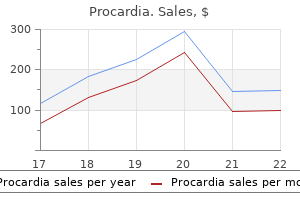
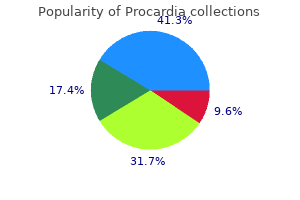
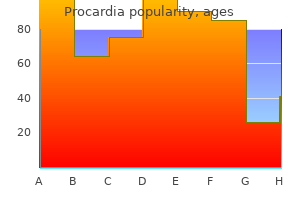
Procardia 30 mg cheap with mastercard
A second technique is to use either a urine reagent strip or automated know-how to decide the glucose cardiovascular system stress 30 mg procardia order fast delivery, pH blood vessels narrowing in head buy procardia 30 mg lowest price, and/or O2 content of the platelet product. While cheap, these methods are typically considered to be suboptimal due to their lack of sensitivity. In addition, strategies to enhance the sensitivity and specificity of culture methods are being developed. Survey of methods used to detect bacterial contamination of platelet products in the United States in 2011. Detection of bacterial contamination in apheresis platelet merchandise: American Red Cross expertise. Effect of platelet additive solution on bacterial dynamics and their influence on platelet quality in stored platelet concentrates. Detection of bacterial contamination in prestorage culture-negative apheresis platelets on day of concern with the Pan Genera Detection take a look at. A novel strategy to pathogen discount in platelet concentrates utilizing short-wave ultraviolet light. Improving the performance of culture-based bacterial screening by rising the sample volume from 4 mL to eight mL in aerobic tradition bottles. Other coated companies may embody therapeutic apheresis and phlebotomy, infusion and in- and outpatient transfusion, whole blood and apheresis collection, perioperative companies, and tissue banking. Each of these laboratories or providers requires insurance policies and procedures, and medical, administrative and technical oversight. The initial step is to create objectives, and, by way of the method of planning, organizing and implementing, these goals must be achieved. The major elements of planning are the writing and acceptance of mission and vision statements, core values and strategic planning, together with imaginative and prescient, goals and operational and time-line linkages (Box 18. The main parts of organizing are prioritization, coordination, communication and collaboration. The major parts of implementing are monitoring, consequence evaluation, workers development and administration, and continual adjustment and enchancment. Quality methods present a process and procedure structure for optimal pretransfusion testing, post-manufacture processing, cross-matching, issuing and administration of merchandise, and for validation, preventative upkeep, and quality management of applied sciences, to name a couple of of the weather integrated into the quality plan (see Chapter 2). Consultative companies are sometimes requested regarding provision of appropriate or specialized blood products, transfusion reactions, blood management, hemostasis and thrombosis-related check outcome interpretation, and consideration of optimum merchandise for administration. Transfusion committees oversee blood utilization and the creation of pointers, as well as reviewing antagonistic transfusion outcomes. The information should be analyzed and tracked over time to determine levels of efficiency, patterns, developments and variation, compared with external sources, and the results must determine alternatives to improve. These requirements could be met by reviewing the ordering, distribution, dealing with, allotting, administration and effects of blood products. Membership: the members of the transfusion committee embody representatives from the departments that make the most of blood products, such as hematology, surgical procedure, anesthesia and obstetrics; and blood financial institution, scientific laboratory, nursing and hospital administration. The committee should approve the blood supplier, and monitor blood utilization, opposed events, errors, accidents, and the blood bank high quality plan. The committee additionally oversees the development of transfusion apply guidelines, standards for blood product use, and blood administration procedures and thus the parts of a affected person blood administration program (see Chapter 57). Audit: Audit of particular areas, such as turn-around time, specimen mislabeling, wastage and affected person identification, is used to establish areas in need of enchancment. Role of the Transfusion Service Physician 113 the foundation explanation for the deviation may be decided, and a corrective action instigated to ameliorate the issue. An audit of blood administration might include specimen assortment (use of two patient identifiers), blood bank testing (appropriate reagent use and product selection), product dishing out (patient identification, verification of affected person history), and product administration (patient identification, applicable knowledgeable consent, compliance with physician order, transfusion with no different fluid except regular saline and accomplished within four hours). Audits can be potential, occurring at the time of the occasion; concurrent, occurring within 24 hours of the occasion; or retrospective, occurring later than 24 hours after the event. Transfusion Practice Guidelines: Clinical transfusion pointers encompass each the transfusion of merchandise. An audit is performed so as to best perceive present and established transfusion practices. Draft tips are created by a multidisciplinary team based mostly on evidence in the literature. Education of the ordering physicians and different members of the healthcare group ensues, and is required to determined the understandability and likelihood of implementation and compliance. Periodically, repeat auditing is required to assure that the guidelines are being followed and proceed to be appropriate. At a minimum, the process must talk the risks and benefits of transfusion, the alternate options to transfusion, the right to refuse transfusion, and the power to ask questions. In some hospitals, it may be helpful to have a separate and permitted process for refusal of blood product administration. Education is through multiple strategies, together with displays, patient instances, journal membership, high quality assurance tasks and one-on-one conversations. In order to improve the standard of patient care, continued education of residents, fellows, ordering physicians and hospital administrators is obligatory. In addition, ongoing primary science research is needed to better understand the helpful and opposed effects of transfusion and to enhance transfusion administration. Lastly, quality enchancment projects affect patient care by highlighting areas of improvement, such as turn-around time, affected person identification and blood utilization review. An appropriately developed mannequin could benefit the hospital and the supplier, ensuring prime quality service and medical oversight, while financially benefiting the hospital. A prospective audit program to decide blood element transfusion appropriateness at a large college hospital: a 5-year experience. Career activities of physicians taking the subspecialty board examination in blood banking/transfusion medicine. Patient Identification: Accurate affected person identification is crucial for safe transfusion apply. Both forms of request should comprise enough information to uniquely determine the patient, together with two independent patient identifiers. Other required information on a transfusion request includes the type of element requested, the quantity, any particular requirements. Specimen Requirements: Pretransfusion testing may be performed on both serum or plasma. Blood specimens for compatibility testing should be collected after positively identifying the affected person and prior to amassing the specimen. When the pretransfusion specimen is acquired within the laboratory, an appropriately skilled member of the transfusion service must confirm that every one figuring out data on the request is equivalent to the data on the specimen itself. In case of any discrepancy or doubt, the specimen should not be used and another specimen have to be obtained for testing. The transfusion service should accept only these specimens that are fully, accurately, and legibly labeled with indelible ink. As hemolyzed or lipemic specimens might create issues in evaluating test results, it could be very important replace such specimens with new ones, every time potential. Each laboratory should have procedures and policies in place that outline acceptable standards for accepting specimens for pretransfusion testing and describe the way to doc and deal with unsatisfactory specimens. This allows for repeat or further testing if a affected person develops a transfusion reaction.
Osmunda struthiopteris (Ostrich Fern). Procardia.
- Dosing considerations for Ostrich Fern.
- Are there safety concerns?
- How does Ostrich Fern work?
- What is Ostrich Fern?
