicular artery island flap for head and neck oncologic reconstruction: indications, complications, and outcomes. Complications of the pectoralis major myocutaneous flap in head and neck reconstruction. Atlas of regional and free flaps for head and neck reconstruction: flap harvest and insetting. Pharyngoesophageal reconstruction with the anterolateral thigh flap after total laryngopharyngectomy. Patients ought to be instructed to see their dentist/ hygienist extra frequently than each 6 months after receiving radiation remedy. When prosthetic rehabilitation is chosen, maxillary defects are greatest rehabilitated in three phases: surgical, interim, and definitive obturator. The surgical obturator is intended to stabilize surgical packing, help in wound isolation, and permit the patient to converse and swallow, usually with no nasogastric tube. Successful fabrication of a useful maxillary obturator is based on the ideas of retention, stability, and assist. Dental implants placed at the time of ablative surgical procedure are preferable as a result of 6 to 8 weeks of therapeutic are needed before the beginning of radiation therapy, if needed. Electing prosthetic rehabilitation over flap reconstruction permits for direct visible examination of the defect for recurrence. The palatopharyngeal sphincter is formed by the taste bud, lateral pharyngeal partitions, and posterior pharyngeal wall. The lack of ability of the palatopharyngeal sphincter to separate the nasopharynx from the oropharynx is recognized as velopharyngeal inadequacy. The lack of ability of the soft palate to elevate superiorly to kind the palatopharyngeal sphincter is identified as velopharyngeal incompetency. The mucosal surfaces of the oral cavity are exposed to significant doses of radiation remedy throughout therapy of most tumors, except those of the larynx, hypopharynx, and thyroid. The risk of developing osteoradionecrosis of the jaw is significantly elevated at doses higher than 55 Gy. Ideally, dental extractions ought to occur a minimal of 21 days earlier than radiation remedy. After radiation therapy to any of the major salivary glands, patients ought to use a fluoride supplement for the remainder of their lives. Dental implants in the radiation therapy remedy subject should be eliminated earlier than graduation of remedy. After radiation remedy, hyperbaric oxygen should be used before extraction or placement of implants to get rid of the danger of osteoradionecrosis. The accepted hyperbaric oxygen therapy regimen after radiation therapy however earlier than oral surgery consists of 20 "dives," the oral surgical process, then 10 dives. Osteoradionecrosis is more widespread in the mandibular arch than in the maxillary arch. Radiation therapy therapy fields together with muscles of mastication may find yourself in trismus. When the soft palate is anatomically deficient and ends in an incomplete velopharyngeal sphincter, it is named velopharyngeal insufficiency. Patients with acquired defects of the soft palate can probably be affected by velopharyngeal incompetency and velopharyngeal insufficiency. Completely edentulous patients needing taste bud obturators fare significantly better than dentate/ partially dentate sufferers. Implants can tremendously increase stability, thereby increasing the efficacy of a taste bud obturator for partially dentate or completely edentulous sufferers. Fibula free flaps are typically too small in width and top for the position of dental implants and thus should be avoided. Facial prostheses may be retained with adhesives or mechanically via either the character of the surgical defect or craniofacial implants. Craniofacial implants provide superior retention in comparison with typical adhesives. Craniofacial implants prohibit the patient from undergoing postoperative magnetic resonance imaging. Facial prostheses utilizing craniofacial implants might be hooked up via magnets or clips. Auricular prostheses have been proven to present near preoperative ranges of listening to for patients undergoing a total auriculectomy. Sun and chemical publicity will degrade the color and floor of a facial prosthesis. Skin grafts are really helpful around craniofacial implants to cut back the quantity of tissue movement and facilitate ease of cleaning. The short-term results of radiation on the dentition, periodontium, and mucosal surfaces include the following: i. The long-term results of radiation on the dentition, periodontium, and mucosal surfaces embrace the following: i. After a segmental resection without reconstruction, the remaining mandible deviates away from the resection. After a segmental resection with out reconstruction, sufferers can typically prepare the mandible to seat in full occlusion with stretching and follow. Mandibular defects usually result in obliteration of the buccal and lingual vestibules, thereby bettering the match and function of a prosthesis. A history of poor dental compliance indicated by poor oral hygiene and multiple missing and decayed tooth. Symptomatic impacted or incompletely erupted enamel not fully lined by alveolar bone. The following surgical points are related to palatal resection so that the functional outcome of an obturator is maximized: i. Depending on the size and placement of the defect of the palate and/or maxilla, the following could occur: i. Posterior and superior motion of the middle third of the taste bud, the anterior motion of the posterior pharyngeal wall, and the medial movement of the lateral pharyngeal partitions. Posterior and inferior motion of the middle third of the taste bud, the anterior movement of the posterior pharyngeal wall, and the medial movement of the lateral pharyngeal partitions. Posterior and superior movement of the middle third of the taste bud, the posterior motion of the posterior pharyngeal wall, and the medial movement of the lateral pharyngeal partitions. Posterior and superior movement of the middle third of the soft palate, the anterior movement of the posterior pharyngeal wall, and the inferior motion of the lateral pharyngeal walls.
