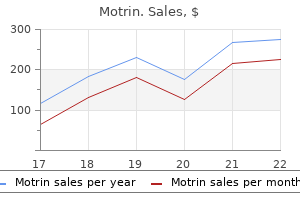
400 mg motrin cheap free shipping
The transverse (T) tubules invaginate cardiac muscle cells at the Z lines pain medication dogs can take motrin 400 mg generic with visa, are steady with the cell membranes neck pain treatment kerala motrin 400 mg generic with mastercard, and function to carry motion potentials to the cell interior. The T tubules type dyads with the sarcoplasmic reticulum, which is the positioning of storage and launch of Ca2+ for excitation-contraction coupling. Excitation-Contraction Coupling As in skeletal and easy muscle, excitation-contraction coupling in cardiac muscle interprets the action potential into the production of rigidity. The following steps are concerned in excitation-contraction coupling in cardiac muscle. A longer cycle size signifies a slower coronary heart rate, and a shorter cycle size signifies a sooner heart fee. Changes in heart rate (and cycle length) change the period of the action potential and, in consequence, change the durations of the refractory intervals and excitability. For example, if coronary heart rate will increase (and cycle length 4-Cardiovascular Physiology � a hundred forty five Cardiac action potential size of the inward Ca2+ present in the course of the plateau of the action potential. Ca2+ release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum causes the intracellular Ca2+ focus to enhance even additional. Ca2+ now binds to troponin C, tropomyosin is moved out of the method in which, and the interplay of actin and myosin can occur. Actin and myosin bind, cross-bridges form after which break, the thin and thick filaments transfer past one another, and pressure is produced. A critically essential concept is that the magnitude of the stress developed by myocardial cells is proportional to the intracellular Ca2+ concentration. As a results of these transport processes, the intracellular Ca2+ concentration falls to resting ranges, Ca2+ dissociates from troponin C, actin-myosin interplay is blocked, and rest occurs. Contractility Contractility, or inotropism, is the intrinsic capacity of myocardial cells to develop drive at a given muscle cell length. Agents that produce an increase in contractility are mentioned to have optimistic inotropic results. Positive inotropic agents increase each the rate of tension improvement and the height rigidity. Agents that produce a lower in contractility are said to have negative inotropic effects. Negative inotropic agents decrease each the speed of rigidity development and the peak tension. The cardiac motion potential is initiated in the myocardial cell membrane, and the depolarization spreads to the interior of the cell through the T tubules. Entry of Ca2+ into the myocardial cell produces an increase in intracellular Ca2+ concentration. This process known as Ca2+-induced Ca2+ release, and the Ca2+ that enters in the course of the plateau of the motion potential is called the trigger Ca2+. Two factors determine how much Ca2+ is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum on this step: the quantity of Ca2+ beforehand stored and the Contractility correlates directly with the intracellular Ca2+ focus, which in turn depends on the quantity of Ca2+ launched from sarcoplasmic reticulum stores during excitation-contraction coupling. The 146 � Physiology amount of Ca2+ launched from the sarcoplasmic reticulum depends on two factors: the dimensions of the inward Ca2+ present in the course of the plateau of the myocardial motion potential (the size of the trigger Ca2+) and the amount of Ca2+ previously stored in the sarcoplasmic reticulum for launch. Therefore the bigger the inward Ca2+ present and the bigger the intracellular shops, the higher the rise in intracellular Ca2+ focus and the greater the contractility. Effects of the Autonomic Nervous System on Contractility the results of the autonomic nervous system on contractility are summarized in Table four. Of these results, an important is the optimistic inotropic effect of the sympathetic nervous system. Stimulation of the sympathetic nervous system and circulating catecholamines have a optimistic inotropic effect on the myocardium. This positive inotropic effect has three important features: increased peak rigidity, increased price of rigidity development, and sooner fee of rest. Faster relaxation signifies that the contraction (twitch) is shorter, allowing more time for refilling. This impact, just like the sympathetic effect on heart rate, is mediated via activation of 1 receptors, which are coupled by way of a Gs protein to adenylyl cyclase. Two completely different proteins are phosphorylated to produce the rise in contractility. The coordinated actions of these phosphorylated proteins then produce a rise in intracellular Ca2+ focus. Increased Ca2+ uptake by the sarcoplasmic reticulum has two effects: It causes sooner relaxation. Because the G protein on this case is inhibitory, contractility is decreased (opposite of the impact of activation of 1 receptors by catecholamines). Two components are answerable for the decrease in atrial contractility brought on by parasympathetic stimulation. Together, these two effects lower the quantity of Ca2+ entering atrial cells during the motion potential, decrease the trigger Ca2+, and decrease the quantity of Ca2+ released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Effect of Heart Rate on Contractility Perhaps surprisingly, modifications in heart price produce changes in contractility: When the guts rate will increase, contractility increases; when the guts rate decreases, contractility decreases. The mechanism can be understood by recalling that contractility correlates instantly with intracellular Ca2+ concentration during excitationcontraction coupling. For example, an increase in coronary heart fee produces an increase in contractility, which could be explained as follows: (1) When coronary heart price will increase, there are extra action potentials per unit time and a rise within the complete quantity of set off Ca2+ that enters the cell through the plateau phases of the motion potentials. Furthermore, if the increase in heart rate is brought on by sympathetic stimulation or by catecholamines, then the size of the inward Ca2+ present with every motion potential also is increased. When coronary heart fee doubles, for example, the tension developed on each beat increases in a stepwise style to a maximal value. This enhance in rigidity occurs as a outcome of there are extra motion potentials per unit time, more whole Ca2+ entering the cell in the course of the plateau phases, and extra Ca2+ for accumulation by the sarcoplasmic reticulum. The frequency of the bars shows the heart fee, and the height of the bars exhibits the tension produced on each beat. Notice that the very first beat after the increase in heart price shows no enhance in tension because further Ca2+ has not but accrued. On subsequent beats, the effect of the extra accumulation of Ca2+ by the sarcoplasmic reticulum turns into evident. Tension rises stepwise, like a staircase: With each beat, extra Ca2+ is amassed by the sarcoplasmic reticulum, till a maximum storage degree is achieved. Although the tension developed on the extrasystolic beat itself is lower than regular, the very next beat exhibits increased tension. An unexpected or "additional" amount of Ca2+ entered the cell in the course of the extrasystole and was amassed by the sarcoplasmic reticulum. The increase in intracellular Na+ focus alters the Na+ gradient across the myocardial cell membrane, thereby altering the operate of a Ca2+-Na+ exchanger. This exchanger pumps Ca2+ out of the cell towards an electrochemical gradient in exchange for Na+ transferring into the cell down an electrochemical gradient. When the intracellular Na+ focus increases, the inwardly directed Na+ gradient decreases. As a result, Ca2+-Na+ exchange decreases as a result of it is determined by the Na+ gradient for its power source.