- Sore throat, skin wounds, and boils.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96498
30 mg procardia cheap mastercard
If bone-to-bone repairisnot possible blood vessels skin procardia 30 mg safe, manysurgeons could elect to deal with the affected person without resorting to surgical procedure capillaries types buy cheap procardia 30 mg on line. Complete tears, except current with other related accidents or in a highdemandathlete,arerarelysurgicallyrepaired. Surgical optionsincludeprimaryrepair,allograftreconstruction, and restore with anchor fixation for avulsion accidents. Injuries to this region of the knee could also be related to injuries to the popliteus tendon, iliotibial band, popliteofemoral ligament, and peroneal nerve. Posterolateral ligaments are often injured by a hyperextension mechanism, regularly with a blow to theanteromedialtibia. The external rotation recurvatum take a look at can also be obvious on standing, giving an elevated varusappearancetotheknee. On plain radiographs, a "lateral capsular signal" shows avulsion of the midportion of the lateral capsular ligament with a small fragment of proximal lateraltibia. Casesofmildinstabilitymaybe treated nonoperatively just like that for lesser-grade sprains. Atthetimeofinjury,thepatientexperiences sudden ache, which can be associated with a tearing sensationabouttheknee. Also, the patient might not be succesful of maintain a passively extended knee towards gravity. In both instances, surgical procedure is required to reestablish the continuity of the quadriceps mechanism. After postoperative immobilization for 8 to 10 weeks, sufferers progressively begin protected range-ofmotion exercises and should use a cane or walker for someday. Circulation and nerve operate should be carefully evaluated before and after discount. Whereas apatelladislocation entails the patellofemoral joint, a knee dislocation entails the tibiofemoral articulation. Striking the knee towards the dashboard throughout an automobile accident is the most common reason for harm, however athletic injuries are also frequent causes. Classification of knee dislocations relies on the place of the tibia in relation to the femur. Lateral,medial,androtational dislocations may also happen, as may combination patterns corresponding to anterolateral and posterolateral. Tear or thrombosis of popliteal artery is a frequent complication, requiring immediate repair or replacement. Four-compartment fasciotomy must be carried out at the first signal of compartment syndrome. Inanteriordislocations, stretching of the artery and vein is extreme and sometimes ends in vascular harm. Obese children are extra vulnerable to this drawback because of increasedloadontheirjoints. Ifthedefectislarge,thejointmaybecomeincongruous, leading to mechanical indicators and signs. A necroticappearing flap of cartilage is lifted from the diseased medial femoral condyle. The medial femoral condyle is most commonly concerned, however osteonecrosis additionally may occur in the lateral femoral condyle and the tibial plateau (usuallymedial). Smallerlesions(<5cm2)typicallyhavea higher clinical prognosis and could additionally be satisfactorily handled with activity modification and use of assistive units similar to a cane. Progressive signs might necessitate drilling of the lesion, realignment osteotomy,ortotalkneereplacement. Complete fracture, displaced Type I tibial spine fracture the phrases tibial backbone, tibial eminence, and intercondylar eminence are used interchangeably to designate the nonarticular portion of the adjoining medial and lateral tibial plateaus to which the anterior cruciate ligament is connected anteriorly. Injuries that sometimes cause ruptures of the anterior cruciate ligament in adults often cause a fracture of the tibial spine in kids 7 to 14 years of age. On the date of harm, the affected person underwent debridement of the right tibia with application of an external fixator and retrograde nailing of the best femur, and intramedullary nailing of the left tibia. Nine days after harm, intramedullary nailing of the right tibia and open reduction and plating of the right calcaneus have been done. Becausethis is an intra-articular fracture, anatomic reduction is required for return of knee operate. Duringsurgery,allsoft tissue is removed from the fracture site and the tibial backbone is changed in its anatomic place and fixated with sutures or a screw. In the fetus, skinny synovial membranes divide the knee joint into three compartments (medial,lateral,andpatellar). Inthefifthmonthoffetal improvement, these partitions normally degenerate and thekneejointbecomesonecavity. Most synovial folds comprise a considerable amount of elastin and areolar tissue and are thus extensible and asymptomatic. Many are detected during routine arthroscopic procedures performedforotherreasons. Whenthekneeisextended, the patella protects the anterior side of the femoral condyles, however when the knee is flexed, the medial condyleismorevulnerable. Physical Examination and Special Tests � Plica checks: the patient is supine and relaxed. With the tibia internally rotated, the examiner passively With flexion, plica sweeps across condyle. Arthrosopic resection of medial plica using motorized instrument After resection, preexisting condylar erosion (due to irritation by plica) may be seen. Examining fingers positioned along the medial patellofemoral joint might really feel a click, possiblysometenderness,orevenapopofapathologicplica. Typically, the prepatellar bursa, pes anserinus bursa, tibial collateral ligament bursa, and deep infrapatellar bursaareinvolved. Careful physical examination and routine laboratory studies, such as a white blood cell rely and determination of the degrees of inflammatorymarkers,arebothimportantpartsofthe assessment of a patient with an acute presentation of bursitis. The patient may current with lateral knee pain on activity, tightness of the iliotibial band, and occasionallypopping. Initial remedy options embody iliotibial band stretching workout routines, anti-inflammatory brokers, ultrasound to the lateral femoral epicondyle, and corticosteroid injection. Rarely, in refractory instances, surgery can be accomplished to release an space of tightness or debride any focal areas ofinflammation. Diffuse Villonodular Synovitis this condition sometimes occurs in adults between 20 and forty years of age. A single joint of the decrease limb, mostfrequentlytheknee,isthemostcommonsiteof involvement. Lateinthedisease,thepathologicchangesmaycause stress indentation of bone and generally precise invasion of bone on the articular margins with subsequentbonedestruction.
Buy 30 mg procardia free shipping
The axillary lymph nodes are arranged in five principal teams: pectoral blood vessels breaking in eyes procardia 30 mg buy line, subscapular jugular arteries procardia 30 mg order otc, humeral, central, and apical. These nodes obtain lymph from the posterior side of the thoracic wall and scapular area. The humeral (lateral) nodes consist of four to six nodes that lie along the lateral wall of the axilla, medial and posterior to the axillary vein. These nodes receive almost all of the lymph from the higher limb, besides that carried by the lymphatic vessels accompanying the cephalic vein, which primarily drain directly to the apical axillary and infraclavicular nodes. Efferent vessels from the central nodes pass to the apical nodes, that are positioned on the apex of the axilla along the medial aspect of the axillary vein and the first part of the axillary artery. The apical nodes receive lymph from all other teams of axillary nodes as well as from lymphatics accompanying the proximal cephalic vein. Of the five teams of axillary lymph nodes, most lymphatic vessels from the higher limb terminate within the humeral (lateral) and central lymph nodes, but those accompanying the upper part of the cephalic vein terminate in the apical lymph nodes. Lymph passing via the axillary nodes enters efferent lymphatic vessels that kind the subclavian lymphatic trunk, which usually empties into the junctions of the internal jugular and subclavian veins (the venous angles). The positions of the 5 teams of axillary nodes, relative to one another and the pyramidal axilla. The roots of the plexus often cross through the hole between the anterior and the center scalene (L. The sympathetic fibers carried by every root of the plexus are acquired from the gray rami of the middle and inferior cervical ganglia as the roots cross between the scalene muscle tissue. This massive nerve community extends from the neck to the upper limb by way of the cervico-axillary canal (bound by the clavicle, 1st rib, and superior scapula) to provide innervation to the higher limb and shoulder area. The brachial plexus is typically shaped by the anterior rami of the C5�C8 nerves and the larger a half of the anterior ramus of the T1 nerve (the roots of the brachial plexus). Observe the merging and continuation of sure roots of the plexus to three trunks, the separation of each trunk into anterior and posterior divisions, the union of the divisions to form three cords, and the derivation of the primary terminal branches (peripheral nerves) from the cords as the merchandise of plexus formation. The anterior rami of spinal nerves C5�C8 (plus T1, concealed right here by the third part of the subclavian artery) constitute the roots of the brachial plexus. Merging and subsequent splitting of the nerve fibers conveyed by the roots form the trunks and divisions on the level shown. Four branches of the supraclavicular part of the plexus arise from the roots (anterior rami) and trunks of the brachial plexus (dorsal scapular nerve, lengthy thoracic nerve, nerve to subclavius, and suprascapular nerve), and are approachable via the neck. Counting facet and terminal branches, three branches arise from the lateral cord, whereas the medial and posterior cords every give rise to five branches (counting the roots of the median