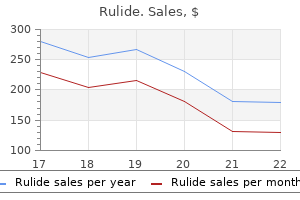
Rulide 150 mg order
Infants youthful than 6 months old typically present without systemic signs of an infection but may have fever or a septic presentation treatment 7 discount rulide 150mg without prescription. Initially medicine daughter lyrics rulide 150 mg purchase, irritability and anorexia are outstanding, followed by evidence of ache on motion or of decreased use of a limb (pseudoparalysis). Careful attention must be given to joint examination due to the excessive risk of joint extension and secondary septic arthritis. A historical past of antecedent upper respiratory tract or pores and skin infection is present in over 50% of cases. Systemic signs consist primarily of fever and irritability in affiliation with refusal to stroll, limp, or decreased use of an extremity. A small percentage present with extra severe systemic symptoms, together with chills, lethargy, irritability, anorexia, vomiting, and dehydration. At this age, kids are often unable to localize ache, however by remark they may be discovered to keep away from shifting the concerned extremity or to hold a particular joint in flexion constantly. Soft tissue swelling and warmth may be noted overlying a metaphysis, but it may be delicate or absent in early instances or undetectable if the proximal femur is involved. Even with cautious examination, focal tenderness could also be difficult to detect early within the course. Children older than 2 years old with acute osteomyelitis are sometimes febrile however hardly ever toxic. They are more doubtless to localize pain, and point tenderness is generally simple to elicit. Unless sympathetic effusion has developed, the adjacent joint could additionally be passively moved via its full vary of motion, though this exacerbates the ache. Osteomyelitis in sites apart from the long bones of the extremities may be difficult. Although fever and an irregular gait are the most common presenting complaints, lower stomach and groin ache, hip or buttock pain, sciatica, and thigh pain (with swelling) may be outstanding early complaints. Often, the initial clinical image suggests appendicitis, pelvic abscess, or femoral osteomyelitis. A excessive stage of suspicion and cautious examination are essential to set up the analysis. The onset of ache within the decrease stomach quite than the periumbilical region, absence of gastrointestinal signs or rebound tenderness, and normal findings on rectal examination assist distinguish pelvic osteomyelitis from acute appendicitis. Furthermore, although most patients have pain on hip movement in a number of planes, vary of motion is either regular or solely barely restricted, and with cautious examination, point tenderness can usually be detected. Acute Osteomyelitis Due to Contiguous Spread Acute osteomyelitis resulting from the contiguous spread of infection should be suspected in patients with prior puncture wounds, deep lacerations, surgical incisions or hardware, open fractures, abscesses, or cellulitis who experience a sudden onset of elevated pain at the website. This ache is perceived as deep, extreme, and constant and is aggravated by movement. Osteomyelitis because of extension of primary delicate tissue infection may present as worsening after a period of initial enchancment or failure to response to antimicrobials. Diagnostic Methods in Acute Osteomyelitis Standard laboratory and radiographic studies are of restricted use within the analysis of acute osteomyelitis. These markers are useful in figuring out an inflammatory process and for serial measurement to document response to remedy. Plain radiographic modifications lag behind the clinical manifestations and may be refined. Subsequently, the swelling will increase, obliterating fascial planes, and extends to contain subcutaneous tissues. These gentle tissue changes may be difficult to appreciate each time osteomyelitis includes vertebrae or pelvis; however, in cases of pelvic osteomyelitis, clouding of the obturator foramen, distortion of the fascial planes around the adjacent hip, and even displacement of the bladder could additionally be detectable. Technetium scans are additionally helpful in delineating extra foci in the uncommon patients with multiple websites. Standard radiographs stay essential in identifying fractures and malignancies, which can simulate the looks of osteomyelitis on bone scans. Importantly, 5% to 20% of children with acute osteomyelitis can have a false-negative bone scan in the course of the first few days. Fever, hip and thigh pain, and refusal to stroll had been the chief complaints in this 5-year-old youngster with osteomyelitis of the proximal femur. On inspection, she lay still, holding the left leg externally rotated and flexed at the hip and knee. A, the first noticeable change, occurring about 3 days after onset, is deep soft tissue swelling, seen here adjacent to the metaphysis of the distal tibia on the left. B, In this neonate, a radiolucency is evident in the proximal metaphysis of the proper femur, which can additionally be displaced upward and laterally. On aspiration of the hip, purulent fluid was obtained, confirming the suspicion of rupture of the infection into the hip and of secondary septic arthritis. C, this 1-year-old feminine introduced with four days of fever and lack of proper arm use. E, the late changes of a lytic lesion with sclerotic margins are seen in the best femoral metaphysis of this child who was finishing his course of therapy. Vigorous attempts are important to isolate the causative organism and determine antimicrobial susceptibilities, notably within the period of increasing antibiotic resistance. Aspiration of the positioning of maximal involvement as revealed by imaging supplies materials for Gram stain and culture. Blood cultures are positive in more than 50% of sufferers with acute hematogenous osteomyelitis and should be performed in all suspected cases. Complications of osteomyelitis embody secondary septic arthritis with resultant joint damage, epiphyseal damage with long-term morbidity ensuing from impaired bone growth, progression to persistent osteomyelitis (now fewer than 4% of cases), and barely pathologic fractures. The fee of complications is highest in younger infants who often have extensive bone involvement and secondary septic arthritis by the point the diagnosis is made. Care in medical evaluation and aggressive attempts to verify the diagnosis as early as potential are essential, as are adequate antimicrobial remedy and surgical intervention. Subacute Osteomyelitis Approximately 10% of instances of hematogenous osteomyelitis have an insidious onset and a subacute course characterised by mild to moderate native extremity ache, with or without swelling. In some cases, this subacute course may be related to partial suppression of the infection by antibiotics administered for one more an infection (such as, otitis media or impetigo). In these patients, ache might abate during antimicrobial remedy but worsen once the treatment stops. On examination, native tenderness is clear and overlying soft tissue swelling could additionally be famous. Biopsy is usually required to verify the prognosis and isolate the causative organism. A and B, this 13-year-old boy had a 7-week history of ache and swelling of both ankles.