Syndromes
- 13 calories per pound of desirable body weight if your activity level is low, or if you are over age 55
- Endoscopy -- camera down the throat to see burns in the esophagus and the stomach
- Growth of the penis, scrotum (with reddening and folding of the skin), and testes
- Fluids through a vein (IV)
- Do you have pain somewhere else, like your lower back or thigh?
- You may need to spend 1 or 2 days in bed if the surgery involves the large artery in your belly called the aorta.
- Nausea
- Live with or care for a child 6 months old or younger
- Chest pain
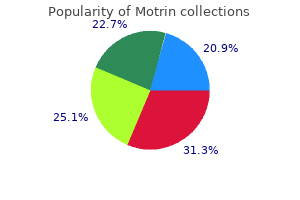
600 mg motrin order with amex
Cell floor molecules appear important in establishing correct mobile groupings in the hindbrain pain treatment for bulging disc motrin 600 mg discount fast delivery. In explicit georgia pain treatment center 400 mg motrin overnight delivery, variations in adhesive properties and boundary restrictions have been found in the cells of even- versus odd-numbered rhombomeres. For instance, a series of experiments by Andrew Lumsden and colleagues revealed that cells from even- or odd-numbered rhombomeres preferentially adhere to cells from other even- or odd-numbered rhombomeres, respectively. In one in vitro study, dissociated cells from odd-numbered rhombomeres reaggregated with cells from the same rhombomere or those from one other odd-numbered rhombomere, however not with cells from even-numbered rhombomeres. Similarly, cells of even-numbered rhombomeres preferentially reaggregated with cells from other even-numbered rhombomeres. Moreover, grafting research in chick embryos confirmed that boundaries are normally established between adjacent rhombomeres. The donor segments were then grafted into the region of lacking segments of the host embryo and allowed to develop for another 1. Some of the signals liable for establishing and maintaining hindbrain segments have been recognized Scientists subsequently decided that the migration of cells between even- and odd-numbered rhombomeres is inhibited by proteins of the Eph household of tyrosine kinase receptors (Ephs) and their associated cell floor ligands (ephrins). The receptors and ligands are sometimes present in alternating patterns alongside the hindbrain. Evidence that some of these receptor�ligand pairs play a job in rhomobmere patterning comes from research of r2�r6. One or more of the corresponding ligands (ephrin A2, ephrin B1, and ephrin B3) are extremely expressed in r2, r4, and r6. The interaction of membrane-bound ephrin ligands with their corresponding Eph receptors results in bidirectional signaling. In this group of rhombomeres (r2�r6), the Eph/ephrin signaling is repulsive, thus offering a mechanism to stop the blending of cells between adjacent rhombomeres. Other research revealed mechanisms by which EphA4 receptor expression is regulated in r4. An ephrin A ligand binds to an EphA receptor to initiate tyrosine phosphorylation (P) and forward signaling in an adjacent cell. The EphA receptor additionally initiates signal transduction and reverse signaling by way of the membrane-attached ephrin A ligand. The ephrin A ligand interacts with co-receptors (not shown) to provoke sign transduction in the ligand-bearing cell. The resulting bidirectional signaling limits migration between adjoining rhombomeres. The transcription issue Krox 20 can be current in r3 and r5 and regulates expression of those Eph receptors. The neural structures associated with r3 and r5 are additionally lost and the growth of axons from cranial nerve neurons originating within the r2, r4, and r6- these associated with the trigeminal, facial, and glossopharyngeal nerves, respectively-are rerouted inside the shortened hindbrain construction. Another transcription issue important in hindbrain improvement was recognized within the Kreisler mouse, a strain of mice carrying a Kreisler 1 (Krml1/MafB) gene mutation. Kreisler is a member of the Maf (musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma) transcription factor family, a big group of transcription factors named for the origin of the first identified member. The lack of r5 and r6 ends in several abnormalities of the related hindbrain buildings, together with lack of the abducens and glossopharyngeal cranial nerves and malformations of the inside ear that normally develops adjacent to r5. Both Krox20 and Kreisler/MafB transcription components also regulate expression of other genes required for regular rhombomere growth (for example, Hox genes, that are mentioned below). Thus, the expression patterns of a quantity of completely different molecules interact to establish and keep the rhombomere boundaries that function a first step in establishing future anatomical and mobile specializations of the nervous system. In reality, many of the genes that regulate physique segmentation along the A/P axis of bugs are extremely conserved across species and are utilized in hindbrain patterning. Understanding how such genes are organized and controlled within the fruit fly Drosophila offers insight into how segmentation genes operate within the vertebrate hindbrain. The physique plan of Drosophila is an effective model for studying the roles specific genes play in segmentation the fruit fly has confirmed an exceptionally helpful mannequin for investigating genes that regulate segmentation of each the primary body axis and the nervous system. Scientists use X-ray or chemical exposure to mutate single genes and observe how those genes impression normal development. Some of those mutations give rise to altered body plans, similar to flies with missing or misplaced physique parts or, in extreme instances, our bodies with no observable body segmentation. For instance, beneath regular conditions the top section provides rise to antennae, whereas the thoracic segments give rise to legs and wings. As scientific techniques superior, investigators were in a place to identify lots of the genes that triggered the noticed developmental modifications on this physique plan organization. These genes are arranged so as from the 3 end to the 5 finish of the chromosome so that anterior segments develop in response to the genes expressed closer to the three end, while progressively more posterior areas develop in response to the genes expressed nearer to the 5 end. This is identified as the principal of co-linearity, the place the relative place of a gene along the chromosome corresponds to the relative position along the A/P axis. The Hox genes are present in 4 clusters (A�D) on 4 completely different chromosomes (chromosomes 6, eleven, 15, and 2). Similar to Drosophila, the relative place of a Hox gene from the three to 5 end of the cluster corresponds to the relative position alongside the A/P physique axis. Segmentation genes include those of the hole, pair-rule, and phase polarity dn 3. Each class of genes works in sequence to divide the physique into smaller and smaller segments along the A/P axis. The gap genes are the primary class to be lively and set up the larger boundaries of the top, thorax, and stomach. Many of those genes, together with caudal, hunchback, Kr�ppel, and orthodenticle, contribute to a quantity of aspects of neural improvement. Combinations of gap genes then control the expression of the pair-rule genes that divide the three segments into smaller models. Segment polarity genes also play essential roles in establishing traits of the cells which would possibly be restricted to a given phase. Similar to the hole genes, the pair-rule and phase polarity genes play further roles at different phases of neural improvement. Mammalian homologs of some of the widespread segmentation genes necessary in neural improvement are listed in Table 3. The prefix "homeo" refers to similarity or sameness; mutations in homeotic genes brought on one phase of the fruit fly body to turn out to be much like another. The outstanding conservation throughout species is highlighted in research by which experimental substitution of a mouse Hox Table three. The antennepedia advanced includes the labial, proboscipedia, Deformed, Sex combs decreased, and Anntennepedia genes. The bithorax complex consists of the Ultrabithorax, Abdominal A, and Abdominal B genes.