nerve as individual branches). The medial and lateral pectoral nerves come up from the medial and lateral cords of the brachial plexus, respectively (or from the anterior divisions of the trunks that kind them, as proven here for the lateral pectoral nerve). The programs of the median and musculocutaneous nerves, and the standard pattern of branching of their motor branches are shown. The course of the ulnar nerve and the typical sample of branching of its motor branches. The programs of the axillary and radial nerves and the typical pattern of branching of their motor branches. In either case, the direction of blood flow in the subscapular artery is reversed, enabling blood to attain the third part of the axillary artery. While potential collateral pathways (peri-articular anastomoses) exist around the shoulder joint proximally, and the elbow joint distally, surgical ligation of the axillary artery between the origins of the subscapular artery and the profunda brachii artery will minimize off the blood provide to the arm as a result of the collateral circulation is inadequate. In metastatic cancer of the apical group, the nodes often adhere to the axillary vein, which can necessitate excision of part of this vessel. Enlargement of the apical nodes might hinder the cephalic vein superior to the pectoralis minor. Compression of Axillary Artery the axillary artery could be palpated within the inferior part of the lateral wall of the axilla. Compression of the third part of this artery against the humerus could also be essential when profuse bleeding happens. Dissection of Axillary Lymph Nodes Excision and pathologic evaluation of axillary lymph nodes are often essential for staging and figuring out the suitable treatment of a cancer, corresponding to breast cancer (see p. Because the axillary lymph nodes are organized and obtain lymph (and subsequently metastatic breast most cancers cells) in a selected order, eradicating and analyzing the lymph nodes in that order is necessary in figuring out the degree to which the cancer has developed, and is prone to have metastasized. Lymphatic drainage of the higher limb may be impeded after the removal of the axillary nodes, leading to lymphedema, swelling as a end result of accumulated lymph, especially within the subcutaneous tissue. If the nodes round this nerve are clearly malignant, typically the nerve has to be sacrificed because the nodes are resected to enhance the likelihood of full removing of all malignant cells. Aneurysm of Axillary Artery the primary part of the axillary artery may enlarge (aneurysm of axillary artery) and compress the trunks of the brachial plexus, inflicting pain and anesthesia (loss of sensation) within the areas of the pores and skin supplied by the affected nerves. Injuries to Axillary Vein Wounds within the axilla typically contain the axillary vein because of its massive measurement and uncovered position. When the arm is fully kidnapped, the axillary vein overlaps the axillary artery anteriorly. A wound in the proximal part of the axillary vein is especially dangerous, not solely because of profuse bleeding but additionally because of the chance of air getting into it and producing air emboli (air bubbles) in the blood. Because the needle is superior medially to enter the vein as it crosses the rib, the vein actually punctured (the level of entry) in a "subclavian vein puncture" is the terminal a half of the axillary vein. In addition to the five anterior rami (C5�C8 and T1) that type the roots of the brachial plexus, small contributions may be made by the anterior rami of C4 or T2. In the latter kind, the inferior trunk of the plexus could additionally be compressed by the first rib, producing neurovascular symptoms in the higher limb. Variations can also happen within the formation of trunks, divisions, and cords; within the origin and/or mixture of branches; and in the relationship to the axillary artery and scalene muscle tissue. For example, the lateral or medial cords could obtain fibers from anterior rami inferior or superior to the usual ranges, respectively. Disease, stretching, and wounds in the lateral cervical area (posterior triangle) of the neck (see Chapter 8), or within the axilla might produce brachial plexus accidents. In incomplete paralysis, not all muscle tissue are paralyzed; subsequently, the particular person can move, but the actions are weak compared with these on the traditional side. Injuries to superior components of the brachial plexus (C5 and C6) normally outcome from an extreme enhance within the angle between the neck and shoulder. This stretches or ruptures superior elements of the brachial plexus or avulses (tears) the roots of the plexus from the spinal wire. Observe the extreme enhance within the angle between the top and the left shoulder during this delivery. Compression of the axillary artery and vein causes ischemia of the higher limb and distension of the superficial veins. These signs and symptoms of hyperabduction syndrome end result from compression of the axillary vessels and nerves. Chronic microtrauma to the superior trunk of the brachial plexus from carrying a heavy backpack can produce motor and sensory deficits within the distribution of the musculocutaneous and radial nerves. The nerve fibers concerned are usually derived from the superior trunk of the brachial plexus.
Procardia 30 mg buy line
Details regarding all four parts of the male urethra are offered and compared in Table 3 cardiovascular or weights first procardia 30 mg buy with visa. Posterolateral to this part of the urethra are the small bulbo-urethral glands and their slender ducts cardiovascular disease prevention programs buy procardia 30 mg cheap, which open into the proximal part of the spongy urethra. There are additionally many minute openings of the ducts of mucus-secreting urethral glands into the spongy urethra. The innervation of the intermediate a part of the urethra is the same as that of the prostatic part: autonomic (efferent) innervation by way of the prostatic nerve plexus, arising from the inferior hypogastric plexus. The sympathetic innervation is from the lumbar spinal wire ranges via the lumbar splanchnic nerves, and the parasympathetic innervation is from the sacral levels via the pelvic splanchnic nerves. The visceral afferent fibers follow the parasympathetic fibers retrogradely to sacral spinal sensory ganglia. The testes and epididymides and their coverings are described with the stomach (see Chapter 2). Anterior scrotal arteries, terminal branches of the exterior pudendal arteries (from the femoral artery), provide the anterior facet of the scrotum. Attempting to method this "straight-line" place as a lot as potential facilitates passage of a catheter or other transurethral system. Lymphatic vessels from the scrotum carry lymph to the superficial inguinal lymph nodes (Table 3. The scrotum is split into proper and left halves by the cutaneous scrotal raphe, which is steady with the penile and perineal raphes. The penis contains three erectile plenty: two corpora cavernosa and a corpus spongiosum (containing the spongy urethra). The skin of the penis extends distally because the prepuce, overlapping the neck and corona of the glans. The pores and skin of the penis is thin, darkly pigmented relative to adjacent pores and skin, and linked to the tunica albuginea by free connective tissue. The inferior anal (rectal) nerve branches from the pudendal nerve at the entrance to the pudendal canal and, with the perineal department of S4, supplies the external anal sphincter. The fibers of the suspensory ligament are quick and taut, anchoring the erectile bodies of the penis to the pubic symphysis. The pudendal nerve conveys the majority of sensory, sympathetic, and somatic motor fibers to the perineum. The cavernous nerves arise from the prostatic plexus of males and from the vesical plexus of females. The fibers of the fundiform ligament are comparatively long and unfastened and lie superficial (anterior) to the suspensory ligament. Chapter 3 � Pelvis and Perineum 423 primarily by the dorsal nerve of the penis, a terminal department of the pudendal nerve, which arises within the pudendal canal and passes anteriorly into the deep perineal pouch. Lymphatic drainage from the intermediate and proximal elements of the urethra and cavernous our bodies drain into the internal iliac lymph nodes, whereas most vessels from the distal spongy urethra and glans penis move to the deep inguinal nodes, however some lymph passes to the external inguinal nodes. Details in regards to the attachments, innervation, and actions of those muscle tissue are supplied in Table 3. Simultaneous contraction of the superficial perineal muscular tissues (plus the deep transverse perineal muscle) during penile erection supplies a firmer base for the penis. They drive blood from the cavernous areas within the crura into the distal elements of the corpora cavernosa, which will increase the turgidity (firm distension) of the penis throughout erection. Because of their perform throughout erection and the exercise of the bulbospongiosus subsequent to urination and ejaculation to expel the last drops of urine and semen, the perineal muscle tissue are generally more developed in males than in females. When a male is stimulated erotically, arteriovenous anastomoses by which blood is often capable of bypass the "empty" potential areas or sinuses of the corpora cavernosa are closed. The bulbospongiosus and ischiocavernosus muscles compress veins egressing from the corpora cavernosa, impeding the return of venous blood. As a end result, the corpora cavernosa and corpus spongiosum turn into engorged with blood near arterial pressure, inflicting the erectile our bodies to become turgid (enlarged and rigid), and an erection happens. During emission, semen (sperms and other glandular secretions) is delivered to the prostatic urethra via the ejaculatory ducts after peristalsis of the ductus deferentes and seminal glands.