Discount rumalaya gel 30 gr with visa
Use a temporalis flap to assist the attention soft tissues muscle relaxant headache order rumalaya gel 30 gr amex, affix the palatal prosthetic spasms from kidney stones 30 gr rumalaya gel discount otc, and then shut all incisions. Use a composite microvascular free flap with or with no palatal prosthetic to reconstruct the orbital flooring and palatal defect. What are essential considerations in maintaining a functioning left eye postoperatively and maintaining good eye symmetry? Coverage of all free bone grafts and alloplastic material with vascularized tissue E. A lateral rhinotomy incision with lip-split and eyebrow extensions is sufficient for a total maxillectomy procedure. Adenocarcinoma is the second commonest malignancy of the sinonasal cavities and mostly involves the ethmoid sinus. With present strategies of craniofacial resection, the salvage fee for regionally recurrent adenoid cystic carcinoma exceeds 30%. There is a robust association between adenoid cystic carcinoma and publicity to tobacco smoke. Adenoid cystic carcinoma has a excessive price of systemic disease at initial presentation. Chemoradiation remedy is the popular main therapy for adenoid cystic carcinoma invading the orbit. Lymphatic spreading to regional nodes is the primary route of metastasis for this most cancers. This approach requires an entire transfixion incision of the membranous septum linked to bilateral intercartilaginous incisions within the nasal cavities. This approach requires bilateral gingivobuccal incisions to the maxillary tuberosities on either side. This approach can be combined with Le Fort I osteotomies for entry to the nasopharynx and clivus. This approach is ideally suited to cancers of the superolateral facet of the maxillary antrum at the zygomatic recess. This incision avoids facial incisions and is wellsuited to tumors of the nasal cavity involving the inferomedial walls of both maxillary sinuses. A unilateral Le Fort I combined with a paramedian osteotomy of the palate may provide better publicity to the nasopharynx compared with bilateral Le Fort I osteotomies. For evaluation of the skull base and intracranial extension of cancer, which combination of research is most informative? Endoscopic cranium base approaches may be mixed with transfacial approaches to obtain higher tumor visualization and resection. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy could have a role in the management of this illness with intensive skull base invasion and is really helpful on protocol. The infraorbital nerve could be followed through a transfacial strategy all the way to the foramen rotundum. The cells had indistinct borders with scant cytoplasm and "salt and pepper" chromatin. A affected person underwent craniofacial resection through a Weber-Ferguson incision with Lynch and glabellar extensions. The affected person was then referred for postoperative adjuvant chemoradiation remedy consultation. Eighteen months later, the patient developed bilateral submandibular cervical plenty. There has been no further evidence of illness since the parotidectomy 6 months ago. The case in Question 74 illustrates the next necessary information regarding esthesioneuroblastoma besides A. Elective radiation remedy of the neck should be thought-about for advanced stage illness. The ophthalmic division of the trigeminal nerve travels through the superior orbital fissure. The oculocardiac reflex can be prevented by injection of lidocaine into the orbital apex delicate tissues throughout exenteration. Radiation therapy to either side of the neck Concurrent chemoradiation remedy Palliative chemotherapy Bilateral modified radical neck dissection alone E. A whole-body scan exhibits no evidence of tumor recurrence in the main site, handled neck, or at distant sites. Sinonasal renal cell-like adenocarcinoma can be distinguished from metastatic renal clear cell carcinoma by lack of vimentin and renal cell antigen. Inverted papilloma is the most typical benign sinonasal tumor throughout the pediatric population. Place the next lesions in the right order of deteriorating 5-year survival charges (from highest to lowest survival rate): A. Place the following most cancers subsites in the right order of deteriorating outcomes (from greatest to worst outcomes): A. A maxillary swing operation requires a WeberFerguson incision with subciliary extension and permits entry to the infratemporal fossa. Local failure is the commonest sample of failure after treatment of sinonasal cancers. There may be a beneficial role for neoadjuvant chemotherapy for locally extensive tumors of the sinonasal cavity with important intracranial extension. Which of the next statements about sinonasal neuroectodermal most cancers are correct? Sinonasal rhabdomyosarcomas are treated with surgical procedure followed by adjuvant radiation therapy. Surgery is advocated as the most effective palliation for patients with isolated metastatic renal cell carcinoma to the maxillary sinus. Irradiation of neck nodes is a vital component of therapy in sinonasal rhabdomyosarcomas. A 63-year-old man presents with an ulcerative lesion involving the left facet of his onerous palate. The patient additionally has left-sided ptosis and ophthalmoplegia with double imaginative and prescient on left lateral gaze. The affected person ought to have a total maxillectomy and orbital exenteration adopted by radiation remedy. Chondrosarcomas of the nasal cavity are the most typical type of sarcoma in this location. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy could additionally be an possibility for patients with domestically superior illness earlier than surgery. Sinonasal neuroendocrine carcinomas stain positive for cytokeratin and neuron-specific markers. For sinonasal cancers, which of the next are independent prognosticators for disease specific survival? B Core Knowledge · Industrial publicity to nickel, leather-based, wooden dust, textile dust, chromium, formaldehyde, and asbestos are causative elements for sinonasal oncogenesis.
Syndromes
- Cysts
- The most severe type of muscle atrophy is neurogenic atrophy. It occurs when there is an injury to, or disease of, a nerve that connects to the muscle. This type of muscle atrophy tends to occur more suddenly than disuse atrophy.
- Antibiotics for infections in the bile ducts
- Check the sensation (feeling) on your feet
- Fever
- Insomnia
- Alcohol abuse
- An abnormal aortic aneurysm that is leaking
- The last part moves downward, toward the feet. It is called the descending aorta.