Discount motrin 400 mg with mastercard
Pay by the rules: keep away from Medicare audits and scale back fee denials with a sound technique and correct documentation pain treatment sickle cell purchase motrin 400 mg with mastercard. What components of the Patient/Client Management Model ought to be documented in the medical document A bodily therapist assistant sees a affected person in an acute care setting very first thing within the morning sports spine pain treatment center hartsdale ny motrin 400 mg buy overnight delivery. How would possibly an entry be written in order that it communicates that the care the affected person obtained is "skilled" When is it acceptable to create your individual abbreviations or symbols for use in a medical report What documentation format can be acceptable to document cancellations or missed appointments Give an instance of a medical report entry that includes a planned intervention and a rationale. For the following entries, indicate examples which may be inappropriate by writing an "I" next to the item. Write the next info in a more clear and concise manner, as it will appear within the medical record. The patient walked seventy five toes in the hallway of the hospital with the therapist lightly touching her again. The therapist was wanted to help present the affected person with assist to preserve stability. The patient demonstrated the following range of motion measurements: lively range of motion for the right elbow was 130� flexion and 10� of hyperextension. Chapter 6 the patient propelled his wheelchair around the hospital, exterior on the sidewalk, and up and down a quantity of ramps with you offering verbal reminders on trunk positioning for going up and down the ramps. The patient was capable of put her ankle-foot orthosis on and take away it independently. She was also in a position to independently examine her skin for any irritated areas after she eliminated the orthosis. You instructed the affected person to carry out 10 repetitions of each train as part of her residence exercise program. The workouts included ankle pumps, quadriceps setting, short arc quadriceps strengthening from 45� to 0�, and heel slides. During a busy morning in a hospital, you have been working with a affected person who told you that she was going to be discharged and wished house health providers, primarily physical remedy. Indicate whether the knowledge would fall into the S, O, A, or P portion of the observe. Jones comes into the clinic right now and tells you that his fingers grew to become swollen and that he has had ache at a degree of 7 out of 10 since the final remedy session. He goes on to say that he has not been able to carry out any of the vary of movement workout routines you gave him because of the unbelievable quantity of ache he has been having. He stated that he has modified his postoperative dressing once a day for the reason that last visit, and he has had slightly little bit of purple drainage on the bandages. She goes on to say that she has carried out the vary of motion exercises twice already this morning, and she or he is working on making an attempt to get her knee to bend as a lot as she shall be ready to. While strolling utilizing a normal walker, she asks if she will be ready to begin utilizing a cane soon. Smith comes into the physical therapy division and tells you that he notices enchancment in his walking since starting the energetic vary of movement exercises for his ankle. He goes on to tell you that he nonetheless has ache when strolling on gravel, carpet, and stairs. His job requires him to do lots of strolling on uneven terrain, and he desires to have the power to do that without pain earlier than returning to work. The supervising physical therapist informed you that the affected person is demonstrating confusion and slurred speech, however her daughter is usually current during the periods. She also tells you that she is afraid to get off the bed because of her fear of falling once more. He also says that he has hassle performing the range of motion workouts that you just showed him over the last session. The patient tells you that, due to the ache, she seems like her hip is going to give out when she stands on it. The affected person went up and down four stairs with a handrail that was on the right facet going up and on the left coming down; the affected person used a straight cane. The patient walked with the therapist at his side (but not touching him) for a hundred feet, twice; very important signs earlier than train have been blood strain 125/85, 15 for respirations, and 77 for heart fee; vitals after were 135/85 for blood pressure, 17 for respirations, and 87 for heart price; the affected person carried out ankle pumping, elbow flexion, shoulder flexion, and knee extension for 10 repetitions before and after exercise. The patient walks independently with crutches, weightbearing as much as he can tolerate on the involved extremity for a hundred toes. List the kinds of information that can be present in each component of an preliminary evaluation note. List the questions that the bodily therapist assistant should ask when reviewing the evaluation notice to guide decision associated to provision of chosen interventions. Locate and use data in the initial analysis notice to decide which interventions are to be offered and how these interventions must be performed. Sarah approached the outpatient physical therapy clinic with a sense of pleasure and an air of expectation. This could be her first day of affected person care as a licensed physical therapist assistant. She knew that she had an necessary position to play in her new place, and now she no longer had a medical teacher or her school lecturers serving to her to make choices. As John began to focus on with Sarah the affected person care activities that he was directing her to perform that day, her questions continued to bother her. Sarah was assured as she began her day of patient care because she had a clear understanding of the bodily therapy process and her function in it. Based on this understanding, Sarah knew what was anticipated of her, and he or she knew what to count on from John, her supervising bodily therapist. Even although the affected person may need had several physical therapy periods, it is going to be important so that you simply can review the initial evaluation notice to gain a clear picture of the plan of care established by the bodily therapist. Once you be taught the questions that you want to ask when reviewing an evaluation observe, you must be capable of find the knowledge that you simply need, whatever the documentation format used. In this chapter, we take a extra in-depth have a look at the bodily therapist preliminary evaluation observe. We then discuss the way you, as a physical therapist assistant, will use the initial note to decide how to proceed with offering chosen interventions as directed by the physical therapist. As noted in Chapters 2 and 6, documentation of bodily therapist providers ought to occur throughout the episode of care. The only type of notice that may not be present in a patient document is a re-evaluation. A re-evaluation will not be required when a affected person progresses in a smooth and uninterrupted fashion within a quick while body.