[newline]During ejaculation, semen is expelled from the urethra by way of the exterior urethral orifice. After ejaculation, the penis progressively returns to a flaccid state (remission), resulting from sympathetic stimulation, which causes constriction of the sleek muscle within the coiled helicine arteries. The bulbospongiosus and ischiocavernosus muscles loosen up, allowing extra blood to be drained from the cavernous spaces within the corpora cavernosa into the deep dorsal vein. Urethral stricture may end result from exterior trauma of the penis or an infection of the urethra. The spongy urethra will increase enough to allow passage of an instrument roughly 8 mm in diameter. Penis Prepuce Glans penis External urethral orifice Distension of Scrotum the scrotum is easily distended. In persons with large indirect inguinal hernias, for example, the gut might enter the scrotum, making it as giant as a soccer ball. In the simplest and commonest type, glanular hypospadias, the exterior urethral orifice is on the ventral side of the glans penis. The embryological foundation of penile and penoscrotal hypospadias is failure of the urogenital folds to fuse on the ventral surface of the penis, finishing the formation of the spongy urethra. As there are modified sebaceous glands in the prepuce, the oily secretions of tacky consistency (smegma) from them accumulate in the preputial sac, situated between the glans and prepuce, inflicting irritation. In adults, circumcision is normally carried out when phimosis or paraphimosis occurs. Impotence and Erectile Dysfunction Inability to obtain an erection (impotence) may result from several causes. � Immediately inferior to the membrane, the urethra enters the corpus spongiosum and turns into the spongy urethra, the longest part of the male urethra. � the spongy urethra has expansions at each finish, the intrabulbar and navicular fossae. The intermediate part follows visceral paths and the spongy half follows somatic paths. � Its inside subdivision by a septum of dartos fascia is demarcated externally by a median scrotal raphe. � the anterior side of the scrotum is served by anterior scrotal blood vessels and nerves, continuations of external pudendal blood vessels and branches of the lumbar nerve plexus. � the posterior aspect of the scrotum is served by posterior scrotal blood vessels and nerves, continuations of inner pudendal blood vessels and branches of the sacral nerve plexus. � Sympathetic innervation of smooth dartos muscle and sweat glands assists thermoregulation of the testes. � It is formed mainly of thin, mobile skin overlying three cylindrical bodies of erectile cavernous tissue, the paired corpora cavernosa, and a single corpus spongiosum containing the spongy urethra. � the ischiocavernosus muscular tissues ensheath the crura, and the bulbospongiosus muscle ensheaths the bulb, its most anterior fibers encircling essentially the most proximal a part of the penile body and deep dorsal vessels.
Discount 30 mg procardia otc
These joints are discussed with the again in Chapter 4; the sternoclavicular joints are mentioned in Chapter 6 cardiovascular outcomes definition procardia 30 mg generic online. The heads of the ribs connect so intently to the vertebral our bodies that only slight gliding actions occur on the (demi)facets (pivoting around the intra-articular ligament) of the joints of the heads of ribs; nonetheless cardiovascular jobs in nc buy generic procardia 30 mg online, even slight motion right here may produce a comparatively large tour of the distal (sternal or anterior) finish of a rib. A superior costotransverse ligament is a broad band that joins the crest of the neck of the rib to the transverse course of superior to it. The aperture between this ligament and the vertebra permits passage of the spinal nerve and the posterior branch of the intercostal artery. The superior costotransverse ligament could also be divided into a strong anterior costotransverse ligament and a weak posterior costotransverse ligament. These proceed as thin, broad membranous bands passing from the costal cartilages to the anterior and posterior surfaces of the sternum, forming a felt-like covering for this bone. Consequent strain modifications lead to air being alternately drawn into the lungs (inspiration) through the nostril, mouth, larynx, and trachea and expelled from the lungs (expiration) through the identical passages. Concurrently, intra-abdominal pressure decreases and belly viscera are decompressed. As a result of this and the absence of resistance to the previously compressed viscera, the domes of the diaphragm ascend, diminishing the vertical dimension. Because the ribs slope inferiorly, their elevation additionally leads to anterior�posterior motion of the sternum, especially its inferior end, with slight movement occurring on the manubriosternal joint in young individuals, in whom this joint has not yet synostosed (united). The posterolateral features of the 5th�7th intercostal areas are essential sites for posterior thoracotomy incisions. Surgeons use an H-shaped incision to incise the superficial side of the periosteum that ensheaths the rib, strip the periosteum from the rib, and then excise a wide segment of the rib to acquire higher entry, as might be required to enter the thoracic cavity and take away a lung (pneumonectomy), for example. After the operation, the lacking items of ribs regenerate from the intact periosteum, although imperfectly. Rib fractures are painful because the damaged parts move throughout respiration, coughing, laughing, and sneezing. Flail Chest Multiple rib fractures may allow a sizable segment of the anterior and/or lateral thoracic wall to move freely. The unfastened section of the wall strikes paradoxically (inward on inspiration and outward on expiration). A fracture of the sternal body is usually a comminuted fracture (a break resulting in a number of pieces). The most typical website of sternal fracture in elderly folks is on the sternal angle, the place the manubriosternal joint has fused. Because of the remarkable elasticity of the ribs and costal cartilages in children, chest compression may produce harm within the thorax even in the absence of a rib fracture. In elderly people, the costal cartilages lose some of their elasticity and turn into brittle; they could endure calcification, making them radiopaque. Median Sternotomy To gain access to the thoracic cavity for surgical operations in the mediastinum-such as coronary artery bypass grafting, for example-the sternum is divided (split) in the median aircraft and retracted. Such "sternal splitting" additionally provides good publicity for elimination of tumors in the superior lobes of the lungs. After surgery, the halves of the sternum are usually joined utilizing wire sutures or clips. Rib dislocations are frequent in body-contact sports activities; complications may result from strain on or damage to close by nerves, vessels, and muscular tissues. Sternal biopsy is usually used to get hold of specimens of marrow for transplantation and for detection of metastatic most cancers and blood dyscrasias (abnormalities). Partial clefts involving the manubrium and superior half of the body are V- or U-shaped and can be repaired during infancy by direct apposition and fixation of the sternal halves. In separations of the 3rd�10th ribs, tearing of the perichondrium and periosteum normally happens. As a result, the rib might transfer superiorly, overriding the rib above and inflicting pain. Instead of ascending throughout expiration, the paralyzed dome descends in response to the positive stress within the lungs. Thoracic Outlet Syndrome Anatomists check with the superior thoracic aperture as the thoracic inlet as a outcome of non-circulating substances (air and food) could enter the thorax only through this aperture. � Laterally and anteriorly the cage consists of 12 ribs that are continued anteriorly by costal cartilages. � the superior thoracic aperture is a small passageway for the transmittal of constructions to and from the neck and higher limbs. Structures passing between the thorax and abdomen traverse openings in the diaphragm. Joints of thoracic wall: the joints allow and determine movements of the thoracic wall. � Posteriorly, ribs articulate with the semiflexible thoracic vertebral column through costovertebral joints. Movements of thoracic wall: the movements of most ribs happen around a usually transverse axis that passes via the top, neck, and tubercle of the rib. � Contraction and relaxation of the superiorly convex diaphragm alters its vertical dimensions. � Increasing dimensions produce inhalation, and decreasing dimensions produce exhalation. The true muscle tissue of the thoracic wall are the serratus posterior, levatores costarum, intercostal, subcostal, and transversus thoracis. On the idea of its attachments and disposition, the serratus posterior inferior was stated to depress the inferior ribs, preventing them from being pulled superiorly by the diaphragm. These muscles, notably the serratus posterior superior, have been implicated as a source of persistent ache in myofascial pain syndromes. The superficial layer is formed by the external intercostals, the inside layer by the internal intercostals. The deepest fibers of the latter, mendacity internal to the intercostal vessels, are considerably artificially designated as a separate muscle, the innermost intercostals. Axio-appendicular, neck, and anterolateral belly muscles overlying thoracic wall. The pectoralis major has been eliminated on the left facet to expose the pectoralis minor, subclavius, and exterior intercostal muscular tissues. These muscles are steady inferiorly with the external oblique muscular tissues within the anterolateral stomach wall. The inferior internal intercostal muscular tissues are continuous with the inner oblique muscular tissues within the anterolateral abdominal wall. The inside intercostals-weaker than the exterior intercostal muscles-are most lively throughout expiration-especially their interosseous (vs.