Rumalaya gel 30 gr generic
It may be difficult by onerous exudates muscle relaxant review rumalaya gel 30 gr buy discount online, macular edema or hole muscle relaxant anxiety effective 30 gr rumalaya gel, epiretinal membrane, bleed, uveitis, exudative retinal detachment, fibrotic bands inflicting tractional or rhegmatogenous retinal detachment, vitreous hemorrhage, neovascular glaucoma, postpapilledema optic atrophy, and phthisis bulbi. Exophytic tumors come up from the outer retina and occur mostly within the peripapillary region. Sturge-Weber Syndrome (Encephalotrigeminal Angiomatosis) Glaucoma occurs in approximately 71% of sufferers and is extra widespread when the cutaneous hemangioma includes the eyelid and when prominent conjunctival or episcleral hemangiomas are current. The early-onset glaucoma is as a end result of of trabeculodysgenesis with a flat, anterior iris insertion like main infantile glaucoma. Later-onset glaucoma is due to elevated episcleral venous strain, although anomalous angle structures may have a role. Choroidal hemangiomas may be circumscribed, discrete, showing as yellowish, elevated, circular areas, which disappear or decrease in visibility with scleral depression. Neurofibromatosis Type 2 (Central Neurofibromatosis) Common ocular options are cataracts (posterior subcapsular cataract, capsular, cortical or mixed) creating in third decade in two-thirds sufferers, options due to acoustic neuroma (decreased Wyburn-Mason Syndrome Unilateral racemose hemangioma (arteriovenous malformation) is seen within the fundus characterized by dilated, bright purple arteries and veins which communicate with out an intervening capillary mattress. Similar lesions are current in ipsilateral midbrain, basofrontal area or the posterior fossa, which may spontaneously bleed or cause epilepsy. Ataxia-Telangiectasia (LouisBar Syndrome) Ocular options include conjunctival telangiectasia (bilateral dilated and corkscrew, bulbar conjunctival vessels at interpalpebral area) developing at age of 47 years, ocular motor apraxia with head thrusts and the lack to generate saccades and lack of optokinetic responses develop at a later age. Ocular features are orbital varices and retinal varicosities, glaucoma, cataracts, heterochromia, and Marcus-Gunn pupil. Classic diabetic cataract consists of snowflake cortical opacities occurring in the younger diabetic. Nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy is characterized by microaneurysm, intraretinal hemorrhages (superficial or splinter hemorrhage and deep or dot blot hemorrhage), cotton wool spots (soft exudates) and onerous exudates. Proliferative diabetic retinopathy is characterised by neovascularization of within one disc diameter of optic disc or in retina, vitreous hemorrhage, preretinal hemorrhage, tractional retinal detachment, combined tractional and rhegmatogenous retinal detachment, and neovascular glaucoma. Other ocular features are nystagmus, strabismus, and vitreous hemorrhage, most likely as a end result of coagulopathy, retinal scarring and pigmentary changes. Deposition of the corneal crystals begins within the anterior stroma and progress posteriorly, and starts from the periphery of the cornea to the middle. The crystal can get deposited in subepithelial tissues of conjunctiva; in sclera and episclera; in epithelium and stroma of iris; in pigmented and nonpigmented epithelium and connective tissue of ciliary physique; in choroid, primarily within fibrocytes and histiocytes; in retinal pigment epithelium; in meninges and fibrovascular pial septae of the optic nerves; and in extraocular muscles. Retinal options like progressive pigmentary retinopathy, yellow mottling of the macula, glistening crystallike deposits at retina might current earlier than corneal involvement. Glaucoma is because of pupillary-block brought on by thickening and rigidity of the iris as a end result of crystal deposition, narrow anterior chamber in youngsters, or main open angle glaucoma in adults. Nephropathic late onset form is milder with less severe and late involvement of kidney and eye. In non-nephropathic or ocular or grownup or benign form, only cornea is concerned sparing retina and kidney. Mucopolysaccharidoses Ocular features are progressive corneal clouding, pigmentary retinal degeneration, optic atrophy, generally papilledema, and in some cases glaucoma. Corneal involvement is characterised by punctate corneal opacification and diffuse stromal haze. Lowe Oculocerebrorenal Syndrome It is a uncommon X-linked recessive dysfunction affecting the central nervous system, eyes, and kidneys. The diagnostic triad includes congenital cataracts, mental retardation, and renal tubular dysfunction. Other options are hypotonia and areflexia, proximal tubular acidosis, aminoaciduria, phosphaturia, frontal prominence, chubby cheeks, sunken eyes, failure to thrive and low-molecular-weight proteinuria. It is considered one of rare circumstances in which congenital glaucoma and congenital cataract coexist. Systemic features are liver illness (icterus), basal ganglia dysfunction (abnormal movements) or psychiatric disturbances. Cornea is concerned in practically all patients and is characterised by a zone of copper granules in the peripheral a half of Descemets membrane (Kayser-Fleischer ring, best detected on gonioscopy when subtle) beginning near superior and inferior limbus which change colour (golden to greenish yellow, bronze, or brownish) underneath various sorts of illumination and may disappear with penicillamine remedy. The Kayser-Fleischer ring is usually absent in sufferers with acute liver disease and in asymptomatically affected siblings of sufferers with Wilsons disease. Ocular features are sunken eyes because of decreased orbital fats; pale, steely, stubby and sparse eyebrows; mild blue or grey irides with a fragile stromal pattern, generalized hypopigmentation of the fundus with increased visibility of the choroidal sample, tortuosity of the retinal arterioles, poorly defined macular landmarks, disc pallor evolving