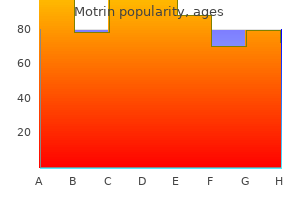
Buy discount motrin 400 mg online
This will also provide you with a clear expectation of how quickly the physical therapist expects the patient to progress pain treatment center colorado springs cheap motrin 600 mg visa. Goals established by the physical therapist are listed within the evaluation section of the observe with clearly detailed expected timelines for reaching the goals treatment pain right upper arm discount 600 mg motrin. As famous previously, you want to just remember to establish the functional objectives or the connection between impairment targets and functional actions to be sure that you make sound decisions associated to the implementation of interventions. The bodily therapy prognosis is often an announcement that relates impairments to function (eg, decreased left lower-extremity energy leading to limitations in self-care activities). The physical therapy prognosis will, at occasions, be present in the issue section as nicely, but it ought to at all times be discovered inside the assessment element of the observe. The prognosis must be discovered as a direct assertion throughout the assessment part of the notice. The prognosis will also be communicated by the objectives and time frame by which the objectives are to be met. This info will give you a common thought of what to expect from the patient. Further info provided within the the rest of the observe helped Sarah to fill in the details in order that she had a clearer picture of what to anticipate of S. Questions 7 and eight: "Are there any contraindications or precautions that I must bear in mind as I work with this 67 affected person Often, these shall be directed by the physician, particularly when related to restoration after a surgical process. When a contraindication is directed by the physician, it regularly is discovered within the problem element of the observe. Additional precautions and contraindications might be found inside the assessment or plan sections of the notice. For instance, you could be asked to present transfer coaching for a patient who has left-side weakness because of a current stroke. The chart indicates that the affected person has beforehand had a right transtibial amputation. At different instances, pain scores are utilized to determine what the intensity of the intervention must be. The type of data wanted depends upon the particular interventions being offered, the rationale for the intervention, the goals, and the time frame in which goals are anticipated to be achieved. Frequently, sufferers share necessary information days and even weeks after the preliminary analysis that they forgot about on the time. This might assist to explain discrepancies in power positive aspects between the legs if any are observed in future periods. As you evaluate the evaluation observe, you should determine whether or not the patient has a history of a cardiovascular condition or is taking any medicines that can alter regular cardiovascular responses. Some interventions are directed towards ache management, and Interpreting the Physical Therapist Initial Evaluation When you review the objective information, you need to image in your mind how the affected person will look and act. This will permit you to anticipate appropriate responses to therapeutic intervention and can assist you to to establish inappropriate responses. As you learn the assessment portion of the note, you might be able to mentally outline how the affected person should progress. This will guide you within the day-to-day decisions about what needs to occur with the affected person. A evaluate of the plan section will tell you the anticipated duration of the episode of care. For instance, you know that the affected person had laboratory work carried out earlier in the day. It is imperative that you ask clarifying questions prior to initiating care to ensure the safety of the affected person and to enhance the effectiveness of care. In addition to offering information that helps the physical therapist assistant to proceed with patient care, the analysis notice offers a clue as to what the interim note should include. Using the case examples offered in Examples 7-6 via 7-8, practice reviewing preliminary evaluation notes to put together for a treatment session. What are the targets set by the physical therapist and patient concerning recognized problems Are there any contraindications or precautions that I must remember as I work with this affected person Are there any other special issues that I have to remember as I work with this affected person What checks do I need to carry out prior to initiating interventions to be sure that the affected person is protected and capable of take part within the chosen intervention(s) Interpreting the Physical Therapist Initial Evaluation seventy one Anytown Community Hospital: Skilled Nursing Facility Physical Therapy Evaluation Patient: J. Gross vary of movement left decrease extremity restricted because of orthopedic precautions; different extremities and trunk unimpaired. Tests and Measures and Observation Strength: 4/5 to 4+/5 throughout bilateral higher extremities and right lower extremity. Supine to/from sit with moderate help of 1, Sit to/from stand with minimal help of 1. Intervention: Initiated mattress mobility coaching, transfer training, and gait coaching utilizing front wheeled walker; active assistive vary of motion to left lower extremity, together with ankle pumps, quad units, ham sets, glut sets, short arc quads, straight leg elevate, hip abduction, and heel slides 2 x 10. Does not know hip precautions for useful duties Short-Term Goals: To be met inside 2 days 1. Increase left lower-extremity energy to 3/5 throughout hip and 4-/5 knee to be succesful of meet the above practical objectives. Increase left lower-extremity power to 3+/5 all through hip and 4/5 knee to have the ability to meet the above useful objectives. She had been experiencing feelings of fatigue and weakness the night before and had gone to bed early. Her husband owns his personal enterprise as an electrician and can have the ability to reduce his "hours of labor" to assist her if wanted. She would like to return to as many of her earlier activities as attainable but voices she understands she might need to use a cane, walker, or wheelchair to get round. She is most concerned about with the power to care for her home together with doing dishes, laundry, and general home cleansing tasks. Gross strength impaired all through trunk and bilateral upper extremities and decrease extremities proper greater than left. Neuromuscular System: Balance and motor management impaired all through trunk and all 4 extremities. Left higher and lower extremities demonstrate diminished coordination with all activities. Due to the severe deficits, prognosis for vital restoration is poor; however, pt. A trial of structured aggressive remedy is indicated to see how much useful return is feasible for this pt. Fair static and fair- dynamic sitting steadiness to permit for slideboard switch objective.
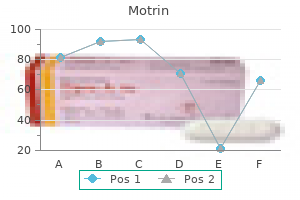
Motrin 600 mg purchase amex
Thereafter pain treatment lupus buy motrin 600 mg low cost, the strain decreases as blood flows by way of the pulmonary arteries regional pain treatment center whittier 400 mg motrin cheap overnight delivery, arterioles, capillaries, venules, and veins and again to the left atrium. An necessary implication of these decrease pressures on the pulmonary side is that pulmonary vascular resistance is far decrease than systemic vascular resistance. This conclusion can be reached by recalling that the entire circulate via the systemic and pulmonary circulations should be equal. Because pressures on the pulmonary aspect are much decrease than pressures on the systemic aspect, to achieve the same circulate, pulmonary resistance should be decrease than systemic resistance (Q = P/R). To function a pump, the ventricles should be electrically activated after which contract. The heart consists of two sorts of muscle cells: contractile cells and conducting cells. Contractile cells constitute the overwhelming majority of atrial and ventricular tissues and are the working cells of the guts. Action potentials in contractile cells result in contraction and era of force or strain. Another characteristic of the specialized conducting tissues is their capacity 132 � Physiology to generate action potentials spontaneously. The motion potential spreads throughout the myocardium within the following sequence: 1. The motion potential is first conducted to the bundle of His via the common bundle. It then invades the left and right bundle branches after which the smaller bundles of the Purkinje system. Conduction through the His-Purkinje system is extremely fast, and it rapidly distributes the motion potential to the ventricles. The motion potential also spreads from one ventricular muscle cell to the subsequent, by way of low-resistance pathways between the cells. Rapid conduction of the action potential throughout the ventricles is essential and permits for efficient contraction and ejection of blood. The cardiac motion potential is initiated in the sinoatrial node and spreads throughout the myocardium, as shown by the arrows. It signifies that the pattern and timing of the electrical activation of the heart are regular. Concepts Associated With Cardiac Action Potentials the