Procardia 30 mg overnight delivery
The central band inserts into the base of the center phalanx sindrome cardiovascular x order procardia 30 mg line, and the lateral slips converge to insert into the base of the distal phalanx heart disease outline buy procardia 30 mg without prescription. It may play a special proprioceptive position in sensing sudden inversion after which contracting reflexively to shield the anterior tibiofibular ligament, essentially the most commonly sprained ligament of the body. These dissections reveal the continuation of the anterior and lateral leg muscular tissues into the foot. The thinner parts of the deep fascia of the leg have been eliminated, leaving the thicker parts that make up the extensor and fibular retinacula, which retain the tendons as they cross the ankle. At the ankle, the vessels and the deep fibular nerve lie halfway between the malleoli and between the tendons of the lengthy dorsiflexors of the toes. This dissection reveals the muscular tissues of the anterolateral leg and dorsum of the foot. The frequent fibular nerve, coursing subcutaneously throughout the lateral aspect of the head and neck of the fibula, is probably the most generally injured peripheral nerve. In this deeper dissection of the anterior compartment, the muscle tissue and inferior extensor retinaculum are retracted to show the arteries and nerves. It is likely one of the two terminal branches of the frequent fibular nerve, arising between the fibularis longus muscle and the neck of the fibula. The deep fibular nerve then exits the compartment, persevering with throughout the ankle joint to supply intrinsic muscles (extensors digitorum and hallucis brevis), and a small area of the pores and skin of the foot. The smaller terminal department of the popliteal artery, the anterior tibial artery, begins at the inferior border of the popliteus muscle. Here the tendons of the two muscular tissues of the lateral compartment (fibularis longus and brevis) enter a standard synovial sheath to accommodate their passage between the superior fibular retinaculum and the lateral malleolus, using the latter as a trochlea as they cross the ankle joint. These muscular tissues have their fleshy bellies within the lateral compartment however are tendinous as they exit the compartment throughout the widespread synovial sheath deep to the superior fibular retinaculum. However, as a end result of the fibularis longus and brevis pass posterior to the transverse axis of the ankle (talocrural) joint, they contribute to plantarflexion at the ankle-unlike the postaxial muscle tissue of the anterior compartment (including the fibularis tertius), that are dorsiflexors. In follow, the primary function of the evertors of the foot is to not elevate the lateral margin of the foot (the widespread description of eversion) however to depress or repair the medial margin of the foot in help of the toe off section of walking and, especially, working and to resist inadvertent or extreme inversion of the foot (the place during which the ankle is most susceptible to injury). When standing (and significantly when balancing on one foot), the fibularis muscle tissue contract to resist medial sway (to recenter a line of gravity, which has shifted medially) by pulling laterally on the leg while depressing the medial margin of the foot. Because the nerve and blood vessels supplying the complete posterior compartment and the only of the foot move via the deep subcompartment, when swelling occurs it results in a compartment syndrome that has serious penalties, such as muscular necrosis (tissue death) and paralysis. The retinaculum is subdivided deeply, forming separate compartments for each tendon of the deep muscle group, as properly as for the tibial nerve and posterior tibial artery as they bend across the medial malleolus. The posterior compartment and the muscular tissues inside it are divided into superficial and deep subcompartments/muscle groups by the transverse intermuscular septum. The gastrocnemius and soleus share a common tendon, the calcaneal tendon, which attaches to the calcaneus. These muscle tissue are sturdy and heavy as a end result of they carry, propel, and accelerate the burden of the physique when strolling, working, leaping, or standing on the toes. It then widens as it inserts on the posterior surface of the calcaneal tuberosity. The calcaneal tendon sometimes spirals a quarter flip (90�) during its descent, so that the gastrocnemius fibers connect laterally and the soleal fibers attach medially. Although they share a common tendon, the two muscular tissues of the triceps surae are capable of acting alone, and often do so: "You stroll with the soleus however win the lengthy leap with the gastrocnemius. A deep bursa of the calcaneal tendon (retrocalcaneal bursa), located between the tendon and the calcaneus, allows the tendon to glide over the bone. It is a fusiform, two-headed, two-joint muscle with the medial head slightly bigger and extending more distally than its lateral associate. The three heads of the triceps surae muscle attach distally to the calcaneus by way of the spiraling fibers of the calcaneal tendon. The transverse intermuscular septum has been split to reveal the deep muscles, vessels, and nerves. The popliteus acts on the knee joint, whereas the opposite muscular tissues plantarflex the ankle with two continuing on to flex the toes. However, due to their smaller measurement and the close proximity of their tendons to the axis of the ankle joint, the "non-triceps" plantarflexors collectively produce only about 7% of the entire drive of plantarflexion, and on this the fibularis longus and brevis are most vital. The soleus has a steady proximal attachment within the form of an inverted U to the posterior elements of the fibula and tibia, and a tendinous arch between them, the tendinous arch of soleus (L. The soleus can be palpated on all sides of the gastrocnemius when the individual is standing on their tiptoes. This vestigial muscle is absent in 5�10% of people and is extremely variable in size and form when current (most commonly a tapering slip concerning the measurement of the small finger). It acts with the gastrocnemius but is insignificant as both a flexor of the knee or a plantarflexor of the ankle. The plantaris has been thought of to be an organ of proprioception for the bigger plantarflexors, as it has a high density of muscle spindles (receptors for proprioception). When the foot is off the ground and the knee is flexed, the popliteus can aid the medial hamstrings (the "semimuscles") in rotating the tibia medially beneath the femoral condyles. The tendon then crosses deep to the tendon of the flexor digitorum longus in the sole of the foot. Close to its origin, the posterior tibial artery provides rise to its largest department, the fibular artery, which runs lateral and parallel to it, also throughout the deep subcompartment. During its descent, the posterior tibial artery is accompanied by the tibial nerve and veins. Deep to the flexor retinaculum and the origin of the abductor hallucis, the posterior tibial artery divides into medial and lateral plantar arteries, the arteries of the solely real of the foot. The fibular artery offers muscular branches to the popliteus and other muscles in each the posterior and the lateral compartments of the leg. Distally, the fibular artery gives rise to a perforating branch and terminal lateral malleolar and calcaneal branches. The perforating department pierces the interosseous membrane and passes to the dorsum of the foot, where it anastomoses with the arcuate artery. The circumflex fibular artery arises from the origin of the anterior or posterior tibial artery at the knee and passes Chapter 5 � Lower Limb 603 laterally over the neck of the fibula to the anastomoses around the knee. The nutrient artery of tibia, the most important nutrient artery within the physique, arises from the origin of the anterior or posterior tibial artery. This oval elevation signifies the level of the top of the fibula and the bifurcation of the popliteal artery into the anterior and posterior tibial arteries. Extensors and flexors of toes are being contracted concurrently, demonstrating extensor tendons without elevating toes from ground. The shaft of the fibula is subcutaneous only in its distal half, proximal to the lateral malleolus; this is the common web site of fractures. Palpate them, noting that the tip of the lateral malleolus extends farther distally and posteriorly than the medial malleolus. The soleus can be palpated deep to and on the sides of the superior part of the calcaneal tendon.
Syndromes
- Bleeding or clotting in the area where the catheter was inserted
- Medicine (antidote) to reverse the effect of the poison
- Cognitive problems (such as intellectual disability)
- Anemia
- Scarring
- Diuretics
- Your angina symptoms occur while you are at rest.