with time, nystagmus, strabismus, blepharitis, dacryostenosis, and potential tear deficiency. Lid lag, soft tissue involvement and proptosis are the commonly seen, but restricted eye muscle motility; severe strabismus and optic neuropathy are often not seen. Myeloid sarcoma (granulocytic sarcoma) is caused by malignant cells of myeloid origin with characteristic green colour (chloroma). Orbital involvement often presents at about age 7 years with speedy onset of proptosis, generally bilateral, which may be related to ecchymosis and lid edema. Chronic leukemia is characterized by microaneurysms, retinal venous occlusions, peripheral retinal neovascularization, and choroidal infiltrates giving rise to leopard skin look. Systemic Disorders Lipid Storage Disorders They are normally autosomal recessive lysosomal storage disorders resulting in deposition of lipid in viscera, central nervous system and retina because of deficiency in certain enzymes concerned in lipid metabolism. The typical fundus discovering is cherry pink spot, because of accumulation of lipids in the ganglion cell layer of the retina, giving the retina a white appearance. As ganglion cells are absent at the foveola, this area retains relative transparency and contrasts with the encompassing opaque retina, and choroidal vasculature is strikingly visible at fovea resulting in cherry red appearance. The late stage of the disease is characterized by degeneration of the retinal nerve fiber layer and consecutive optic atrophy. Anemia and Thrombocytopenia Ocular options are retinal venous tortuosity which can be associated to the severity of anemia, particularly in beta-thalassemia major; dot/blot and flame-shaped hemorrhages, cotton wool spots and Roth spots which are unassociated with period and kind of anemia and seen with thrombocytopenia in aplastic anemia; and optic neuropathy with centrocecal scotomas in pernicious anemia. Mucolipidosis Type I (Sialidosis) Corneal clouding, macular cherry-red spot, optic atrophy and generally punctate lens opacities. Hyperviscosity Syndrome this can be a group of diseases characterised by elevated blood viscosity as a outcome of polycythemia or to abnormal plasma proteins. Ocular features are retinal hemorrhages and venous dilatation, retinal vein occlusion and conjunctival telangiectasia. Sickle Cell Retinopathy Sickle cell retinopathy may be proliferative or nonproliferative. It is characterized by peripheral arteriolar occlusion and ischemia, peripheral arteriovenous anastomoses, sea-fan neovascularization of which 3040% of bear autoinfarction, vitreous hemorrhage, extensive fibrovascular proliferation and retinal detachment. Other options are comma or cork screw formed vascular conjunctival lesions, circumscribed areas of ischemic iris atrophy, and rubeosis iridis. Farber Disease Macular cherry-red spot, pingueculum-like conjunctival lesions and nodular corneal opacity. Gaucher Disease Type I, has ocular features together with white deposits in anterior chamber constructions (the corneal endothelium, pupillary margin, the angle, and ciliary body), prominent pingueculae, grayish perimacular retina with some white spots, pigmentary modifications in the macula, macular atrophy, abnormally permeable retinal vasculature, not often corneal opacity and uveitis. Langerhan Cell Histiocytosis Ocular features are unilateral or bilateral osteolytic orbital lesions and gentle tissue involvement usually within the superotemporal quadrant leading to proptosis, strabismus because of extraocular muscle involvement, and vision loss due to optic nerve involvement. Other ocular options are hypoplastic, colobomatous or pigmented optic nerve head, microphthalmos, iris colobomas, persistent pupillary membranes and cataract. Behзet Syndrome (Adamantiades-Behзet Disease) It consists of triple symptom complicated of recurrent aphthous oral ulcers, genital ulcers and uveitis. Other systemic manifestations are erythema nodosum, arthritis, and meningoencephalitis.
30 gr rumalaya gel discount with amex
Avoidance of contact sports activities for three months in sufferers with infectious mononucleosis is advisable because of the danger of splenic rupture muscle relaxer 7767 30 gr rumalaya gel proven. Castleman illness is characterized by progressive lymph node enlargement muscle relaxant no drowsiness rumalaya gel 30 gr free shipping, iron-deficiency anemia, and risk of progression to non-Hodgkin lymphoma. High nodal ratio (the variety of constructive metastatic lymph nodes divided by the number of lymph nodes eliminated at neck dissection) iv. Poorly differentiated histological type in major oropharynx cancer i, iii, iv i, iii, vi v, vi, vii ii, iii, iv iv, vi, vii fifty two. A 37-year-old affected person with a 2-cm unilateral medullary thyroid carcinoma and a radiologically unfavorable neck v. Which of the next primary sites may drain initially to lymph nodes positioned above the lower border of the mandible (facial nodes)? Arrange the next eventualities based on the probability of harboring occult cervical metastases within the radiologically negative neck, giving the most probably first. Arrange the next threat components so as of significance in predicting cervical metastases in a affected person with oral cavity most cancers and a clinically unfavorable neck, giving the best risk factor first. Arrange the following in order of probability of obtaining regional management, from best probability to least. Neck dissection alone for administration of the neck in a affected person with T1N1 oral cavity cancer and a single ipsilateral 2. Neck dissection alone for administration of the neck in a affected person with T1N1 tonsil most cancers and a single ipsilateral 2. Therapeutic neck dissection in a affected person with an preliminary diagnosis of T2N0 oral cavity cancer who develops neck "metastases" in degree I 6 months after surgical procedure to the primary tumor and observation of the neck vi. Salvage neck dissection in a affected person with an initial analysis of T1N1 tonsil most cancers