Rulide 150mg
Hammerich L medicine 666 colds cheap rulide 150mg without a prescription, Tacke F: Role of gamma-delta T cells in liver irritation and fibrosis medicine 93 948 generic 150mg rulide overnight delivery. Kenna T, et al: Distinct subpopulations of gamma delta T cells are present in normal and tumor-bearing human liver. Hoh A, et al: the exercise of gammadelta T cells towards paediatric liver tumour cells and spheroids in cell tradition. Sun R, Gao B: Negative regulation of liver regeneration by innate immunity (natural killer cells/interferon-gamma). The success of current therapies of chronic liver irritation in reaching antifibrotic results may be measured by prolonged survival and presumably a decreased prevalence of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatic Inflammation as a Driver of Hepatic Fibrosis Liver inflammation is commonly associated with hepatocyte necrosis and apoptosis. Recent research have also recognized macrophages as crucial regulators of fibrosis. As with myofibroblasts, these cells are derived from either resident tissue populations, similar to Kupffer cells, or from bone marrow immigrants. Studies now counsel that the pathogenesis of fibrosis is tightly regulated by distinct macrophage populations that exert unique useful actions all through the initiation, maintenance, and determination phases of fibrosis. Unlike the acute setting, where the cellular players are predominantly neutrophils, continual inflammatory infiltrates are typified by mononuclear cells similar to macrophages, lymphocytes, and plasma cells. The persistence of these cells may end up in further tissue injury and set off a woundhealing response within the form of angiogenesis and fibrosis. Kupffer cells are located in the hepatic sinusoids, which enables them to instantly pattern the antigens that are transported from the gastrointestinal tract by way of the portal vein, making certain early publicity to pathogenic bacteria, and to be in close contact with other circulating immune cells. Therefore Kupffer cells have an important homeostatic position in defending the host and are capable of inducing both immunogenic and tolerogenic immune responses. In common, Th2-polarized responses promote fibrosis, whereas Th1 cytokines could additionally be antifibrogenic. However, this effect is observed solely within the early stage of liver fibrosis, not in superior liver fibrosis. Mouse fashions with selective increases of hepatocyte apoptosis by hepatocyte-specific deletion of cytoprotective factors develop liver fibrosis. This usually leads to mild irritation coupled with the recruitment and native differentiation of circulating immune cells (mainly monocytes), contributing to the reestablishment of homeostasis. In this setting, immune cells are stimulated to secrete a large panel of proinflammatory and hepatotoxic factors, leading to a vicious cycle connecting inflammation and cell death that mediates severe hepatotoxic effects. They control a broad spectrum of biologic processes, including cell proliferation, differentiation, growth, metabolism, apoptosis, secretion, and viral an infection. Mice poor in miR-122 displayed a phenotype of hepatic inflammation, fibrosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma, suggesting that miR-122 has an antiinflammatory function in the liver. The miR-29 household consists of miR-29a, miR-29b, and miR-29c, differing in only two or three bases. These results were confirmed in numerous fashions of liver fibrosis and have been independent of the mouse pressure analyzed. Therefore the inhibition of Smad7 in response to miR-21 enhancement during fibrosis is an important profibrogenic pathway, which might turn out to be a beautiful target for future therapeutic approaches. In addition, miR-122 could indirectly inhibit liver fibrosis by way of inhibition of the Conclusion the inflammatory response in the liver contributes to a fantastic extent to the development of acute and persistent liver ailments, together with fibrosis. Understanding the features of these immune cells, in addition to these of hepatic mesenchymal cells, and core pathways in liver fibrogenesis might assist us establish novel therapeutic targets for the treatment of liver fibrosis. Spicer J, Brodt P, Ferri L: Role of irritation in the early phases of liver metastasis. Mallet V, et al: Brief communication: the relationship of regression of cirrhosis to outcome in persistent hepatitis C. Abergel A, et al: Histological response in patients treated by interferon plus ribavirin for hepatitis C virus-related extreme fibrosis. Poynard T, et al: Impact of interferon alfa-2b and ribavirin on development of liver fibrosis in patients with continual hepatitis C. Sobesky R, et al: Modeling the influence of interferon alfa therapy on liver fibrosis progression in continual hepatitis C: a dynamic view. Mohamadnejad M, et al: Impact of immunosuppressive remedy on liver fibrosis in autoimmune hepatitis. Schvarcz R, Glaumann H, Weiland O: Survival and histological resolution of fibrosis in patients with autoimmune persistent lively hepatitis. Nishiguchi S, et al: Randomised trial of effects of interferon-alpha on incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in persistent energetic hepatitis C with cirrhosis. Hellerbrand, et al: Expression of intracellular adhesion molecule 1 by activated hepatic stellate cells. Winau F, et al: Ito cells are liver-resident antigen-presenting cells for activating T cell responses. Imamura M, et al: Suppression of macrophage infiltration inhibits activation of hepatic stellate cells and liver fibrogenesis in rats. Hintermann E, et al: Mechanism of autoimmune hepatic fibrogenesis induced by an adenovirus encoding the human liver autoantigen cytochrome P450 2D6. Xu J, et al: the types of hepatic myofibroblasts contributing to liver fibrosis of different etiologies. Parola M, Marra F, Pinzani M: Myofibroblast-like cells and liver fibrogenesis: Emerging ideas in a rapidly moving scenario. Bucala R, et al: Circulating fibrocytes define a model new leukocyte subpopulation that mediates tissue repair. Kisseleva T, et al: Bone marrow-derived fibrocytes take part in pathogenesis of liver fibrosis. Desmouliere A, et al: Extracellular matrix deposition, lysyl oxidase expression, and myofibroblastic differentiation through the initial levels of cholestatic fibrosis within the rat. Barry-Hamilton V, et al: Allosteric inhibition of lysyl oxidase-like-2 impedes the event of a pathologic microenvironment. Kisseleva T, et al: Myofibroblasts revert to an inactive phenotype throughout regression of liver fibrosis. Tacke F, Weiskirchen R: Update on hepatic stellate cells: pathogenic function in liver fibrosis and novel isolation techniques. Pellicoro A, et al: Liver fibrosis and restore: immune regulation of wound healing in a stable organ. Ramachandran P, et al: Differential Ly-6C expression identifies the recruited macrophage phenotype, which orchestrates the regression of murine liver fibrosis. Krizhanovsky V, et al: Senescence of activated stellate cells limits liver fibrosis.
Buy discount rulide 150 mg line
The morphologic characteristics and quantity of the endoplasmic reticulum differ in the completely different zones of the liver lobule symptoms jaw pain generic rulide 150mg with mastercard. Free ribosomes and polyribosomes are also current within the hepatocyte cytoplasm medications list template 150 mg rulide generic. Vesicles containing these proteins are directed to the proximate (cis) cisternae of the Golgi apparatus, for additional processing. Abundant free ribosomes within the cytoplasm participate within the synthesis of some proteins that will be secreted however synthesize essentially the entire structural proteins for the hepatocyte. Proteins which are to stay inside the cytoplasm or are destined to enter the nucleus, peroxisomes, or mitochondria are fully synthesized by free ribosomes. The Golgi complicated is a three-dimensional construction in hepatocytes, characteristically consisting of a stack of 4 to six parallel cisternae, typically with dilated bulbous ends containing electrondense material. This structure reveals a convex or proximal portion facing the nucleus and the endoplasmic reticulum (cis-Golgi), the place small vesicles transfer proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi, and a concave half (trans-Golgi), which connects with a post-Golgi trans-Golgi network that directs proteins in the course of their last destinations: to organelle membranes of the cell, the plasma membrane, or for secretion. The Golgi complicated is able to fast and reversible structural reorganization right into a tubuloglomerular community, while sustaining its biosynthetic capabilities. The outer membrane possesses special pores that permit the passage of molecules smaller than approximately 2000 Da. The space between internal and outer membranes presents a low-density matrix and ranges from approximately 7 nm to 10 nm in thickness. Mitochondria have a relatively low-density internal matrix in which lamellar or tubular cristae and a variable quantity of small dense granules may be observed. Several lessons of lysosomes could be identified within the hepatocyte cytoplasm: � Primary lysosomes, small in dimension, are thought-about from a useful perspective to be in a resting phase. The residual bodies comprise the residues of nondigested materials or pigments such as lipofuscins (which are thought of undigestible permanent residues). Lipofuscin granules are probably the most numerous lysosomal our bodies current in human hepatocytes. Hepatocyte iron deposits may also occur as single membrane-bound lysosomal bodies (residual bodies) forming aggregates of iron-containing electrondense particles (siderosomes-hemosiderin granules). In addition to hepatocytes, liver endothelial cells and Kupffer cells71 additionally accumulate intracellular iron underneath conditions of iron overload. In the hepatocyte the cytoskeletal organization depends on the association of the three main parts of this construction: the microfilaments, the intermediate filaments, and the microtubules. Microfilaments, made from actin, and microtubules, consisting of tubulin, are each concerned in intracellular motility. Microtubules are implicated in determining cell