cell, which is called an inward current. The permeant ion then will move into or out of the cell in an attempt to reestablish electrochemical equilibrium, and this present move will alter the membrane potential. For instance, contemplate the impact of decreasing the extracellular K+ concentration on the resting membrane potential of a myocardial cell. The K+ equilibrium potential, calculated by the Nernst equation, will turn into extra unfavorable. K+ ions will then move out of the cell and down the now larger electrochemical gradient, driving the resting membrane potential toward the new, extra negative K+ equilibrium potential. For instance, the resting permeability of ventricular cells to Na+ is sort of low, and Na+ contributes minimally to the resting membrane potential. However, through the upstroke of the ventricular action potential, Na+ conductance dramatically increases, Na+ flows into the cell down its electrochemical gradient, and the membrane potential is briefly pushed toward the Na+ equilibrium potential. At threshold potential, the depolarization turns into selfsustained and gives rise to the upstroke of the motion potential. Action Potentials of Ventricles, Atria, and the Purkinje System the concepts applied to cardiac motion potentials are the identical concepts which are applied to motion potentials in nerve, skeletal muscle, and clean muscle. The following part is a abstract of these rules, that are mentioned in Chapter 1: 1. The membrane potential of cardiac cells is decided by the relative conductances (or permeabilities) to ions and the focus gradients for the permeant ions. If the cell membrane has a high conductance or permeability to an ion, that ion will flow down its electrochemical gradient and attempt to drive the membrane potential toward its equilibrium potential (calculated by the Nernst equation). If the cell membrane has low conductance or permeability to an ion or is impermeable to the ion, that ion will make little or no contribution to the membrane potential. By conference, membrane potential is expressed in millivolts (mV), and intracellular potential is expressed relative to extracellular potential; for instance, a membrane potential of -85 mV means eighty five mV, cell interior adverse. The resting membrane potential of cardiac cells is set primarily by potassium ions (K+). The conductance to K+ at relaxation is excessive, and the resting membrane potential is near the K+ equilibrium potential. Since the conductance to sodium (Na+) at rest is low, Na+ contributes little to the resting membrane potential. Changes in membrane potential are brought on by the flow of ions into or out of the cell. The action potential in these tissues shares the next characteristics (Table 4. Action potential length varies from 150 ms in atria, to 250 ms in ventricles, to 300 ms in Purkinje fibers. These durations could be compared with the brief period of the action potential in nerve and skeletal muscle (1�2 ms). Recall that the period of the motion potential also determines the duration of the refractory durations: the longer the action potential, the longer the cell is refractory to firing one other action potential. The cells of the atria, ventricles, and Purkinje system exhibit a secure, or constant, resting membrane potential. The action potential in cells of the atria, ventricles, and Purkinje system is characterised by a plateau. The plateau is a sustained period of depolarization, which accounts for the long length of the action potential and, consequently, the lengthy refractory periods. An motion potential in a Purkinje fiber (not shown) would look just like that in the ventricular fiber, but its length could be barely longer. In ventricular, atrial, and Purkinje fibers, the motion potential begins with a phase of fast depolarization, called the upstroke. As in nerve and skeletal muscle, the upstroke is attributable to a transient improve in Na+ conductance (gNa), produced by depolarization-induced opening of activation gates on the Na+ channels. At the peak of the upstroke, the membrane potential is depolarized to a price of about +20 mV. Thus dV/dThis greatest (the fee of rise of the upstroke is fastest) when the resting membrane potential is most unfavorable, or hyperpolarized. This correlation is based on the relationship between membrane potential and the place of the inactivation gates on the Na+ channel (see Chapter 1). Phase 1 in ventricular, atrial, and Purkinje fibers is a quick interval of repolarization, which immediately follows the upstroke.
East India Root (Alpinia). Motrin.
- Are there safety concerns?
- How does Alpinia work?
- Dosing considerations for Alpinia.
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- Intestinal gas, infections, spasms, fever, reducing swelling (inflammation), and other conditions.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96299
600 mg motrin buy with mastercard
First-order neurons synapse on second-order neurons in relay nuclei allied pain treatment center new castle pa 400 mg motrin generic with amex, which are positioned in the spinal twine or within the brain stem pain treatment center hattiesburg ms motrin 600 mg overnight delivery. Usually, many first-order neurons synapse on a single second-order neuron inside the relay nucleus. These interneurons course of and modify the sensory data obtained from the first-order neurons. Axons of the second-order neurons go away the relay nucleus and ascend to the following relay, located within the thalamus, the place they synapse on third-order neurons. En path to the thalamus, the axons of those second-order neurons cross on the midline. The relay nuclei course of the knowledge they receive via native interneurons, which can be excitatory or inhibitory. Fourthorder neurons reside within the applicable sensory area of the cerebral cortex. As noted, there are secondary and tertiary areas, as properly as association areas within the cortex, all of which combine complicated sensory info. Sensory Receptors Consider again the first step within the sensory pathway by which an environmental stimulus is transduced into an electrical sign in the sensory receptor. This part discusses the various kinds of sensory receptors, mechanisms of sensory transduction, receptive fields of sensory neurons, sensory coding, and adaptation of sensory receptors. Types of Receptors Receptors are categorized by the sort of stimulus that prompts them. The 5 forms of receptors are mechanoreceptors, photoreceptors, chemoreceptors, thermoreceptors, and nociceptors. Chemoreceptors are activated by chemical substances and are involved in olfaction, taste, and detection of oxygen and carbon dioxide within the management of breathing. Nociceptors are activated by extremes of stress, temperature, or noxious chemicals. Sensory Transduction and Receptor Potentials Sensory transduction is the method by which an environmental stimulus. The conversion typically involves opening or closing of ion channels in the receptor membrane, which ends up in a move of ions (current flow) across the membrane. Current move then results in a change in membrane potential, referred to as a receptor potential, which will increase or decreases the probability that motion potentials will occur. The following collection of steps happens when a stimulus activates a sensory receptor: 1. The environmental stimulus interacts with the sensory receptor and causes a change in its properties. Photons of light are absorbed by pigments in photoreceptors on the retina, inflicting photoisomerization of rhodopsin (a chemical in the photoreceptor membrane). Chemical stimulants react with chemoreceptors, which activate Gs proteins and adenylyl cyclase. These adjustments cause ion channels in the sensory receptor membrane to open or close, which ends up in a change in current circulate. The resulting change in membrane potential, either depolarization or hyperpolarization, is known as the receptor potential or generator potential. Receptor potentials are graded electronic potentials, whose amplitude correlates with the dimensions of the stimulus. Because receptor potentials are graded in amplitude, a small depolarizing receptor potential still may be subthreshold and therefore inadequate to produce an motion potential. However, a bigger stimulus will produce a larger depolarizing receptor potential, and if it reaches or exceeds threshold, action potentials will occur. If the receptor potential is hyperpolarizing (not illustrated), it moves the membrane potential away from the edge potential, all the time lowering the likelihood that action potentials will occur. Receptive Fields A receptive subject defines an space of the physique that when stimulated results in a change in firing rate of a sensory neuron. Receptor potentials may be either depolarizing (shown) or hyperpolarizing (not shown). B, If a depolarizing receptor potential brings the membrane potential to threshold, then an motion potential happens within the sensory receptor. There are receptive fields for first-, second-, third-, and fourth-order sensory neurons. For instance, the receptive area of a second-order neuron is the world of receptors in the periphery that causes a change within the firing fee of that second-order neuron. The smaller the receptive subject, the extra exactly the feeling could be localized or identified. Thus first-order sensory neurons have the simplest receptive fields, and