who develops a recurrent metastatic cervical mass on the ipsilateral (previously treated) aspect of the neck, 1 yr after present process tonsillectomy plus neck dissection plus postoperative radiation therapy viii. Which of the next statements relating to functional outcomes of neck dissection are true? Despite preservation of the higher auricular nerve, most sufferers may have numbness of the neck. The danger of postoperative decrease lip weak spot is elevated when dissection of degree I is carried out. Which of the following statements are true concerning remedy of the neck with chemoradiation therapy for established metastatic disease? The presence of N3 neck illness is considered a contraindication for nonsurgical remedy. Neck dissection performed inside 6 weeks of completion of remedy may present the next incidence of residual cancer in lymph nodes than neck dissection performed past 12 weeks after completion of therapy. Large-volume neck disease has a lower probability of response to chemoradiation therapy than does small-volume neck disease. Which of the following statements concerning metastatic cervical cancers of unknown primary website are true? In instances in which the histological sort is unsure, immunohistochemical analysis with S100 should be carried out to exclude lymphoma. The phrenic nerve may be distinguished from branches of the cervical plexus by its direction (lateral to medial). Bilateral neck dissection concurrently whole laryngectomy has been related to an increased rate of salivary fistula. Runs from lateral to medial, over the scalenus anterior muscle, deep to the transverse cervical vessels. Runs from medial to lateral, over the scalenus anterior muscle, deep to the transverse cervical vessels. Runs from medial to lateral, over the scalenus anterior muscle, superficial to the transverse cervical vessels. Runs from lateral to medial, over the scalenus anterior muscle, and has a variable relationship with the transverse cervical vessels. Modified radical or radical neck dissection, with sacrifice of the sternomastoid muscle and accent nerve or inside jugular vein, if these buildings are concerned. Induction chemotherapy with the selection of additional surgical therapy relying on the response. During the course of a neck dissection, the surgeon inadvertently punctures the lower finish of the internal jugular vein, causing profuse bleeding. Raise the top of the mattress, establish the tear, and restore it with polypropylene sutures (5-0 Prolene). Raise the top of the mattress, determine the tear, and repair it with a patch graft from a saphenous vein. Lower the head of the mattress, use two suctions, determine the tear, and restore it with polypropylene sutures. Pack the lower part of the wound with moist gauze and request a thoracic surgical procedure session, leaving the pack in place till a partial upper sternotomy is carried out. Sharply dissect the most cancers from the accessory nerve, with the purpose of eradicating all macroscopic illness; nerve sacrifice should be reserved for cases of nerve encasement or lack of ability to separate all grossly visible illness from the nerve. Perform sharp dissection with the aim of separating as much cancer as attainable from the accessory nerve, then deal with the affected person with postoperative chemoradiation remedy. Convert to a radical neck dissection, levels I via V, with sacrifice of the accent nerve, sternomastoid muscle, and internal jugular vein. Which of the following is the most acceptable rule of thumb for when lateral selective neck dissection must be carried out for sufferers with papillary thyroid carcinoma? For which of the next cancers does the presence of metastatic neck disease portend the worst prognosis in phrases of total survival? The probability of viable tumor in cervical lymph nodes being found at neck dissection is A. Which of the next sufferers whose necks are managed with statement is most vulnerable to developing a recurrence in the neck? Which of the next salivary cancers arising in the parotid gland is more than likely to metastasize to cervical nodes? The incidence of discovering further metastatic nodes with completion neck dissection is A. Tumor seen on histological examination to be clearly arising from the wall of the branchial cyst C. The treatment of alternative for lymphadenopathy attributable to atypical mycobacteria in kids is A. Supplies the sternomastoid, levator scapulae, and trapezius muscle, aiding in elevation and rotation of the scapula. Supplies the upper and middle fibers of the trapezius, however not the lower fibers, such that injury leads to unopposed depression and "winging" of the scapula. Supplies the decrease fibers of the trapezius, which is answerable for rotation of the scapula. Supplies the sternomastoid muscle, which assists in elevating the clavicle and turning the head to the ipsilateral facet. Provides a contribution to the accent nerve, which is liable for proprioceptive function of the trapezius muscle.
Proven rumalaya gel 30 gr
The greater petrosal nerve (preganglionic sympa thetics) joins the deep petrosal nerve (postgangli onic parasympathetics) to form the nerve of the pterygoid canal muscle relaxant you mean whiskey 30 gr rumalaya gel free shipping. The thyroid gland begins embryological de velopment inside the fetal oropharynx at 3 weeks muscle relaxant id buy rumalaya gel 30 gr with mastercard. The preganglionic fibers involved within the parotid gland parasympathetic supply journey from the superior salivatory nucleus via the glossopharyngeal nerve, the tympanic plexus, and the greater petrosal nerve, and the postganglionic fibers journey by way of the otic ganglion and the auriculotemporal nerve to the parotid. The preganglionic fibers involved in the parotid gland sympathetic supply start within the interomediolateral horn nucleus between T1 and T3 and enter the sympathetic chain; postganglionic fibers start at the superior cervical ganglion and follow the exterior carotid to the parotid. The geniculate ganglion branches