form, completing mitosis, and regulating the intracellular transport of vesicles. Many experimental research have proven that microfilaments play an energetic position in the dilatation and contraction of bile canaliculi,seventy four,seventy five thereby contributing to management of bile canalicular caliber and bile circulate. In the liver they present a relationship with Mallory our bodies (the structural marker of human alcoholic liver disease). They are situated around the nucleus, close to the cell border, within the cytoplasmic community, and around the bile canaliculi. Cytoplasmic Contents the hepatocyte is extremely wealthy in non�membrane-bound cytoplasmic inclusions, including glycogen granules, lipid droplets, and pigments of assorted natures. Glycogen is depleted throughout fasting, disappearing first from periportal hepatocytes and then from centrilobular cells. In this style, hepatocytes represent a serious metabolic vitality reserve during fasting, thus supporting systemic glucose homeostasis. Lipid inclusions seem as empty vacuoles in histologic sections, or osmiophilic droplets by transmission electron microscopy, and are usually not surrounded by membranes. Lipid droplets include triglycerides in their inside, and are coated with a monolayer of phospholipids. A variable amount of iron-containing granules are sometimes present inside the hepatocyte cytoplasm, which is heavily dependent upon the iron status of the host. With an roughly spherical shape, the iron-containing protein ferritin consists of a protein shell the Hepatic Sinusoid the hepatic sinusoid is a singular, dynamic, microvascular structure that serves because the principal web site of trade between the blood and the perisinusoidal area. Hepatic stellate cells, specialised pericytes that extend processes all through the space of Disse and serve as myofibroblasts throughout times of hepatic injury and repair 4. The sinusoidal endothelial cell fenestrae are so abundant that, on scanning electron microscopy, the greater part of the cell has a netlike look. The sinusoidal endothelial cell fenestrae vary greatly in size, but generally fall into two size classes: small fenestrae (0. Thus, endothelial cell porosity is greater within the perivenular zone than within the periportal zone. The larger fenestrae lie between sinusoidal endothelial cells, and a few workers contemplate that they could be artifacts as a outcome of fixation. For example, lack of cell-matrix interaction ends in loss of fenestrae in cultured sinusoidal endothelial cells, whereas cells plated on human amnion basement membrane retain their fenestrae. Transport of particulates considerably bigger than the size of the fenestrae is postulated to be achieved by the forced sieving and endothelial massage concomitant with the passage of blood cells, particularly leukocytes, through the sinusoids and the resulting interaction of those cells with the endothelial wall. These include bristle-coated pits (which are invaginations from the cell membrane), bristle-coated micropinocytotic vesicles, endosomes, switch tubules, and lysosomes. A giant variety of endogenous compounds could also be endocytosed, a few of that are effete molecules and are cleared from the circulation and others that are modified and seem to bear transcytosis to hepatocytes, maybe in a extra selective style than macromolecular solutes passing solely through the fenestrae. Capillarization of sinusoids with defenestration of sinusoidal endothelial cells in liver disease leads to activation of hepatic stellate cells and induces deposition of extracellular matrix within the area of Disse. Maintenance/ restoration of sinusoidal fenestrations and prevention of capillarization help protect stellate cell quiescence and minimize/reverse fibrosis. They belong to the mononuclear phagocytic system, but manifest phenotypic differences that distinguish them from other macrophages. They are of considerable importance in host defense mechanisms and in addition have an essential function in the pathogenesis of varied liver ailments. The luminal floor reveals many of the structural options associated with macrophages: small microvilli and microplicae and sinuous invaginations of the plasma membrane. Although Kupffer cells are thought of to be fixed-tissue macrophages, they seem capable of actively migrating along the sinusoids, each with and in opposition to the blood circulate, and can migrate into areas of liver injury and into regional lymph nodes. Their major capabilities include the removing by ingestion and degradation of particulate and soluble material from the portal blood, and in this they discriminate between "self " and "nonself " particles. They act as scavengers of microorganisms and degenerated normal cells, similar to effete erythrocytes, circulating tumor cells, and numerous macromolecules. The efficiency of this clearance operate is shown by the fact that removal of particulate material is limited solely by the magnitude of hepatic blood circulate; elimination of particles could approach single-pass efficiency. Kupffer cells also phagocytose useless hepatocytes, generated either by way of apoptosis or necrosis.
Order rulide 150 mg otc
The American Academy of Pediatrics has categorised sports activities into risk categories (Tables 22 treatment yeast infection home remedies 150 mg rulide otc. Clearance for participation in organized youth sports is mostly divided into three classes: (1) full treatment group order 150 mg rulide visa, unrestricted participation is allowed; (2) approval of coach, trainer, or staff physician is required, and the athlete may have outlined limits on participation or require rehabilitation; and (3) clearance is deferred due to underlying illness process or the necessity to consider additional for such a course of earlier than giving clearance. Risk of Injury In early and center childhood, threat of sports-related damage is relatively low. Being smaller and having less muscle energy than adolescents, youngsters achieve much less velocity and thus encounter less pressure in falls and collisions. In this age range, injuries are more probably to be incurred during leisure play and within the strategy of studying a model new sport. With puberty, gains in measurement, strength, and velocity mix with increased competitiveness and depth of play to substantially increase each the incidence and severity of accidents. Even so, the overwhelming majority of injuries incurred during organized sport are minor in nature; lower than 10% are critical; and catastrophic spinal and head accidents and sudden cardiac, pulmonary, and heat-related deaths are rare occasions. Injuries are extra likely to happen during follow sessions as a end result of practices outnumber formal competitions or video games, although incidence of accidents per unit of time played is larger in the course of the latter. The incidence of overuse injuries, specifically, has risen in parallel with the trend toward increasing group of sports activities. Children are particularly vulnerable to overuse injuries during times of fast development, when the speed of bone development exceeds that of surrounding soft tissues, resulting in decreased flexibility. Intensive coaching for a particular sport, especially when initiated at a low level of fitness; abrupt increases in level of activity; lack of preconditioning; and participation in multiple sports activities during the course of a year are different predisposing factors, as are training practices that fail to teach kids proper athletic methods and to monitor and limit repetitive motions. Youths with ligamentous laxity (up to 7% of school-age children) and joint malalignment (such as patellofemoral monitoring disorder) may be harm inclined without special preconditioning. Back flexion with knees straight, going through towards and away from examiner (range of movement, thoracic and lumbosacral backbone; backbone curvature; hamstring flexibility). Inspection of decrease extremities, contraction of quadriceps muscular tissues (alignment, symmetry). In female athletes, especially gymnasts, dancers, and longdistance runners, undue calorie restrictions to maintain "best weight," together with intensive coaching regimens, results in amenorrhea, decreased estrogen ranges, and lack of bone density, which has been demonstrated to predispose to early hip and vertebral fractures. These include weather circumstances, corresponding to high warmth and humidity (with attendant danger of dehydration and heat illness) and extreme cold or swimming in cold water (frostbite, hypothermia). Children are particularly vulnerable to hyperthermia and hypothermia due to their bigger surface area�to-volume ratio. They even have a decreased price and delay in onset of sweating, compared with adults, making it more difficult for them to dissipate heat. Finally, they have to be inspired to drink enough fluids, because their own thirst ranges tend to not be enough to guarantee alternative of losses. Finally, uneven or unsafe subject conditions or playing surfaces; improper, poorly designed, or ill-fitting tools (including shoes); and lack of or failure to use applicable security gear are different significant elements. Participation in some kinds of organized sports activities carries an inherently larger risk and thus larger rates and degrees of severity of 22 Orthopedics 835 Table22. When children are discovered to have circumstances that make certain activities probably harmful, counseling by physicians and coaches regarding safe and enjoyable alternative sports which are of curiosity to the child can be most useful. Such regimens additionally emphasize the following: � Warm-up and cool-down durations � Learning correct talent techniques. The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends limiting the body checking allowed for hockey players 15 years old and younger to cut back accidents. From American Academy of Pediatrics, Committee on Sports Medicine and Fitness 2000-2001: Medical situations affecting sports activities participation, Pediatrics 107:1205�1209, 2001. This is by advantage of their requiring greater ranges of cardio depth, their placing high static and/or dynamic stresses on the body, or because high-velocity contacts or collisions are a part of the activity.