30 mg procardia cheap otc
One gram of magnesium sulfate provides approximately four mmol (8 mEq blood vessels end to end procardia 30 mg generic on-line, or 98 mg) of elemental magnesium coronary heart disease statistics 2012 uk buy procardia 30 mg without a prescription. Because Mg2+ antagonizes Ca2+, blood strain and cardiac function should be monitored, although blood stress and cardiac output usually change little during Mg2+ infusion. Treatment of hypomagnesemia during cardiopulmonary bypass was discovered to decrease the incidence of postoperative ventricular tachycardia from 30% to 7% and increase the frequency of steady sinus rhythm from 5% to 34%. Patients with renal insufficiency have a diminished capacity to excrete Mg2+ and require cautious monitoring. Repletion of systemic Mg2+ shops normally requires 5 to 7 days of therapy, after which day by day maintenance doses must be offered. Magnesium could be given orally, normally in a dose of 60 to 90 mEq/day of magnesium oxide. Hypocalcemic, hypomagnesemic sufferers should obtain Mg2+ as the chloride salt, as a result of sulfate can chelate Ca2+ and further cut back serum Ca2+. Other rarer causes of delicate hypermagnesemia are hypothyroidism, Addison illness, lithium intoxication, and familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia. Magnesium potentiates the motion of nondepolarizing muscle relaxants and reduces K+ launch in response to succinylcholine. In emergency conditions and in patients with renal failure, Mg2+ can be removed by dialysis. Diuretics probably the most outstanding property of diuretics is that they reduce reabsorption of Na+ and Cl- at completely different sites within the nephron, thereby growing urinary Na+ and water losses. This makes them useful in treatment of quite a lot of conditions, corresponding to edematous states, hypertension, heart failure, renal dysfunction, hypercalcemia, nephrolithiasis, glaucoma, and mountain illness. Their efficacy, security, and optimal dosing are, however, primarily based on small and underpowered trials. Loop diuretics act in the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle; thiazide-type diuretics act within the distal tubule and connecting section; and potassium-sparing diuretics act within the aldosteronesensitive principal cells within the cortical collecting tubule. They return reabsorbed Na+ to the systemic circulation and maintain intracellular Na+ concentration at low levels. Each of the major nephron segments has a unique Na+ entry mechanism; inhibition of this step is the most important mechanism at which each of the completely different courses of diuretics acts. Approximately two-thirds of filtered Na+ is reabsorbed within the proximal tubule by major and secondary active transport. The net diuresis is small because a lot of the extra fluid is reclaimed at more distal segments, particularly on the loop of Henle. The major uses of those diuretics are for edematous states and metabolic alkalosis. Adverse effects are acidosis, bicarbonaturia, hypokalemia, paresthesias, and renal stones (hypercalciuria, phosphaturia). The osmolarity can reach a maximum of 1200 mOsm/L on the tip of the medullary interstitium in antidiuresis. Loop diuretics (furosemide, torsemide, bumetanide, ethacrynic acid) can result in excretion of 20% to 25% of filtered Na+ in large doses. Clinical uses of loop diuretics embody acute pulmonary edema, acute renal failure, anion overdose, heart failure, hypercalcemia, hypertension, and refractory edema. Adverse effects are allergy symptoms, alkalosis, hypocalcemia, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, hyperuricemia, hypovolemia, and ototoxicity (ethancrynic acid > furosemide). Potassium-Sparing Diuretics Spironolactone, amiloride, and triamterene are weak diuretics that act on the stage of the amassing tubules and ducts. Normally, aldosterone exerts its mineralocorticoid action via interaction with particular receptors, increasing insertion of Na+ channels on the luminal membrane, thereby increasing exercise of Na+/K+ and H+ exchangers. Na+ entering by way of the channels increases intracellular constructive cost, and thereby extrusion of K+ into the lumen. Spironolactone is an aldosterone receptor inhibitor, whereas amiloride and triamterene block Na+ channels. Thus they trigger a minor improve in urinary Na+ but a considerable lower in urinary K+ with attainable hyperkalemia and acidosis. Clinical uses embody hyperaldosteronism, hypertension, coronary heart failure, and feminine hirsutism (spironolactone). Adverse effects include acidosis, hyperkalemia, azotemia, gynecomastia, and libido changes (spironolactone) and nephrolithiasis (triamterene). Thiazides Hydrochlorothiazide, indapamide, and metolazone are natural acids that are each filtered and secreted and inhibit the Na+/Cl- transporter on the luminal membrane of the distal convoluted tubule. Chloride additionally returns to blood by such a mechanism, whereas Ca2+ returns by a Ca2+/Na+ antiporter. If the Na+/Cl- cotransporter is inhibited by thiazides, hypokalemia and alkalosis occur. Adverse effects are allergies, alkalosis, hypokalemia, hyperuricemia, hypovolemia, hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia, hypercalcemia, and sexual dysfunction. Osmotic Diuretics Mannitol is a non-reabsorbable sugar that acts as an osmotic diuretic, inhibiting water reabsorption in the proximal convoluted tubule (main site), thin descending loop of Henle, and the amassing ducts. However, retention of the hypertonic mannitol can induce further volume growth. Major scientific makes use of embrace early levels of oliguria, early phases of mind edema, and postischemic acute renal failure. It can be generally used in neurosurgical anesthesia to provide good working situations. Step 4 corresponds to inhibition of Na+ reabsorption in the proximal tubule, and step 5 corresponds to the thick ascending loop of Henle. In sufferers who remain edematous, the circulatory quantity could be depleted and tissue perfusion decreased. Adverse Effects of Diuretics At excessive doses diuretics produce opposed results, such as hypotension, hypovolemia, electrolyte abnormalities, renal dysfunction, and neurohumoral activation. This known as prerenal azotemia as a result of the defect is in renal perfusion quite than in renal perform. This can happen when epinephrine during a stress scenario transfers K + into cells via 2-receptor agonism. Hyponatremia Hyponatremia is a common aspect effect in edematous patients with heart failure or cirrhosis. The fluid ought to have a sodium concentration close to the physiologic vary to keep away from perioperative hyponatremia, the commonest complication of perioperative fluid remedy. The small quantity of glucose within the solution additionally prevents lipolysis and the discharge of ketone bodies and free fatty acids. Although fluids of this kind are adequate for many pediatric sufferers, particular person patient characteristics should, as always, be considered when selecting the sort of fluid to use. Key Points � Themajorelectrolytes(sodium,potassium,calcium,phosphate, and magnesium) are crucial to basic physiologic features, including action potential era, cardiac rhythm management, muscle contraction, and power storage, among many others. It is handled first with quantity resuscitation when needed followed by repletion of the free water deficit, and by addressing the underlying cause. In anesthesia apply, hyperkalemic cardiac toxicity is associated with the administration of succinylcholine to sufferers with upper motor neuron lesions or extreme burns. Carbohydrate-inducedhypophosphatemia(refeedingsyndrome), mediated by insulin-induced mobile phosphate uptake, is the most generally encountered kind in hospitalized patients.