are the higher superficial petrosal nerve, the lesser petrosal nerve, and the external petrosal nerve. In the pterygoid canal, the greater petrosal nerve joins the deep petrosal nerve to become the nerve of the pterygoid canal. The nerve of the pterygoid canal synapses in the pterygopalatine ganglion, and postsynaptic fibers through V2 (the maxillary nerve) supply the lacrimal gland and mucous glands of the nasal and oral cavities. The lesser petrosal nerve carries postganglionic parasympathetic secretory fibers to the parotid gland via the otic ganglion. Removal of bone alongside the lateral surface of the digastric ridge is a useful approach for identi fication of the facial canal at the stylomastoid foramen. The Cernea classification describes the course of the external department of the superior laryngeal nerve in relation to the cricothyroid muscle. The infratemporal fossa is bounded posteriorly by the spine of the sphenoid and the articular tubercle of the temporal bone. The infratemporal fossa is bounded superiorly by the greater wing of the sphenoid and the beneath floor of the squamous portion of the temporal bone. The lateral pterygoid muscle originates on the infratemporal surface of the higher wing of the sphenoid bone and the medial facet of the lateral pterygoid plate. The parathyroid glands are each exclusively sup plied by the inferior thyroid artery of the thyrocer vical trunk. In the intestine, the activated form of vitamin D in creases calcium absorption through the calciumbinding protein calbindin. The squamous epithelium and superficial lamina propria serve as the vocal mucosal vibratory com ponent in phonation. The posterior cricoarytenoid muscle abducts the vocal cords by adducting the rima glotti dis. The vocal ligament is composed of the superfi cial and intermediate layers of the lamina pro pria. The "physique" of the vocal wire consists of the thyroarytenoid and vocalis muscular tissues. Oral cavity (a) the superior surface of the taste bud (b) Vallecula (c) Aryepiglottic folds (d) Fossa of Rosenmьller (e) Postcricoid (f) Glossotonsillar sulci (g) Retromolar trigone (h) Upper margin of the cricoid (i) Posterior hard palate (j) Lingual aspect of the epiglottis fifty two. Assign true (T) or false (F) to the next state ments: (a) the larynx ascends as a baby grows. Assign true (T) or false (F) to the next state ments: (a) the second lamella types the ethmoid bulla. A perforated membranous sheet extending from the orbital rim to the eyelid, incorporating superiorly the levator palpebrae superioris and inferiorly the tarsal plate in the lower eyelid. A membranous sheet extending from the or bital rim to the eyelid anastomosing with the superior and inferior tarsal plates. A steady fibrous sheet extending from the orbital rim to the decrease tarsal plate. A perforated membranous sheet extending pos terior to the levator palpebrae superioris and lower tarsal plate. A paralyzed tongue protrudes to the ipsilateral side of nerve harm due to unopposed A. The nerve travels deep to the stylohyoid and posterior belly of the digastric muscle. The nerve presents innervation to the intrinsic and extrinsic muscular tissues of the tongue. Contains the duct of Rivinus, which is formed when anterior sublingual ducts fuse into a sin gle duct. The eustachian tube opens throughout swallowing or yawning due to the next muscles, except the A. C higher thoracic esophagus starts 20 to 25 cm from the incisors, the middle thoracic esophagus starts 25 to 30 cm from the incisors, and the decrease thoracic esopha gus and esophagogastric junction begin 30 to 40 cm from the incisors. A single sheet of fascia covers the posterior stomach of the omohyoid, fixing it to the clavicle, and a thin sheet passes in front of the strap muscle tissue. Above the hyoid, it covers the mylohyoid and the anterior stomach of the digastric and splits into two layers, investing the mandible. It envel ops the parotid gland and submandibular gland be fore extending up to cover the masseter and ultimately inserts into the zygomatic arch. The muscular division invests the sternohyoid, sternothyroid, thyrohyoid, and omo hyoid muscle tissue. This layer extends from the hyoid and thyroid cartilages to the sternum, clavicle, and scapu la. This covers the posterior compartment of the neck deep to the extra superficial visceral compartment. It lies deep to the nice vessels of the neck but superficial to the phrenic nerve. The prevertebral division is anterior to the vertebral bodies, enclosing the vertebral muscu lature and inserting into the transverse processes. The alar division extends throughout the midline, from transverse process to transverse course of. It contains the vault, the lateral wall (includ ing the fossa of Rosenmьller and the mucosa cover ing the torus tubaris), and the posterior wall. The constructions in the oropharynx embody the bottom of the tongue, the inferior (anterior) floor of the taste bud, uvula, anterior and posterior tonsillar pillars, pharyngeal tonsils, posterior wall, and lateral wall. The buildings within the hypopharynx embody the pyri form sinus, lateral wall, posterior wall, and postcricoid wall (which is the anterior wall of the hypopharynx). The inferior boundary of the supraglot this is the horizontal plane by way of the lateral mar gin of the ventricle at its junction with the superior floor of the vocal twine. It accommodates the ascending mandibular ramus, the posterior physique of the mandi ble, and the muscular tissues of mastication. Anteriorly is the infratemporal face of the maxilla and posteriorly the foundation of the ptery goid course of and the higher wing of the sphenoid. In the pterygoid canal, the higher petrosal nerve (preganglionic parasympa thetics) joins the deep petrosal nerve (postganglionic sympathetics) to become the nerve of the pterygoid canal. The nerve of the pterygoid canal synapses in the pterygopalatine ganglion, and postsynaptic fibers via the V2 maxillary nerve provide the lacrimal and mucous glands of the nasal and oral cavities.