[newline]Among these, competitive wrestling, football, and gymnastics are the top three, adopted by cross-country snowboarding, soccer, basketball, observe, volleyball, softball, and baseball in approximate order of frequency (see classification system of sport actions primarily based on contact/collision risk [see Table 22. Such sports could current particularly high dangers to youngsters with underlying persistent well being conditions (see the Sport Selection and Participation for Children with Underlying Problems or Chronic Conditions section, later). Those during which high-speed or angular momentum is attained carry notably high dangers for significant trauma. These embody bike riding, skateboarding, inline High to Moderate Dynamic and Static Demands Boxing* Creworrowing Cross-countryskiing Cycling Downhillskiing Fencing Football Icehockey Rugby Running(sprint) Speedskating Waterpolo Wrestling Low Dynamic and Low Static Demands Bowling Cricket Curling Golf Riflery *Participation not beneficial by the American Academy of Pediatrics. Conditioning and Training the rise in participation of youth in sports activities activities and the everincreasing desire to enhance efficiency have led to new concern for understanding the physiologic responses of the growing baby to common and increasingly demanding train regimens. These elements are essential in issues of the two major kinds of sports training programs: endurance and energy training. Endurance coaching consists of a long-term specific train program designed to improve train functionality during extended sports participation. This is completed by specifically rising the quantities of "overload" on a graduated foundation and may be sport specific, for example, operating. Basic to endurance coaching is aerobic conditioning, which requires sustained rhythmic movement of huge muscle groups at a level of intensity that ends in increases in coronary heart fee and respiratory rate. The really helpful frequency is three to 5 instances per week for about 15 minutes. In younger kids, conditioning is usually greatest approached through play activities which are more engaging to them with their shorter consideration spans. Strength coaching entails the use of progressive resistance exercises to increase the power to exert force or resist drive. It is designed to enhance capacity to perform a sport and to help in harm prevention by growing power. Rather, it seems to increase firing of motor neurons and synchronization of motor models. Close supervision by a knowledgeable adult, who displays technique and the intensity and period of classes, is crucial to ensure optimum benefit and prevent injury. Training begins with no added load until the child has developed persistently good method. When the kid is comfortably in a position to do between 8 and 15 repetitions, then weight or resistance can be added in small increments. When improved basic health is also a aim, power coaching must be mixed with a tailored aerobic conditioning program. Specific strengthening workouts and their target muscle groups are presented in Table 22. Strength training may be especially beneficial in preconditioning athletes with ligamentous laxity and in those with patellofemoral malalignment. By strengthening muscular tissues around the concerned joints, mostly the shoulder and knee, joint stability may be improved and the risk of glenohumeral and patellar subluxations and of other injuries may be reduced. Finally, fastidiously supervised and graduated strength training is a crucial part of post-injury rehabilitation. Stretching exercises can prove useful as part of a preconditioning program, in warm-ups earlier than sport participation, and in rehabilitation. They are designed to enhance flexibility or ease of motion of a joint via its normal vary of movement. A stretching program is especially important for children and adolescents throughout growth spurts, when bone progress outstrips that of the soft tissues surrounding adjacent joints, thereby lowering flexibility. Children should be supervised closely, a minimal of initially, to ensure that their actions are slow and smooth, progressing to the purpose at which resistance is felt, whereupon they need to maintain still without bouncing for a count of 10. From American Academy of Pediatrics, Committee on Sports Medicine and Fitness, 1995-1996: Protective eyewear for younger athletes, Pediatrics ninety eight:311�313, 1996.
Discount rulide 150 mg on line
Oda M symptoms 9 days post ovulation cheap rulide 150mg with amex, et al: Hepatic sinusoidal endothelial fenestrae are a stationary type of fused and interconnected caveolae internal medicine 150mg rulide cheap free shipping. Braet F, et al: A novel construction involved in the formation of liver endothelial cell fenestrae revealed by using the actin inhibitor misakinolide. Wisse E, et al: the liver sieve: consideration regarding the structure and function of endothelial fenestrae, the sinusoid wall and the house of Disse. Elvevold K, et al: the liver sinusoidal endothelail cell: a cell sort of controversial and complicated identity. Scoazec J-Y, Feldmann G: In situ phenotyping study of endothelial cells of the human hepatic sinusoid: results and functional implications. Volpes R, et al: Immunohistochemical research of adhesion molecules in liver irritation. Wisse E, et al: the liver sieve: concerns in regards to the structure and function of endothelial fenestrae, the sinusoidal wall and the house of Disse. Reider H, et al: Functional spectrum of sinusoidal endothelial liver cells: filtration, endocytosis, artificial capacities and intercellular communication. Wisse E: An electron microscopic examine of the fenestrated endothelial lining of rat liver sinusoids. Smedsrod B, et al: Advanced glycation finish products are eliminated by scavenger-receptor-mediated endocytosis in hepatic sinusoidal Kupffer and endothelial cells. Steffan A-M, et al: Phagocytosis, an unrecognized property of murine endothelial liver cells. Svistounov D, et al: Hepatic disposal of advanced glycation end merchandise throughout maturation and growing older. Muro H, et al: Fc receptors of liver sinusoidal endothelium in regular rats and humans: a histologic research with soluble immune complexes. Iwamura S, et al: Appearance of sinusoidal inclusion-containing endothelial cells in liver illness. Iwamura S, et al: Hepatic sinusoidal endothelial cells can store and metabolize serum immunoglobulins. Giugliano S, et al: Hepatitis C virus infection induces autocrine interferon signalling by human liver endothelial cells and release of exosomes, which inhibits viral replication. VanOosten M, et al: Vascular adhesion molecule-1 and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression on rat liver cells after lipopolysaccharide administration in vivo. Friedman S: A silent associate no longer: sinusoidal endothelial cells in liver homeostasis and illness. Ding B, et al: Divergent angiocrine indicators from vascular area of interest balance liver regeneration and fibrosis. Zuo Y, et al: Novel roles of liver sinusoidal endothelial cell lectin in colon carcinoma cell adhesion, migration and in-vivo metastasis to the liver. Canbay A, et al: Kupffer cell engulfment of apoptotic our bodies stimulates death ligand and cytokine expression. Lumsden A, et al: Endotoxin ranges measured by a chromogenic assay in portal, hepatic and peripheral venous blood in sufferers with cirrhosis. Nakamoto N, Kanai T: Role of Toll-like receptors in immune activation and tolerance within the liver. Meli R, et al: Role of innate response in non-alcoholoic fatty liver illness: metabolic complications and therapeutic tools. Strauss O, et al: the immunophenotype of antigen presenting cells of the mononuclear phagocyte system in regular human liver-a systematic evaluate. Rifai A, Mannik M: Clearance of circulatory IgA immune complexes is mediated by a specific receptor on Kupffer cells in mice. Klein I, et al: Kupffer cell heterogeneity: useful properties of bone marrow derived and sessile hepatic macrophages. Bouwens L, et al: Cytokinetic analysis of the increasing Kupffer cell population in rat liver. Naito M, et al: Yolk sac macrophages-a attainable Kupffer cell precursor in the fetal mouse liver. In Wisse E, et al, editors: Cells of the hepatic sinusoid, Rijswijk, 1989, Kupffer Cell Foundation. Ito T: Cytological studies on stellate cells of Kupffer and fat-storing cells within the capillary wall of the human liver. Ramadori G: the stellate cell (Ito-cell, fat storing cell, lipocyte, perisinusoidal cell) of the liver. Wake K: Perisinusoidal stellate cells (fat-storing cells, interstitial cells, lipocytes), their associated construction in and around liver sinusoids, and vitamin A-storing cells in extrahepatic organs. Yin C, et al: Hepatic stellate cells in liver improvement, regeneration, and most cancers. Coulouarn C, Clement B: Stellate cells and the event of liver most cancers: Therapeutic potential of concentrating on the stroma. Blomhoff R, Wake K: Perisinusoidal stellate cells of the liver: essential roles in retinol metabolism and fibrosis. LeBail B, et al: Fine structure of hepatic sinusoids and sinusoidal cells in illness. Schirmacher