Procardia 30 mg overnight delivery
Initially cardiovascular disease updates cheap 30 mg procardia fast delivery, this technique was used to detect the presence of the Y chromosome in ladies who had obtained pink blood cell transfusions from a minimum of one male donor fragile x cardiovascular effective procardia 30 mg. Novel processes for inactivation of leukocytes to stop transfusion-associated graft versus host illness. The impact of common leukodepletion of the blood supply on hemovigilance reviews of posttransfusion purpura and transfusion-associated graft versus host disease. However, transfused blood products have extra effects on recipient immunity apart from technology of alloantibodies. Current immunosuppressive medications have significantly reduced the advantages of the transfusion effect. Decreased Likelihood of Recurrent Spontaneous Abortions: It has been observed that transfusion of allogeneic blood, from paternal or different sources, has a helpful impact in stopping recurrent spontaneous abortion in women presumably by lowering the T-cell response and generating suppressor T-cells. For example, published information counsel that transfusion could improve most cancers recurrence and/or metastasis, presumably due to decreased antitumor immunity. In each of these situations, an equally massive variety of reviews show no statistically vital effects. However, humoral and mobile immunity symbolize distinct response pathways, which may be mutually antagonistic. In this fashion, enhanced antibody responses and mobile immunosuppression may concurrently happen. Thus, whereas secondary outcomes of transfusion may be real and reproducible, appreciable scrutiny should be applied to decide whether the mechanism of such outcomes is due to results on the immune system. Transfusion of purple blood cells after extended storage produces dangerous effects that are mediated by iron and irritation. Patients with transfusion-requiring anemias could accumulate close to 10 g of iron every year. Hepcidin is the central regulator of systemic iron homeostasis and is insufficiently elevated in states of primary and secondary iron overload, thought to both cause or compound the degree of iron overload, respectively. The scientific manifestations, analysis, and administration of iron overload are discussed under. The supply of iron to erythroid precursors in the bone marrow and to other tissues is basically maintained by every day recycling of iron from senescent erythrocytes. Only 1�2 mg of iron on average is absorbed daily from the diet to replace ordinary iron losses. Iron absorption is tightly regulated to keep iron stability as a result of no physiological mechanism exists for iron elimination in humans and different animals. Pathophysiology: Due to this limitation in iron excretion, patients with transfusion-requiring anemias are topic to a major iron load, typically leading to parenchymal iron deposition and overload. Furthermore, illnesses related to iron overload in the absence of transfusion. It is thought that hepcidin is regulated by iron, hypoxia, inflammation, and erythropoiesis. Primary iron overload ailments are associated with inadequate hepcidin, which leads to inappropriately excessive iron absorption. How tissue iron accumulates and leads to toxicity has not been clearly delineated. Normally, iron circulates sure to transferrin (which is highly iron saturated in iron-overloaded patients) or ferritin (whose plasma levels typically mirror iron shops but additionally improve in continual inflammatory states). Thus, excess iron results in the era of reactive oxygen species which have the potential to oxidize lipids, proteins, and nucleic acid, leading to tissue injury in a quantity of organs. Much of this data on the results of chronic transfusion is extrapolated from long-term research of transfusion-requiring patients with �-thalassemia major. Until the Seventies, transfusion-requiring sufferers with �-thalassemia main died of cardiac iron overload before the age of 20 years. Since then, with the establishment of iron chelation remedy, patients have a protracted survival and a delayed onset of cardiac iron overload. Diagnosis: the analysis of iron overload requires medical correlation of the signs and signs noted above with an estimation of complete physique iron accumulation/ shops. Estimating whole physique iron shops is imprecise and may be accomplished by way of direct and oblique strategies. Direct measurements could be achieved by liver biopsy with increased accuracy albeit as a consequence of an invasive process not with out risk. Iron chelating brokers directly bind iron, and the iron:chelator complex is excreted in the urine or feces. In most instances, compliance with iron chelation therapy considerably Iron Overload 451 reduces the problems of iron overload and leads to an improved quality of life. The therapeutic objective is to preserve liver iron concentration at beneath 5 mg/g liver dry weight and serum ferritin under 1000�1500 g/l. These different chelating brokers exhibit variations in organ specific efficacy and their varying aspect effect profiles require different patient follow-up recommendations. Combination remedy or switching between chelators could additionally be required in cases of inadequate response to individual chelators. Exchange transfusion could also be used as a substitute of easy transfusion which reduces the general transfused iron burden (see Chapters 50 and 74). The changing role of liver biopsy in prognosis and management of haemochromatosis. Iron overload in thalassemia and associated circumstances: therapeutic targets and evaluation of response to chelation therapies. Examples of the broad spectrum of infections of current interest in the transfusion medicine neighborhood are found in Table seventy one. Septic transfusion reactions on account of bacterial contamination, significantly of platelet merchandise, are discussed in Chapter sixty five. These mixed strategies result in a lot decrease donor prevalences and incidences of transfusion transmissible pathogens than in the common population (Table 71. Thirty to 50% of contaminated persons aged 5 years could have signs and symptoms clinically suggestive of hepatitis, and 0. Approximately 25% of these chronically contaminated during childhood and 15% of those that turn out to be chronically infected later die prematurely from cirrhosis or liver cancer, however most remain asymptomatic until the onset of end-stage liver disease. Current residual danger estimates are 1:750,000 or much less in an era of universal immunization. Approximately 20% will have scientific hepatitis after an incubation interval of 7�8 weeks. Chronicity develops in 75�85% of infections, with cirrhosis creating in 20�30% after an average of 20 years. Hepatocellular carcinoma develops in cirrhotics a mean of 30 years following infection.
Procardia 30 mg best
In older youngsters cardiovascular system powerpoint high school cheap procardia 30 mg without a prescription, light closed reduction becomes harder cardiovascular x-ray imaging procardia 30 mg low cost, and extra invasive measures are needed to achieve the objective of a secure discount. Redundant and hypertrophied capitis femoris ligament and contracture of transverse acetabular ligament can also hinder discount. It should avoid excessive stress to the joint yet also keep the femoral head from redislocating. Arthrogram reveals typical bilocular look because of stretching and narrowing of joint capsule. Although there are many units that have historicallybeenemployed tomaintainreduction oftheunstable newborn hip. Forced abduction past this limit may lead to avascular necrosis of femoral head. Posterior strap serves as checkrein to stop hip from adducting to level of redislocation. Ultrasound examination provides glorious detail of the largely cartilaginous femoral head and acetabulum. The examination may additionally be performed while the child is in a Pavlik harness if needed. Zone of redislocation (adduction) Safe zone (of Ramsey) Comfortable abduction limit Maximal abduction Some infants have adductor tightness that forestalls discount, and protected zone turns into narrower. In many instances, adductor muscles loosen up and hip spontaneously reduces after 2 weeks of wearing harness. If not, traction, and presumably adductor tenotomy, is required prior to discount beneath anesthesia. Although age is a crucial consideration for this strategy, perhaps more necessary is patient measurement. The medial femoral circumflex artery is in danger in this strategy and lies in shut proximitytothepsoastendon. Anatomicobstaclestoreduction such as the pulvinar might must be excised to permitreduction. Anastomosis Ascending, transverse, and descending branches of lateral circumflex femoral a. Distribution of medial and lateral circumflex femoral arteries Acetabular labrum Growth plate Posterior superior and posterior inferior branches of medial circumflex femoral a. An oblique incision just distal to and along the course of the iliac crest permits accessand providesa higher cosmetic end result. Inolderchildren with much less remodeling potential, innominate osteotomy can be carried out to enhance the acetabular anatomy. Compromise of the blood supply to the femoral head for even a short while can produce complete death of the femoralhead. Several factors regarding the femoral head blood supply and reduction of the femoral head have been describedbyOgden. Inthenewborn,boththe lateral and medial circumflex femoral arteries provide the femoralhead. Initial lack of blood provide to capital femoral epiphysis; cause unknown Infarction results, evidenced by empty lacunae as a result of demise of osteocytes. Ossification center ceases to develop; on radiograph seems smaller than on uninvolved side. Articular cartilage (nourished by synovial fluid) continues to develop, giving radiographic appearance of widened joint space. The dysfunction happens extra frequently in Asian, Eskimo,andCentralEuropeanpopulations,whereasthe incidenceisdecreasedinblacks,Australianaborigines, AmericanIndians,andPolynesians. As a consequence, affected youngsters are normally shorter than their friends, and the shortness of stature,althoughslight,persistsintoadulthood. Disproportionate progress, abnormalities in skeletal development and maturation, and elevated serum ranges of somatomedin have been demonstrated. Therelationshipbetweengrowth abnormalities, serum somatomedin, and ischemia of the epiphysis of the femoral head remains obscure. Osteoblasts produce bone; osteoclasts resorb bone, significantly in subchondral area. Fracture Subchondral fracture and second ischemic episode If shearing forces on femoral head exceed energy of weakened subchondral bone, fracture of variable extent might occur. Collapse of trabeculae underlying fracture occludes new capillaries, and bone resorption occurs. Although the cause remains unclear, quite a few research have delineated the pathogenesis of LeggCalv�-Perthesdisease. Hip rotation best assessed with affected person in inclined place as a outcome of any restriction could be detected and measured easily. Resumption of endochondral ossification throughout the epiphysis begins peripherally and progresses centrally. Withtheingrowthofcapillaries,osteoclastsandosteoblasts cover the surface of the avascular subchondral cortical bone and the central trabecular bone. The deposition of new trabecular boneand resorption of avascular bone occur simultaneously. Thecontinuationofthis"potential" type of Legg-Calv�-Perthes illness or the event of the "true" kind depends on whether or not a subchondralfractureoccurs. Thereossificationprocess continues uninterrupted, with ultimate resumption of regular development and development. Thesubchondralareaeventually regains its normal energy and stability, and a "head-within-a-head" is visible on radiographs. Inmostcases,thefracture seems to result from regular vigorous activity quite than from a selected injury. Trendelenburg test Left: Patient demonstrates negative Trendelenburg check of regular right hip. Trunk shifts left as affected person attempts to decrease biomechanical stresses across concerned hip and thereby preserve steadiness. Thereisminimal,ifany,extensionofthe subchondral fracture after the initial fracture. Consequently, the complete space is slowly revascularized, with resorption of the fibroosseoustissue,byaprocesstermedcreeping substitution. Potential deformities may be attributable to the completely different rates of growthwithinthefemoralhead-areasnotundergoing resorption develop sooner than the involved area. Changes in Growth Plate Because the blood provide to the growth plate comes fromtheepiphysealside,thetwoischemicepisodesalso produce ischemic adjustments in the growth plate. Changes in Metaphysis Four forms of metaphyseal modifications have been famous: presence of adipose tissue, osteolytic lesions (well- circumscribed areas of fibrocartilage), disorganized ossification,andextrusionofthegrowthplate. Whereas only adipose tissue changes are detected early in the disease, osteolytic lesions are seen in the later phases. When these fibrocartilaginous lesions are in contact with the growth plate, the traditional structure of the expansion plate is lost and the lesions seem on radiographsascysts.