Generic rumalaya gel 30 gr without prescription
The limbs seem tubular and featureless spasms left side abdomen purchase rumalaya gel 30 gr without prescription, missing the standard flexion creases at the elbow muscle relaxer x generic rumalaya gel 30 gr amex, wrists and knees. Muscle mass is lowered, typically resulting in lack of contours to the shoulders and skinny stick-line calves. If the situation is recognized prenatally (as a consequence of lowered fetal mobility and the presence of contractures or deformity), elective cesarean part is normally performed. There is lowered motion in a quantity of joints with a firm block beyond a restricted range. Feeding, swallowing and respiratory difficulties could additionally be encountered in the neonatal interval necessitating supportive remedy. Jaw stiffness, an motionless tongue, hypo/retrognathia, a small jaw and weak respiratory muscles could collectively contribute to the above. The shoulders are adducted and internally rotated, the elbow joints prolonged and the wrists in severe flexion and ulnar deviation. The fingers are variably affected with some joints in flexion and others in extension. The hips typically relaxation ready of flexion, abduction and external rotation. The knees are stiff in extension, although flexion contractures may develop because the child turns into older. Severe knee flexion contractures at delivery are extra attribute of the congenital pterygium syndromes than classic arthrogryposis. Inguinal hernias can occur in up to 15% of individuals owing to generalized muscle weak point. Language growth could also be delayed as a outcome of weak spot of the tongue and muscular tissues of speech. If typical medical features are current, session from a medical geneticist in conjunction with a pediatric orthopedic surgeon and pediatric neurologist might help with diagnosis and identification of particular subtype in individual circumstances. The treating clinician ought to weigh the pros and cons of proceeding additional with the diagnostic process. Long-term remedy choices should keep in mind the severity of the situation, pure historical past and anticipated useful status at maturity. Close coordination between the bodily therapist, occupational therapist and pediatric orthopedic surgeon is necessary all through childhood. Judicious, well-timed surgical intervention together with serial casting, muscle strengthening exercises, night-time splinting of joints and day-time use of orthotics stay the mainstay of treatment. Hip dislocation may be unilateral or bilateral and is current in two-thirds of patients. Conservative administration in a Pavlik harness or hip abduction brace is ineffective typically as is closed discount of the dislocated hip. This process is carried out by way of a minimally invasive strategy with a decreased interval of immobilization (typically round 812 weeks in a hip spica). Flexion contractures may be current at birth or develop later in life with progress. Serial casting and regular stretching workout routines by educated therapist/parents is attempted quickly after start however is profitable in a small variety of circumstances. Where necessary, the surgical procedure can be conveniently timed with open discount of the hip. Neglected knee extension or flexion contractures can have an result on ambulatory potential and are finest dealt with before the first yr of life. Several contracture releases or bony procedures could additionally be required throughout childhood, as recurrences are common. Several authors have reported good preliminary success rates with Ponseti methodology in rigid clubfeet. Treatment of the clubfoot is commenced soon after delivery with serial casting followed by a percutaneous achilles tenotomy. A strict regime of full-time (for 3 months), adopted by night-time use of foot abduction braces up to the age of a minimum of 45 years is beneficial. With the appearance of Ponseti technique, the need for radical bony procedures in young children may be averted. A detailed functional assessment by an occupational therapist and the opinion of the mother and father are essential elements of the choice making process. Typical procedures include humeral osteotomy to enhance flexion on the elbow, dorsal wedge carpectomy to place the wrist in a impartial place and launch of a thumb-in-palm deformity. Surgical correction is reserved for progressive, severe curves that intervene with sitting stability or walking potential. Arthrogryposis refers to a clinical image, the place congenital joint contractures involve two or extra components of the body. Orthopedic management is advanced and must be attempted in a multidisciplinary setting. This would come with vulnerability to deprivation (food, education and parental care), exploitation, abuse, neglect, violence, and diseases. According to World Bank, vulnerability is a relative state-a multifaceted continuum between resilience and absolute helplessness. It outlines the next primary categories of vulnerable youngsters: (i) street kids, (ii) youngsters in the worst forms of baby labor, (iii) kids affected by armed conflict, (iv) youngsters with chronic sickness, (v) orphans, and (vi) youngsters residing with disability. A weak baby may be grouped into multiple of these classes; orphans can also be street kids or having disability. Family conditions that make the child weak Parental discord, disharmony, divorce, drug abuse, dependancy, and alcoholism are essential danger elements. Children are more likely to be vulnerable, if one or both mother and father are physically or mentally handicapped or significantly unwell. The group context Children living in dangerous situations, with exposure to war, crime, abuse, poverty are more probably to be weak. Lack of proper education, play, and living in settlements with poor water, housing and sanitation amenities also prevent the kid from leading a normal life. There had been 35 million kids (age 018) orphaned because of all causes in 2003 in India, and orphans constituted about 9% of the entire children. Direct estimates for orphan young persons are not obtainable however the basic developments from other regions counsel that more than half of the orphans are aged more than 12 years. Early marriage and childbirth make a younger feminine susceptible to malnutrition and domestic violence. Most out there data relate to the prevalence and factors associated to alcohol or smoking or substance abuse. Some other studies have targeted on school-based programs to modify the risk of substance abuse and violence. In basic, school-based programs, especially those focused towards highrisk students, and those involving skilled personnel and peer leaders had a average influence in modifying the outcomes. Vulnerability is a relative state with its diploma and kind various extra time and between countries, and is extremely contextual. Children and young individuals separated from their dad and mom are clearly vulnerable groups. Besides that, extreme poverty, chronic illness-of self or parents-and lack of social support and schooling additionally make kids susceptible to abuse, neglect, deprivation and violence.