P, et al: Hepatocyte growth factor/hepatopoietin A is expressed in fat-storing cells from rat liver but not myofibroblastlike cells derived from fat-storing cells. Wang Y, et al: Hepatic stellate cells, liver innate immunity, and hepatitis C virus. Weiskirchen R, Tacke F: Cellular and molecular functions of hepatic stellate cells in inflammatory responses and liver immunology. Vanderkerken K, et al: Origin and differentiation of hepatic pure killer cells (pit cells). Peng H, Wisse E, Tian Z: Liver pure killer cells: subsets and roles in liver immunity. Vanderkerken K, Bouwens L, Wisse E: Characterization of a phenotypically and functionally distinct subset of huge granular lymphocytes (pit cells) in rat liver sinusoids. Kurosawa M, et al: Neural regulation of hepatic bloodflow in rats: an in vivo examine. In Arias I, et al, editors: the liver: biology and pathobiology, ed three, New York, 1994, Raven Press, pp 1143�1163. For a lengthy time these small and relatively easy molecules, constructed on a steroid spine, have been considered essential for cholesterol metabolism and bile move and important for micelle formation for absorption of fat in the small gut. More just lately, bile acids have been further acknowledged as signaling molecules that regulate metabolism. It will focus on particular inborn errors in bile acid synthesis because these spotlight the important position of bile acids in maintaining hepatic bile move and as signaling integrators of metabolism. Bile acids are synthesized within the liver from cholesterol by a complex sequence of reactions catalyzed by 17 completely different hepatic enzymes positioned within the 20 endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, cytoplasm, and peroxisomes. More just lately the role that every enzyme plays in the regulation of bile acid synthesis has been elucidated from studies of gene knockout animal models and humans with genetic defects in bile acid synthesis. Such differences need to be considered when working with totally different species and animal fashions of illness.
White Mustard Seed (White Mustard). Rulide.
- Are there safety concerns?
- Coughs and colds; bronchitis; arthritis-like pain; swelling (inflammation) of the mouth, throat, and joints; and other conditions.
- Dosing considerations for White Mustard.
- How does White Mustard work?
- What is White Mustard?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96157
Cheap rulide 150 mg
Gait Disturbances Resulting From Weakness or Spasticity Patients with weak spot of the hip abductors (gluteus medius muscle) have a Trendelenburg gait medicine xifaxan 150 mg rulide mastercard. Patients with weakness of the gluteus maximus (seen most commonly in kids with Duchenne muscular dystrophy) have to medications in pregnancy 150 mg rulide cheap visa hyperextend their trunk and pelvis to keep their middle of gravity posterior to the hip joint (see Chapter 16). Proximal muscle weakness can also be demonstrated by observing a toddler getting up from the floor unassisted. A Gower signal indicates weak hip extensors and abductors, necessitating that the affected person use his arms to assist in standing by putting his hands on his anterior thighs and pushing up, progressively shifting his arms upward along the thighs until erect posture is achieved (see Chapter 16). Children with weak spot of the quadriceps femoris muscle could have a relatively regular gait on stage ground however issue climbing stairs. Weakness of the dorsiflexors of the foot leads to foot drop and a steppage gait. When the plantar flexors are weak, the affected person is unable to push off on the end of the stance part, and so the heel and forefoot come off the ground at the identical time. An equine gait, characterised by toe-walking or a toe-to-heel sequence through the stance part, is seen in children with heel twine contracture and limited dorsiflexion. Vestibular or cerebellar dysfunction or generalized weak point tends to end in a wide-based ataxic gait due to irregular steadiness. Absence of the conventional arm swing with strolling is seen in patients with paresis or cerebellar disease. Intoeing and Out-toeing the angular distinction between the lengthy axis of the foot and the ahead line of progression during walking is known as the foot progression angle. The remaining rotational profile of Gait and Gait Disturbances Between the onset of walking and three years old, children are inclined to have a wide-based gait and toddlers typically maintain their arms out to the side to assist balance. By three years old, kids obtain a normal smooth and rhythmic heel-to-toe gait, consisting of two main phases: stance and swing. The stance section begins when the heel strikes the ground, bears all the weight, and progresses to foot flat, midstance, and push-off as weight is transferred from the heel to the metatarsal heads. The swing section starts with acceleration after push-off and progresses through mid swing to deceleration simply before heel strike. Because stance occupies 60% of the time and weight is borne in this part, most gait issues are extra evident in the course of the stance section than through the swing section. Normally the space between the two heels (width of the base) is between 5 and 10 cm, the pelvis and trunk shift laterally about 2. Gait is finest observed by having the patient stroll forwards and backwards in a corridor or in a room with a mirror at one finish. As the affected person walks, the examiner focuses first on general movement after which on the motion of the pelvis, hips, thighs, knees, decrease legs, ankles, and toes in succession, each coming and going. In doing so, he or she appears for the sample of heel-to-toe movement, for shortening of the stance phase, for evidence of limitation of joint movement or weak point, and for positional modifications of the extremities. Others stem from weak spot or spasticity attributable to neurologic or muscular disorders, from leg size inequality, or from deformity. The examiner ought to notice any associated ache and its location, bearing in mind referral patterns (low again to buttocks and lateral thigh; hip to groin, medial thigh, knee, and sometimes buttock) and attempting to determine whether the ache is constant (suggestive of tumor or infection) or intermittent. Femoral anteversion, internal tibial torsion, and metatarsus adductus are frequent causes of extreme intoeing, or pigeon toe, and femoral eversion and exterior tibial torsion are frequent causes of out-toeing, or slew foot (see the Disorders of the Lower Extremity section, later). The incidence of trauma is further elevated by the prevalence of child abuse (see Chapter 6). In fact, past infancy, trauma is the leading reason for dying in children and adolescents and is a supply of great morbidity. A, the foot axis is decided by a line marked from mid heel to the lateral aspect of the second toe. Hip excursion is the distinction between the angular measure of maximal susceptible inside rotation (B) and maximal prone exterior rotation (C). The tibia/fibula axis is set by evaluating the axis of the aircraft of motion of the knee with the affected person prone and knees flexed (D) to the transmalleolar axis (E). Furthermore, immediate consideration should be given to evaluation of the standing of neurovascular buildings distal to apparent fractures, as a result of failure to acknowledge compromise may result in everlasting loss of perform. Finally, traumatic hip dislocations should be lowered inside 6 to 12 hours if the chance of aseptic necrosis and long-term morbidity is to be minimized. Fractures Diagnosis One of the various variables that complicate the diagnosis of the skeletally injured child is that the kid, already in ache, is frightened by his or her latest expertise and by the strangeness of the hospital or emergency division setting. Many children are too younger to give a firsthand historical past, and the cooperation of toddlers is usually limited. Taking an intensive history earlier than making any try and carry out a bodily evaluation helps the examiner set up rapport with the patient and the family. This should include questions regarding the type and course of the injuring drive, the place of the involved extremity on the time of the accident, and the events immediately following the harm, corresponding to measures taken on the scene of the accident. The presence of underlying disorders and the potential of contamination of an open wound must be determined as well. Physicians also should be alert to signs suggestive of inflicted damage or baby abuse. In instances of suspected fracture, splinting, elevation, and topical software of ice might assist scale back discomfort and local swelling. Splinting is particularly essential for displaced and unstable fractures, as a result of it prevents additional delicate tissue accidents and reduces the danger of fats embolization. If younger children are highly anxious, it can be helpful to instruct the father or mother in tips on how to carry out passive range of motion and palpation. The first step in the physical examination is visible inspection of the injured space. The overlying pores and skin and delicate tissues