fourth-order sensory neurons have the most complex receptive fields. The receptive area on the pores and skin for this particular neuron has a central region of excitation, bounded on both aspect by regions of inhibition. All of the incoming data is processed in relay nuclei of the spinal cord or mind stem. The areas of inhibition contribute to a phenomenon referred to as lateral inhibition and assist in the exact localization of the stimulus by defining its boundaries and offering a contrasting border. For example, in seeing a red ball, its measurement, location, colour, and depth all are encoded. The features that can be encoded embody sensory modality, spatial location, frequency, intensity, threshold, and length of stimulus. Stimulus modality is often encoded by labeled strains, which consist of pathways of sensory neurons devoted to that modality. Thus the pathway of neurons dedicated to imaginative and prescient begins with photoreceptors within the retina. Stimulus location is encoded by the receptive area of sensory neurons and may be enhanced by lateral inhibition as previously described. If a stimulus is massive sufficient to produce a depolarizing receptor potential that reaches threshold, it will be detected. Thus large stimuli will activate extra receptors and produce bigger responses than will small stimuli. Thus a light-weight contact of the pores and skin may activate solely mechanoreceptors, whereas an intense damaging stimulus to the pores and skin may activate mechanoreceptors and nociceptors. The intense stimulus can be detected not solely as stronger but in addition as a different modality. Stimulus info also is encoded in neural maps shaped by arrays of neurons receiving information from completely different places on the physique. Some of these codes are based mostly on imply discharge frequency, others are based mostly on the period of firing, whereas others are based on a temporal firing pattern. The frequency of the stimulus could also be encoded directly within the intervals between discharges of sensory neurons (called interspike intervals). However, during a pro- longed stimulus, receptors "adapt" to the stimulus and change their firing charges.
400 mg motrin purchase amex
The ensuing phenotype of an expanded head and mind seen in the Dkk-treated embryos led to the name of the gene pain tongue treatment motrin 400 mg discount otc. Similarly pain treatment center hartford hospital motrin 600 mg overnight delivery, mice missing the Dkk1 gene developed with a truncated head and lowered brain size. Thus, multiple alerts are current within the creating forebrain areas to limit the exercise of midbrain-associated Wnt. Other indicators necessary for limiting Wnt activity in anterior areas of the neural tube embody members of the Six household of homeodomain transcription components which are expressed in the creating forebrain. The restricted expression domains of the Six and Irx members of the family are maintained as a end result of these two proteins suppress each other. Thus, coordinated expression of Wnt and Irx are wanted to pattern posterior diencephalon areas and delineate them from more anterior Six3-expressing areas of the forebrain. The mesencephalon varieties a border with the metencephalon, the region that gives rise to the pons and cerebellum. The IsO produces multiple molecules that pattern the midbrain and anterior hindbrain areas, as properly as alerts that forestall the unfold of other indicators originating within the forebrain or posterior hindbrain. Signaling facilities intrinsic to the mesencephalon and metencephalon regions have been recognized utilizing a number of experimental approaches. For instance, in the late 1980s, transplantation research using quail and chick embryos revealed the presence of cues intrinsic to the mesencephalon and metencephalon. When quail mesencephalon or metencephalon was grafted to corresponding regions of chick embryo, the chick embryos developed the right midbrain or hindbrain structures, respectively. These outcomes indicated that indicators were current in the donor tissue to induce formation of those mind regions. The mesencephalon also produced signals needed to form the cerebellum, in addition to indicators that induced adjacent midbrain tissue. Transplantation studies by which tissue from quail is grafted into chick embryos at comparable phases of growth reveal intrinsic signaling facilities within the midbrain. When considered from the dorsal surface, the model new constructions have been noticed to kind in an opposite, or mirror picture, orientation (top panel) in comparison with the traditional cerebellar/midbrain area (bottom panel). Similar to what was described in forebrain areas, a few of these signals act primarily to keep gene expression patterns, while others repress the exercise of molecules in adjacent structures. Many of the genes for these signals are set up throughout gastrulation or early neural plate phases. In mice missing Otx genes, the areas anterior to the isthmus that usually categorical Otx are respecified and tackle extra posterior-like traits. Similarly, if Gbx is missing, midbrain areas extend extra posteriorly resulting in midbrain-like characteristics in regions posterior to the isthmus. Thus, with the loss of either gene, the adjacent area is ready to dominate and broaden to re-pattern neighboring areas of the neural tube. Later in improvement, extra indicators are employed to limit Otx and Gbx to regions anterior and posterior to the isthmus, respectively. These signals affect the expression of genes that additional sample these areas. Double asterisks point out ectopic regions which might be anterior to these marked by a single asterisk. Tel, telencephalon; Cb, cerebellum; Mb, midbrain; Tc, tectum; Di, diencephalon; Is, Isthmus; ic, isthmic constriction; mes, mesencephalon; v4, fourth ventricle. It has also been proposed that the different effects of these two isoforms outcome from variations in receptor binding energy. Experiments in zebrafish revealed that when this pathway was inhibited, the expression of gbx2 was repressed within the metencephalon whereas otx2 expression was induced in its place. Ligand binding causes the receptor subunits to dimerize and cross-phosphorylate one another. As detailed beneath, Hox genes are necessary for the formation of the extra posterior rhombomere segments of the hindbrain. The suppression of Hox genes in rhombomere 1 (r1) permits the formation of cerebellar tissues from this segment, rather than rhombomere-like structures that might arise following the activation of Hox genes. Wnt also plays a vital position in midbrain and cerebellar improvement, as is demonstrated by the absence of midbrain and cerebellar areas in mice missing Wnt. Loss of any one of these molecules not only causes defects, but also impacts the expression of the other two alerts. For instance, in mice missing the transcription factors En1 and En2, the midbrain and cerebellar areas are dramatically reduced in size. Because Wnt is critical to maintain expression of En, a loss of Wnt likewise disrupts growth of the midbrain and anterior hindbrain. The various signaling molecules within the midbrain�anterior hindbrain area doubtless serve multiple functions in segregating cell varieties, limiting migration of cells into adjacent areas, and sustaining the expression of genes and the transduction of signals that impression last cell destiny. Scientists proceed to make discoveries that assist outline the interplay between signaling centers and boundary formation on this area of the growing nervous system. Wnt and En then inhibit expression of forebrain-associated genes together with Pax6 and Otx2. The actual number of rhombomeres varies from seven to 9, relying on the species and the factors used for designating the segments. Each rhombomere expresses a singular set of proteins that impacts proliferation, differentiation, and axonal growth of the growing hindbrain cells. For instance, the formation of several of the cranial nerves is impacted by early rhombomere boundaries. As shall be seen beneath, defects in rhombomere formation lead to abnormal cranial nerve development. One mechanism used to restrict cells to specific rhombomeres is Rhombomeres form segments that stretch from the junction with the midbrain to the junction with the spinal twine. A number of cell sorts, such as cranial motor neurons related to the trigeminal, facial, abducens, vagus, and glossopharyngeal nerves, originate in specific rhombomeres as proven in rhombomere 2 (r2) by way of rhombomere 7 (r7). Unlike the other rhombomeres, r1, the most important rhombomere, contributes to formation of the cerebellum. In this example, the cells in every rhombomere are shown as a single color to indicate the segregation of cells inside rhombomere boundaries. Grafting experiments in chick embryos examined whether the traditional boundaries between adjoining rhombomeres inhibited the intermixing of cells from even- and odd-numbered rhombomeres. Rhombomere segments have been faraway from one aspect of each donor (surgical aspect, A) and host (grafted aspect, B) embryos at the similar stage of growth. In these grafts, the cells intermingled, unlike those on the untreated facet in which the cells of r4 and r5 remained segregated. Similar outcomes had been obtained if two odd-numbered segments had been grafted subsequent to each other.