30 gr rumalaya gel generic fast delivery
These lesions are smoothly marginated by an intact overlying capsule delineated by perihepatic fats muscle relaxant chlorzoxazone side effects buy 30 gr rumalaya gel mastercard. The development and improvement of adjunctive therapeutic methods back spasms 9 months pregnant generic rumalaya gel 30 gr mastercard, together with angiographic embolization, biliary endostent placement, and imaging-based percutaneous drainage of sterile and infected collections, have been basic to the decreased requirement for surgery in such circumstances. The main issues of liver injury, whether operatively or nonoperatively managed, are hemorrhage, infarction (which can lead to necrosis and delayed bleeding), infection, and liver failure, as properly as biliary injuries, that are discussed in a separate section. Computed tomography on this setting ought to embrace noncontrast, arterial, and portal venous part acquisitions, and image evaluation should include assessment for recurrent bleeding and persistent or new vascular accidents, as nicely as for other problems, together with parenchymal infarction, necrosis, infection, and abscess formation. Liver parenchymal infarction is uncommon after hepatic arterial embolization because of parallel portal venous perfusion, however arterial compromise alone can result in biliary necrosis. Some embolic supplies, together with glue agents, are excessive in attenuation and could be mistaken for foci of distinction extravasation. Computed tomography findings of hemoperitoneum and contrast extravasation from liver harm portend early failure of nonoperative management, as in the case of the spleen, although liver injuries appear more amenable to spontaneous hemostasis. Nevertheless, when high-grade liver injuries are managed conservatively, the chance for complication remains higher than for lower-grade accidents. Although early surgery will often be prompted by bleeding, failure of nonoperative administration of liver harm most frequently results from biliary complications. Surgery Because nonoperative management has turn out to be the dominant paradigm for remedy after blunt hepatic injury, surgical intervention is now generally reserved for the most extreme liver injuries. For this reason, most of the circumstances taken to surgical procedure shall be managed with a damage-control approach, consisting of early laparotomy with rapid systematic exploration and temporizing management of hemorrhage and contamination with expedited temporary closure of the stomach. Prolonged surgical procedure for definitive resection or restore is deferred till after a 48- to 72-hour period of resuscitation and stabilization. Techniques for management of hepatic hemorrhage during damage-control surgery could include software of topical hemostatic brokers, electrocautery, parenchymal suturing, balloon tamponade, and perihepatic packing. The macerated liver was totally resected (B), and the patient received an emergent liver transplant. Early complications after liver trauma surgery embrace rebleeding, stomach compartment syndrome, and hepatic necrosis from traumatic, postembolic, or ligature devascularization. Clinical decompensation in the early part might immediate instant return to surgical procedure rather than repeat imaging, depending on the urgency of the medical scenario. Incomplete belly closure, often with a "Bogota bag" or negative-pressure (vacuum) dressing placement, is commonplace after damage-control laparotomy to cut back the danger for belly compartment syndrome, to allow removing of packing materials, and to carry out definitive restore or resection. Review of the operative notes, if out there, or direct session with the surgeon can improve the accuracy of postsurgical picture interpretation. In either case, reassessment of liver parenchymal and vascular integrity should be performed with consideration to the event of infarction or necrosis. Computed tomography could additionally be requested earlier than a affected person is cleared to return to significant bodily exercise similar to a contact sport, which may be thought-about at 3 to 6 months. Healing liver lacerations might turn out to be more clearly outlined on short-interval follow-up imaging but should lower in dimension over time. Biliary accidents are extremely associated with liver, splenic, and duodenal injuries. Gallbladder accidents could also be categorized into three main categories: contusion, laceration/perforation, or full avulsion. Contusions are thought of to be the mildest of accidents with intramural hematomas and are treated conservatively. Avulsion injuries could contain variable parts of the gallbladder, cystic duct, and artery. Injuries associated with cystic artery transection might lead to main blood loss. Cholecystectomy remains a gold commonplace for management of this form of gallbladder harm. Injuries to the extrahepatic bile ducts are tough to detect and are associated with high morbidity and mortality, particularly if prognosis is delayed. Diagnosis of extrahepatic bile duct harm could additionally be tough, even at surgery, with up to 20% of injuries missed at surgical procedure. Bile duct harm is normally associated with different intra-abdominal organ injuries, most commonly blunt hepatic trauma. Intrahepatic Bile Duct Injury Injuries to the intrahepatic bile ducts are normally seen in sufferers with severe liver injuries. Intrahepatic biliary damage mostly impacts small subsegmental ducts; nonetheless, main ducts may be injured, often adjacent to the hilum. B, Ultrasonogram of the gallbladder demonstrated an identical discovering of diffuse wall thickening (arrowheads). Simple percutaneous drainage with extra endoscopic sphincterotomy and stenting for prolonged or high-volume biliary fistula is recommended for intrahepatic bile duct accidents. Extrahepatic Bile Duct Injury Extrahepatic duct accidents might occur at anatomic fixation, such because the intrapancreatic portion of the widespread bile duct, due to blunt influence or deceleration. Injury to the extrahepatic biliary tree is far less frequent and may be very unlikely to resolve with out percutaneous, endoscopic, or operative interventions. The majority of trauma-related injuries are distant to the hepatic confluence, in contrast to biliary duct damage after laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Roux-en-Y hepaticojejunostomy remains the gold commonplace for extrahepatic injuries. Injury inside the pancreatic head is at all times related to pancreatic or duodenal trauma. Occasionally, bile leak can outcome in biloma formation each within the intrahepatic and extrahepatic areas. Extrahepatic biloma are more than likely caused as a end result of bile leak from intrahepatic bile duct injury. Injury to the gallbladder and extrahepatic ducts is unusual sources for extrahepatic bilomas. Complications Delayed issues as a end result of biliary harm outcomes from bile leak and superinfection. Thickened wall could additionally be a highly suggestive signal of gallbladder injury but not specific for any specific type of harm. Intramural hematoma with a well-distended gallbladder may point out contusion without perforation. Delayed imaging at 4 hours is crucial because sluggish leaks will not be detected with early termination of the study. B, A caudal axial picture demonstrates contusion and hematoma across the duodenopancreatic complicated (curved arrows) with perihepatic fluid (arrowhead). C, Intraoperative cholangiogram demonstrates contrast leak (white arrows) and distal common bile duct harm (red arrow). D, Bile staining within the lesser sac (curved arrows) and intact gallbladder (straight arrow).