are examined for proof of swelling, ecchymoses, abrasions, punctures, and lacerations. Comparison with the opposite extremity and measurement of circumference may be useful when findings are delicate. The location of open wounds is important in ascertaining whether an underlying fracture is open or closed and in assessing the danger of joint penetration. Small puncture wounds or lacerations overlying bony structures from which a bloody, fatty exudate is oozing often reflect communication with the medullary cavity of a fractured bone. Probing of open wounds which might be highly prone to talk with a fracture or joint is contraindicated. The wound must be cleaned and coated with a sterile dressing until its extent could be determined underneath sterile conditions within the working room. After inspection of probably the most obviously injured area, palpation and evaluation of energetic and passive movement could be performed. A, Distortion and angulation of the distal forearm in a child with fractures of the radius and ulna. C, Longitudinal shortening of the thigh in a child with a proximal femur fracture. Although the laceration appeared to be minor, serosanguineous fluid flowed from it on motion of the knee, suggesting penetration of the joint capsule. B, Air is seen within the knee joint and within the overlying gentle tissues in a child who sustained a deep laceration that penetrated the joint capsule. Localized swelling and tenderness on palpation are significant findings and should alert the examiner to the excessive likelihood of an underlying fracture.
Syndromes
- Have you recently traveled out of the country?
- Physical abuse is the known or suspected cause of the burn.
- Septicemia
- Using cocaine on hot weather days, which leads to more harm and side effects because of dehydration
- Eyedrops to prevent infection, treat inflammation, and help with healing
- High octane gasoline manufacturing
- Epidural abscess
- Get plenty of rest.
- The balloon presses against the inside wall of your artery. This opens the artery and sends proper blood flow to your brain. A stent (a wire mesh tube) may also be placed in the blocked area. The stent is inserted at the same time as the balloon catheter. It expands with the balloon. The stent is left in place to help keep the artery open.
150mg rulide cheap overnight delivery
B severe withdrawal symptoms discount 150 mg rulide fast delivery, Panoramic radiograph demonstrating the presence of erupted maxillary third molars and mandibular right third molar but solely partial eruption of the left mandibular third molar medications quit smoking best 150 mg rulide. This is seen most commonly as a comparatively benign infection in infants (as thrush) and in young kids who could additionally be receiving or have lately completed a course of antibiotic treatment. Less frequently, it might be seen in immunocompromised or immunosuppressed children or in these with critical underlying systemic illnesses. Scraping of the lesion reveals a uncooked and erythematous base with bleeding from torn capillaries. Chronic candidiasis, often seen in the immunocompromised host, can lead to marked hypertrophy and fissuring of the tongue mucosa. Treatment consists of local utility of nystatin (fluconazole or other antifungal brokers for severe or continual cases) and control of the underlying causes, including sterilization of nipples used for method feedings. It is important to notice whether or not there was loss of consciousness, in addition to any nausea or vomiting. It can also be necessary to note whether the child has ageappropriate responsiveness, as nicely as how quickly the kid returned to consciousness. In asking in regards to the mechanism of injury, the examiner should decide the forces involved. Did the kid journey and fall whereas walking, or was he or she working; if riding a bike, how briskly was she or he going; within the case of falls, from what peak, onto what kind of surface This provides the examiner a greater idea of the potential severity of harm and risk of related accidents. Physical examination is first directed at figuring out the adequacy and stability of airway, breathing, and circulation adopted by analysis for associated head and neck harm. When these areas have been cleared and/or stabilized, then the examiner could proceed with the orofacial examination, assessing the extent and nature of accidents. Because the presence of underlying injuries is commonly indicated by the degree and nature of overlying delicate tissue trauma, evaluation begins with exterior inspection of facial structures for swelling, deformity, contusions, abrasions, and lacerations. The presence of associated periorbital ecchymoses or swelling; subconjunctival hemorrhage or edema; diplopia; and nasal bleeding should elevate suspicion of frontal cranium and midface fractures. Battle sign, bruising of the mastoid course of, is a sign of basilar skull fracture and should counsel underlying mind trauma. This is followed by remark of occlusion and jaw movement on opening and closing, checking for deviation or trismus. Next, intraoral delicate tissues are inspected for evidence of swelling, hematoma, abrasions, and lacerations. Palpation of facial bones and the labial and lingual surfaces of the dental arches and assessment of abnormal maxillary mobility may be greatest left till final as a outcome of resulting ache could reduce cooperation. All internal and exterior lacerations have to be carefully inspected to check for damage to underlying neural and ductal structures. Thus any evaluation of a gentle tissue injury must include careful attention to the enamel and underlying buildings. The injured area should be cleansed of blood clots, debris, and overseas materials, and then fastidiously examined to determine the extent of tissue involvement. Mechanical debridement of any ragged, necrotic, or beveled margins could additionally be necessary. Saline rinses, careful attention to oral hygiene, antibiotic therapy, and gentle food plan are mainstays of management of all intraoral delicate tissue accidents. Extensive abrasions should be covered with water-soluble, medicated gauze after irrigation. Such an damage to the oral mucosa requires immediate inspection, irrigation, approximation, and suturing. Contusions A contusion, or bruise, normally requires no treatment, and healing proceeds favorably in most cases. However, contusions are sometimes related to underlying injuries; therefore, a careful examination of adjacent structures is indicated. Perforations Perforations are small, deep wounds attributable to sharp objects and are fairly common in youngsters, particularly on account of falls with such an object in the mouth. After cautious inspection and irrigation, bigger wounds should be closed in layers; smaller wounds might not require closure. If doubt exists concerning international bodies and/or contamination, a drain must be left in place and correct antibiotics prescribed. The possibility of harm to massive vessels should be recognized, especially when the perforation includes the posterolateral palate or a tonsillar pillar. Larger avulsions can be handled by reattaching the avulsed tissues or by use of a graft. Thus the adjacent dentition must be rigorously inspected for proof of chipping and for signs of loosening or displacement. The possibility of international body entrapment, immediate or delayed vascular harm (particularly when the laceration entails posterolateral structures), or formation of pharyngeal abscesses ought to be critically thought-about. Lacerations involving the labial frenulum of infants are frequent and require solely restriction of lip manipulation and a gentle diet. Burns Burns involving the oral cavity usually heal rapidly but, when deep, may do so with contracture and scarring. This tends to separate approximately 10 days later, at which period profuse bleeding from the labial artery might happen. Parents need to be told of this possibility and instructed on what action to take if it should happen. Splints fabricated from dental materials are essential in long-term management to stop or decrease contracture by sustaining correct anatomic relationships throughout therapeutic. To scale back threat of an infection, saline irrigation and antimicrobial prophylaxis are indicated for all intraoral lacerations, no matter whether or not sutures are required. Traumatic Ulcers Painful ulcerations may result from mechanical, chemical, or thermal trauma. Injury could additionally be secondary to irritation by objects, trauma throughout mastication, toothbrush trauma, or abnormal habits. Lesions often heal with out scarring, however secondarily contaminated lesions could require antibiotic therapy. Identification and elimination of the behavior is necessary for resolution of habit-related lesions. In this radiograph the condyles bend inward at nearly ninety levels above the fracture strains. Patients undergoing chemotherapy are encouraged to brush two or 3 times per day with a delicate bristle toothbrush. If a affected person develops oral mucositis, chlorhexidine could have to be discontinued as a outcome of its high alcohol content might dehydrate the tissue.