Discount motrin 600 mg fast delivery
In the accumulating ducts flourtown pain evaluation treatment center motrin 600 mg purchase without prescription, the mechanism is similar as that described for the late distal tubule ohio valley pain treatment center buy motrin 400 mg fast delivery. Water will be reabsorbed until the tubular fluid equilibrates osmotically with surrounding interstitial fluid. The ultimate urine will reach the osmolarity present on the tip of the papilla, which, on this instance, is 1200 mOsm/L. The corticopapillary osmotic gradient is established by countercurrent multiplication, a function of the loop of Henle, and by urea recycling, a operate of the internal medullary accumulating ducts. Production of Hyposmotic Urine By definition, hyposmotic (dilute) urine has an osmolarity decrease than blood osmolarity. The closely outlined portion indicates the nephron segments that are impermeable to water, which now embrace the thick ascending limb and the entire distal tubule and accumulating duct. In the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle, NaCl is reabsorbed via the Na+-K+-2Cl- cotransporter. Thus the tubular fluid is diluted, and the fluid leaving the thick ascending limb has an osmolarity of 120 mOsm/L. NaCl is reabsorbed by the Na+-Cl- cotransporter, but the cells are impermeable to water. Thus tubular fluid that leaves the early distal tubule has an osmolarity of one hundred ten mOsm/L. Arrow reveals location of water reabsorption; heavy define reveals water-impermeable parts of the nephron; numbers are osmolarity of tubular fluid or interstitial fluid. These segments are actually impermeable to water: As tubular fluid flows via them, no osmotic equilibration is possible. In impact, the late distal tubule and amassing duct also become diluting segments. Tubular fluid is diluted in the "diluting segments," which reabsorb NaCl with out water. Final urine osmolarity will reflect the mixed capabilities of all the diluting segments together with the thick ascending limb and the early distal tubule, in addition to the remainder of the distal tubule and amassing ducts. There are, nonetheless, two irregular situations by which dilute urine is produced inappropriately: central diabetes insipidus and nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Thiazide diuretics are helpful as follows: (1) They inhibit Na+-Cl- cotransport within the early distal tubule, thereby stopping dilution of the urine on this segment. As more NaCl is excreted, the urine is much less dilute than it might be without therapy. The combination of less water filtered and more water reabsorbed in the proximal tubule signifies that the entire quantity of water excreted is decreased. Free-Water Clearance Free water is outlined as distilled water that is freed from solutes (or solute-free water). In the nephron, free water is generated in the diluting segments, where solute is reabsorbed with out water. The diluting segments of the nephron are the water-impermeable segments: the thick ascending limb and the early distal tubule. A man has a urine circulate price of 10 mL/min, a urine osmolarity of one hundred mOsm/L, and a plasma osmolarity of 290 mOsm/L. Likewise, the ability to concentrate the urine throughout water deprivation is impaired as a end result of loop diuretics also intervene with era of the corticopapillary osmotic gradient (by inhibiting Na+-K+-2Cl- cotransport and countercurrent multiplication). The solute-free water, which is generated in the thick ascending limb and early distal tubule, is excreted in the urine because the late distal tubules and accumulating ducts are impermeable to water under these circumstances (Box 6. All of the solute-free water generated within the thick ascending limb and early distal tubule (and more) is reabsorbed by the late distal tubules and amassing ducts. She has extreme polyuria (producing 1 L of urine every 2 hours) and polydipsia (drinking 3�4 glasses of water each hour). During a 24-hour period in the hospital, the girl produces 10 L of urine, containing no glucose. Her serum osmolarity is 330 mOsm/L, her serum [Na+] is 164 mEq/L, and her urine osmolarity is 7 mOsm/L. Within 24 hours of initiating the treatment, her serum osmolarity is 295 mOsm/L and her urine osmolarity is 620 mOsm/L. Following overnight water restriction, the hanging remark is that the girl continues to be producing dilute (hyposmotic) urine despite a severely elevated serum osmolarity. Diabetes mellitus is ruled out as a reason for her polyuria as a outcome of no glucose is present in her urine. The diagnosis is that the lady has central diabetes insipidus secondary to a head damage. Because she is excreting excessive quantities of free water, serum osmolarity and serum [Na+] increase. The excessive serum osmolarity is an intense stimulus for thirst, inflicting the lady to drink water almost continuously. Volumes of the body fluid compartments are measured by dilution of marker substances. Renal clearance is the amount of plasma cleared of a substance per unit time and is decided by its renal dealing with. The net reabsorption or secretion rate of a substance is the distinction between its filtered load and its excretion fee. Glucose is reabsorbed by a Tm-limited course of: When the filtered load of glucose exceeds the Tm, then glucose is excreted within the urine (glucosuria). Na+ reabsorption is greater than 99% of the filtered load and happens all through the nephron. In the proximal tubule, 67% of the filtered Na+ is reabsorbed isosmotically with water. In the early proximal tubule, Na+ is reabsorbed by Na+-glucose cotransport, Na+-amino acid cotransport, and Na+-H+ change. In the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle, a water-impermeable phase, 25% of the filtered Na+ is reabsorbed by Na+-K+-2Cl- cotransport. In the early distal tubule, the mechanism is Na+-Cl- cotransport, which is inhibited by thiazide diuretics. In the late distal tubule and collecting ducts, the principal cells have aldosteronedependent Na+ channels, that are inhibited by K+sparing diuretics. K+ stability is maintained by shifts of K+ across cell membranes and by renal regulation. The renal mechanisms for K+ steadiness embody filtration, reabsorption in the proximal tubule and thick ascending limb, and secretion by the principal cells of the late distal tubule and collecting ducts. Secretion by the principal cells is influenced by dietary K+, aldosterone, acid-base balance, and circulate price. Under the situations of low K+ consumption, K+ is reabsorbed by -intercalated cells of the distal tubule. Body fluid osmolarity is maintained at a relentless value by modifications in water reabsorption within the principal cells of the late distal tubule and collecting duct. This steadiness is achieved by utilization of buffers in extracellular fluid and intracellular fluid, by respiratory mechanisms that excrete carbon dioxide, and by renal mechanisms that reabsorb bicarbonate and secrete hydrogen ions. In arterial blood the H+ focus is forty � 10-9 equivalents per liter (or 40 nEq/L), which is more than six orders of magnitude lower than the sodium (Na+) focus.