Generic procardia 30 mg fast delivery
On the left aspect cardiovascular system function yahoo answers procardia 30 mg discount without a prescription, the spinalis muscle cardiovascular perfusionist education effective 30 mg procardia, the thinnest and most medial of the erector spinae columns, is displayed as a separate muscle by reflecting the longissimus and iliocostalis columns of the erector spinae. The thoracic and lumbar parts of the deep fascia represent the thoracolumbar fascia. The splenius muscular tissues arise from the midline and prolong superolaterally to the cervical vertebrae (splenius cervicis) and cranium (splenius capitis). The frequent Deep to the erector spinae is an obliquely disposed group of a lot shorter muscles, the transversospinalis muscle group consisting of the semispinalis, multifidus, and rotatores. The rotatores, or rotator muscle tissue, are the deepest of the three layers of transversospinal muscles and are greatest developed within the thoracic region. The elevators of the ribs symbolize the posterior intertransversarii muscular tissues of the neck. Details regarding the attachments, nerve provide, and actions of the minor muscles of the deep layer of intrinsic muscle tissue are offered in Table 4. Many of the muscles appearing on the cervical vertebrae are mentioned in larger detail in Chapter 8(Neck). The back muscular tissues are comparatively inactive within the stand-easy place, but they (especially the shorter deep layer of intrinsic muscles) act as static postural muscular tissues (fixators, or steadiers) of the vertebral column, maintaining pressure and stability as required for the erect posture. Exercise or elimination of excessive, unevenly distributed weight could also be required to restore stability. It was assumed that the higher concentration of spindles occurred because small muscles produce essentially the most exact actions, such as fine postural movements or manipulation and, therefore, require extra proprioceptive feedback. Muscles such as the rotatores, nonetheless, are so small and are placed in positions of such relatively poor mechanical advantage that their capacity to produce the movements described is somewhat questionable. Furthermore, such small muscle tissue are sometimes redundant to other larger muscular tissues that have superior mechanical advantage. Hence, it has been proposed (Buxton and Peck, 1989) that the smaller muscle tissue of small�large muscle pairs operate extra as "kinesiological monitors," or organs of proprioception and that the larger muscles are the producers of motion. The four small muscles of the suboccipital region lie deep (anterior) to the semispinalis capitis muscle tissue and consist of two rectus capitis posterior (major and minor) and two obliquus muscle tissue. The nerve emerges because the vertebral artery courses deeply between the occipital bone and the atlas (vertebra C1) throughout the suboccipital triangle. Note that the obliquus capitis inferior is the one "capitis" muscle that has no attachment to the cranium (skull). The furrow is continuous superiorly with the nuchal groove in the neck and is deepest within the decrease thoracic and higher lumbar regions. The median furrow ends in the flattened triangular space overlaying the sacrum and is replaced inferiorly by the intergluteal cleft. When the upper limbs are elevated, the scapulae move laterally on the thoracic wall, making the rhomboid and teres major muscular tissues visible. The principal muscles producing actions of the craniovertebral joints are summarized in Tables 4. Back sprain is an harm by which only ligamentous tissue, or the attachment of ligament to bone, is concerned, without dislocation or fracture. It results from excessively robust contractions associated to movements of the vertebral column, similar to excessive extension or rotation. Back strain is a typical injury in people who take part in sports activities; it results from overly robust muscular contraction. Under these situations, extended turning of the pinnacle, as occurs when backing up a motorcar, may cause light-headedness, dizziness, and different signs from the interference with the blood provide to the brainstem. Using the again as a lever when lifting puts an unlimited strain on the vertebral column and its ligaments and muscles. Strains may be minimized if the lifter crouches, holds the back as straight as potential, and makes use of the muscular tissues of the buttocks and lower limbs to assist with the lifting. � the deep intrinsic again muscular tissues connect components of the axial skeleton, are largely innervated by posterior rami of spinal nerves, and are organized in three layers: superficial (splenius muscles), intermediate (erector spinae), and deep (transversospinalis muscles). � the intrinsic muscular tissues provide primarily extension and proprioception for posture, and work synergistically with the muscles of the anterolateral belly wall to stabilize and produce actions of the trunk. The cervical enlargement extends from C4 through T1 segments of the spinal twine, and most of the anterior rami of the spinal nerves arising from it kind the brachial plexus of nerves that innervates the higher limbs. The lumbosacral enlargement extends from T11 via S1 segments of the spinal twine, inferior to which the twine continues to diminish because the conus medullaris. The anterior rami of the spinal nerves arising from this enlargement make up the lumbar and sacral plexuses of nerves that innervate the lower limbs. The portion of the spinal twine giving rise to the rootlets and roots that ultimately form one bilateral pair of spinal nerves is designated a spinal wire phase, the identification of which is similar as the spinal nerves arising from it. The more inferior spinal (T1 by way of Co1) nerves bear the identical alphanumeric designation because the vertebrae forming the superior margin of their exit (Table four. By the top of the embryonic interval (8th week), the tail-like caudal eminence has disappeared, and the variety of coccygeal vertebrae is lowered from six to four segments. During the fetal period, the vertebral column grows sooner than the spinal twine; in consequence, the wire "ascends" relative to the vertebral canal. The filum terminale is the vestigial remnant of the caudal a half of the spinal wire that was within the tail-like caudal eminence of the embryo. Its proximal end (the filum terminale internum, or pial a half of the terminal filum) consists of vestiges of neural tissue, connective tissue, and neuroglial tissue covered by pia mater. The spinal dura is separated from the periosteum-covered bone and the ligaments that form the walls of the vertebral canal by the epidural house. This house is occupied by the interior vertebral venous plexus embedded in a fatty matrix (epidural fat). The spinal dural sac has also been opened to reveal the spinal twine and posterior nerve roots, the termination of the spinal cord between the L1 and the L2 vertebral degree, and the termination of the spinal dural sac on the S2 segment. Three membranes (the spinal meninges) cowl the spinal twine: dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater. In a lumbar spinal puncture, the needle traverses the spinal dura and arachnoid simultaneously. The spinal cord is suspended within the dural sac by the filum terminale and the proper and left denticulate ligaments (L. The denticulate ligaments include a fibrous sheet of pia extending halfway between the posterior and anterior nerve roots from the lateral surfaces of the spinal twine. The spinal dura and arachnoid mater have been break up and pinned flat to expose the spinal cord and denticulate ligaments between posterior and anterior spinal nerve roots. The lateral projections indicate extensions of the subarachnoid house into the dural root sheaths across the spinal nerve roots. These arteries run longitudinally from the medulla of the brainstem to the conus medullaris of the spinal wire.