Buy discount rulide 150 mg
The joints are palpated to check for evidence of warmth and tenderness medications you cannot crush rulide 150mg purchase without prescription, vary of motion is assessed medications you cant drink alcohol with trusted 150mg rulide, and evidence of pain on movement is set. Assessment of ligamentous stability round joints is discussed under particular sections of the regional examination. However, it may be very important do not overlook that in circumstances of acute trauma, especially when deformity or hemarthrosis is obvious on preliminary assessment, exams of ligamentous stability ought to be deferred, the extremity splinted, and radiographs obtained to check for possible underlying fracture. Physical Examination the orthopedic examination entails a systematic assessment of posture, stance, and gait; the symmetry or asymmetry of paired musculoskeletal structures and their movement; muscle power and tone; and neurovascular status. Patience and sometimes some degree of creativity are required on the part of the examiner if the patient could be very young. This could be assisted by offering age-appropriate toys for her or him to play with while the history is being taken and by engaging the affected person in play (if circumstances permit) earlier than beginning the extra formal physical examination. After spontaneous exercise is observed, the related components of the orthopedic examination are usually accomplished by area. A full orthopedic examination that assesses each bone, muscle, joint, tendon, and ligament is lengthy, detailed, and infrequently indicated. Even in multiple-trauma victims and patients whose signs point toward an underlying systemic dysfunction, each region is screened and a full assessment accomplished only of those regions where native musculoskeletal abnormalities are discovered. Similarly, in sufferers with focal injuries or deformities, the examination can usually be targeted on the region involved, with the clinician making an allowance for referral patterns for pain and the maxim that all extremities "begin on the again. The patient is then turned and viewed from behind, and the shoulder and scapular peak, the muscle bulk of the trapezius muscle tissue, and the height of the posterior iliac crests and of the depressions over the sacroiliac joints are checked for symmetry. Trapezius strength is decided by having the affected person shrug his or her shoulders, first in opposition to gravity after which in opposition to resistance, as the examiner presses down on the shoulders. The muscular tissues supplying the scapula are tested by having the patient press his or her outstretched arms towards a wall. Winging of the scapula during this maneuver is suggestive of weakness of the serratus anterior muscle. The line of the spinous processes of the vertebrae is noticed for straightness, and the position of the head over the trunk is noted. In the immobilized trauma affected person, these observations are made largely with the patient supine on a backboard after which log-rolled onto his or her aspect. Importantly, in checking for neck injury, the cervical backbone may be cleared clinically if the affected person is awake and alert and has no complaint of neck pain, no evidence of tenderness or paraspinous muscle spasm, and no extremely painful injury elsewhere. A regular baby can touch his or her chin to the chest, lengthen the neck to look immediately above, and bend laterally to forty five levels. He or she is also capable of symmetrical lateral rotation when turning the pinnacle from facet to side. Strength is tested by applying strain to the brow whereas the affected person flexes his or her neck and to the occiput as the affected person extends, and by making use of resistance to the opposite side of the pinnacle as the patient bends and rotates laterally. Thoracolumbar Spine Viewed from the facet, the normal youngster has a lordotic curve in the cervical space with a bony prominence at C7, a gentle thoracic kyphosis, a lumbar lordosis, and a sacral kyphosis. Each affected person is checked for the presence, absence, or accentuation of those curves. The midline of the back is inspected for evidence of abnormal pigmentation and the presence of hemangiomas, nevi, furry tufts, dimples, masses, or defects, which can be related to underlying bony or neural anomalies (see Chapter 16). Flexion, extension, rotation, and lateral bending of the thoracolumbar spine are primarily motions of the thoracolumbar junction and the lumbar area. C, Viewing the patient from the aspect, one can extra easily see even delicate levels of kyphosis and observe lack of reversal of regular lordosis. To verify rotation, the higher arm is held to the facet with the elbow flexed to 90 levels and the kid is requested to turn the forearm toward the body (medial) and then out to the aspect (lateral) (60 to 90 levels is normal). When this angle is larger than 10 levels, the deformity is termed cubitus valgus and, when much less or reversed, cubitus varus (gunstock deformity). The vary of motion of the hinge joint of the elbow has 4 elements: (1) extension, a operate of the triceps (normally to zero levels of flexion); (2) flexion, a function of the biceps (normally to one hundred forty five degrees); (3) supination (normally to ninety degrees); and (4) pronation (80 to 90 degrees). The latter two components are examined by having the patient flip the palm up and down respectively, with the elbow flexed. Because of the proximity of the brachial artery and the median, radial, and ulnar nerves to the elbow joint, accidents of the elbow necessitate a cautious neurovascular examination. Wrist and Hand During examination of the wrist and hand, one ought to observe pores and skin color, verify capillary refill, and palpate the radial and ulnar pulses to assess circulation. Any swelling or edema should be noted, in addition to any irregular posture or position. The presence of intraarticular fluid in the wrist is manifested by swelling and tenderness, particularly evident dorsally, and by restriction of wrist movement. Wrist movement has four parts: flexion with the hand held down (normally 70 to eighty degrees); extension with the handheld up (normally 70 degrees); and ulnar and radial deviation (normally 25 degrees and 15 to 20 levels, respectively). With the patient supine, the limb to be examined is grasped behind the ankle and elevated into hip flexion with the knee in full extension. If pain is produced properly earlier than 90 levels of flexion is achieved, the take a look at is constructive, indicating irritation of a sciatic nerve root. The examiner must also note any evidence of lacking spinous processes (step-off) or their deviation from the midline and palpate the paravertebral muscle tissue for spasm and tenderness. Leg length inequality may be evaluated during the upright standing portion of this check (see the Lower Extremity Examination part, later) and, if present, ought to be corrected with applicable lifts under the short facet so as not to cause a false forward bend test. Any examination of the backbone must embrace a neurologic assessment of strength, tone, reflexes, and sensation. The limb to be examined is grasped behind the ankle and elevated passively into hip flexion with the knee totally prolonged. This maneuver stretches the sciatic nerve because it passes behind the hip joint, and if certainly one of its a quantity of roots has been irritated by a protruded disk, mass, or inflammatory process, ache might be felt with only 15 to 30 degrees of hip flexion. Normally the straight leg could be delivered to ninety levels of hip flexion without problem. Prominent landmarks that are easily palpable include the acromion course of lying laterally and subcutaneously, the clavicle, the spine of the scapula, the coracoid course of, and the bicipital groove. Swelling of the glenohumeral joint capsule and atrophy of the shoulder muscles are finest appreciated by viewing from above with the affected person seated and by comparability with the traditional facet. Assessing vary of motion is essential because many shoulder problems are manifested by a lack of normal movement. Abduction, a function of the deltoid muscle, is tested by having the patient elevate the extended, supinated arm up in order that the hand is immediately above the shoulder (180-degree abduction). Observation of the place at rest (normally a unfastened fist with all of the fingers pointing in the same direction and with the same diploma of flexion) and of use during play is commonly useful. Having the father or mother carry out varied hand and finger motions while attempting to get the kid to imitate these may be useful in some circumstances. Handing the child a small object (such as a key) or a skinny piece of paper (such as a greenback bill) may suffice for assessing opposition of thumb to fingers, which within the older child is examined by having her or him touch the tip of the thumb to the tip of the little finger.
Order rulide 150mg without prescription
The latter include the primary focus and secondary irritation and atelectasis medicine expiration dates 150 mg rulide sale. Infants affected by this endobronchial process usually have a harsh treatment urticaria rulide 150 mg order line, paroxysmal cough that mimics that of pertussis, together with wheezing and rhonchi famous on auscultation. With or with out therapy, collapseconsolidation lesions can re-expand and resolve, clear with residual calcification of the primary complex and regional node (Ghon complex), or scar with progressive contraction of the involved pulmonary segment and bronchiectatic modifications. The organisms disseminate by way of the airways to the rest of the lung, setting up new foci of infection. Clinically, these sufferers have remittent fever, cough, and malaise along with anorexia and weight loss and eventually appear listless and chronically unwell. This may be clinically occult and happen early through the incubation period or shortly thereafter. Major sites of seeding include the pulmonary apices, spleen, and superficial nodes. In some instances, evidence of resulting metastatic lesions is seen 2 to 4 months later, when the child has a nonspecific sickness characterised by low-grade fever and fatigue, splenomegaly, and generalized adenopathy, sometimes related to papulonecrotic skin lesions. Others remain asymptomatic, and their metastatic lesions might either remain dormant or reactivate years later. Miliary disease could additionally be detected by the way in an toddler or baby who undergoes chest radiography as a part of an analysis for low-grade fever with out an apparent source. Other kids experience insidious development of signs or might have a extra abrupt onset of fever, tachypnea, lethargy, and weak spot accompanied by hepatosplenomegaly. Skin lesions, which can be nodular, purpuric, or papulonecrotic, might seem as nicely. Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis Tuberculous Meningitis After lymphohematogenous spread, tuberculous foci may develop in the mind and meninges. She was handled with antibiotics for presumed bacterial pneumonia however showed only partial medical improvement. A and B, She has a collapseconsolidation lesion involving the best lower lobe, with a primary cavity. The ensuing exudate is thick and gelatinous, infiltrating meningeal and cerebral vessels to trigger vasculitis with secondary occlusion and infarction. The onset of signs is often gradual, starting with anorexia, fever, headache, pronounced apathy, irritability, and emotional lability. Within 1 or 2 weeks, drowsiness, vomiting, meningismus, a sluggish pupillary response, and cranial nerve palsies supervene, usually accompanied by hyperreflexia and seizures. Confusion, disorientation, dysarthria, tremors, and athetosis could also be seen throughout this part. Early prognosis and the institution of antituberculous remedy can significantly cut back morbidity and mortality, however even with remedy, problems are widespread in survivors. Very young kids are at biggest danger because of the high price of blood move through their rising bones. Tuberculous osteomyelitis can start as a metaphyseal an infection from hematogenous seeding; by extension from lymphatics, especially from a paravertebral node to a vertebra; or by direct native or hematogenous unfold from a neighboring bone. Fever is absent or low grade, except the lesions develop as part of the process of protracted hematogenous unfold. Pain is often mild compared with that related to other forms of bacterial osteomyelitis. Tuberculous spondylitis includes the vertebral our bodies of two or more thoracic vertebrae however can affect lumbar vertebrae. Pain manifested by crying within the evening and restless sleep; low-grade fever; and postural change with gait disturbance are outstanding. Patients with lumbar illness undertake a wide-based stance and gait with again ache or referred ache to the chest or abdomen. In addition, sepsis, meningitis, pneumonia, and different infections caused by perinatally acquired bacterial infection, together with tetanus in underdeveloped international locations, cause vital neonatal morbidity and mortality, especially in untimely infants. The dialogue on this chapter is restricted to issues that are inclined to have distinctive physical findings. Extensive bony destruction of the T12 vertebral body together with mild collapse of T11 is seen. On examination, extreme paraspinal muscle spasm, marked limitation of flexion, ache on percussion, and hyperreflexia with clonus could also be evident. Initial radiographs show slight disk house narrowing with subsequent wedging and partial collapse of the vertebral physique. The pubertal development acceleration, particularly in ladies of low socioeconomic standing, is the best danger interval for reactivation or the development of progressive main illness. With reactivation, new lesions develop in the same lobe of the old primary advanced and remain localized. Patients have cough and fever, typically accompanied by chest ache, and should exhibit hemoptysis. Chest findings may be regular early on, but moist rales could additionally be heard over the apices after cough or on end-expiration. Small spherical or wedge-shaped infiltrates or linear streaks with mottling could additionally be evident on chest radiograph. With progression, weight loss and fatigue enhance and an early-morning cough productive of accelerating quantities of sputum turns into bothersome. Daily fevers and evening sweats are widespread, and an appearance of continual sickness supervenes. Wet rales, bronchial breath sounds, wheezing, and dullness to percussion are typical bodily findings. Radiographs may reveal mottling, patchy infiltrates, segmental or lobar opacification, and cavitary changes, which can be unilateral or bilateral. Infection of the fetus could develop from both primary maternal an infection or reactivation of virus acquired earlier; primary infection is related to a higher danger for symptomatic disease within the toddler. Approximately 10% of infected infants have indicators or signs at delivery, including small measurement for gestational age, microcephaly, thrombocytopenia, hepatosplenomegaly, hepatitis, intracranial calcifications (see Chapter 16), chorioretinitis, and hearing abnormalities. Treatment of symptomatic infants with valganciclovir seems to offer protection against listening to loss and progressive disease. This is injected intradermally on the volar surface of the forearm, which ought to increase a wheal. A, A newborn with congenital rubella syndrome, including a "blueberry muffin" rash, diffuse petechiae, hepatosplenomegaly, early onset of jaundice, and neurologic despair. Signs of infection could develop any time throughout the first 4 weeks, however most seem before day 21 postpartum. In the event of prenatal acquisition, the infant could die in utero or could additionally be born with jaundice, skin lesions, and indicators of systemic infection. Infants can also be contaminated postnatally from contacts or members of the family with oral herpetic lesions ("cold sores").