Generic motrin 400 mg otc
These results supported the hypothesis that gradients of Shh have been liable for the changes in actin translation associated with the turning response joint and pain treatment center santa maria ca generic 600 mg motrin otc. In mice lacking the Zbp1 gene pain medication for dogs hydrocodone motrin 400 mg discount with amex, for example, the commissural interneurons displayed a disorganized trajectory to the floor plate. Similar results were seen in chick embryos when a mutant type of Zbp1 was electroporated (see Chapter 4) into chick spinal wire. Research investigating whether or not these differences are associated to the animal mannequin used, the age and neuronal subtype investigated, the steering cues utilized, or metabolic differences associated with varied cell tradition conditions are being explored. This section explores how axons are selectively matched to a person goal cell utilizing examples from the vertebrate retinotectal system. The retinotectal system has been a popular model system for investigating axonal pathfinding and target cell recognition because the Nineteen Twenties. The retinal ganglion cells and their target tissue, the optic tectum, are simply identified and accessible for experimental manipulations in a number of vertebrate species. Additionally, because the retinotectal system has been studied for thus a few years, it is extremely properly characterized and thus provides scientists with a wealth of knowledge on which to draw. The following sections describe the findings that first led scientists to investigate axon-target recognition in the retinotectal system and the next experiments used to identify specific cues to regulate the proper mapping of retinal ganglion cell axons throughout the optic tectum. Several scientists at the moment favored the idea that once axons managed to attain the goal tissue, a selected goal cell recognized and fashioned a synaptic connection solely with an axon that supplied a matching sample of neural exercise. The notion of a goal cell responding to the neural activity of an axon was known as the resonance hypothesis-that is, the target cells would resonate only with axons providing matching electrical activity. This speculation was developed over a number of years largely by way of the work of Paul Weiss and colleagues. Among probably the most pivotal experiments that reshaped how scientists think about axonal guidance mechanisms have been those carried out by Roger Sperry from the Forties to the Nineteen Sixties. Although Sperry labored with Weiss, he saw limits to the resonance speculation and so began a series of experiments utilizing the retinotectal system of amphibians to take a look at how axons acknowledge and make correct connections with goal cells. A variety of studies in the early 1900s revealed that if the optic nerve was crushed or severed, the retinal axons would regenerate and reestablish connections inside the optic tectum. New nerve fibers had sprouted from the minimize stump and had managed to grow again to the visual facilities of the brain. And but, this was the only potential rationalization, for without question the newts had regained regular imaginative and prescient. This group additionally found that if an eye fixed from one salamander was transplanted to one other salamander, the retinal axons of the transplanted eye regenerated and restored vision. Because imaginative and prescient was restored even after a quantity of surgeries, Sperry and others recognized that the retinotectal system would offer a method of testing how axonal connections are established with particular target cells. Other scientists hypothesized that the axons regrew in a scientific method to reestablish their unique connections with specifc goal cells. This latter hypothesis was consistent with the thought that a chemical cue directed the axons to a particular goal cell. To take a look at whether or not retinal axons relied on target-derived, chemical cues to project to a particular region of the tectum, Sperry modified the attention surgical procedure approach utilized by Matthey and Stone. In his 1943 report, Sperry completed this surgical procedure on fifty eight adult newts and famous they recovered visual operate over a period ranging from 28�95 days. When the lure was introduced in entrance of its head, it will turn around and begin looking out within the rear; when the bait was behind it, the animal would lunge forward. Even these animals that survived for two years continued to behave as if the visible world have been rotated one hundred eighty levels. Experiments in frogs, toads, and fish revealed similar results following eye rotations. As in the newts, the visible world was inverted and no amount of follow compensated for the inverted visible area. Sperry proposed a mechanism by which retinal axons put out quite a few branches and examined completely different cells until "ultimately the rising tip encounters a cell floor for which it has a specific chemical affinity and to which it adheres. Studies by Roger Sperry from the Nineteen Forties by way of the Sixties indicated that retinotectal projections returned to the original goal cells after experimental manipulations. After the attention was rotated, the optic nerve was reduce and the animal was allowed to recover. The giant arrows indicate the path of movement of an object, while the small arrows point out the direction of head motion. The experimental animals always responded as if the item had been transferring in the other way. In the strictest sense, chemoaffinity would require matching "chemical tags," as Sperry referred to as them, between every axon and every goal cell. Retinotectal maps are found in regular and experimental situations To better perceive the group of retinal axons within the tectum, scientists mapped axonal connections using histological preparations and electrophysiological recordings. This is one example of a topographic map-the consistent, primarily invariant projection of axons from one region of the nervous system onto one other. The behavioral results obtained after the eye rotation surgical procedures indicated that the temporal axons must nonetheless develop to the anterior tectum and the nasal axons to the posterior tectum, even after these experimental manipulations. Throughout the 1950s, Nineteen Sixties, and 1970s, scientists used quite a lot of methods to additional evaluate the mapping of retinotectal projections underneath totally different experimental circumstances. Many of the surgical manipulations had been carried out utilizing frogs, salamanders, or fish, although some have been also performed in chick embryos. One of the methods used to examine retinotectal mapping was to create a "compound eye" during which, for example, two nasal sections of the retina have been grafted right into a single eye so that the grafted nasal section was now on the temporal facet of the eye. These research revealed that the extra nasal axons nonetheless mapped to the posterior area of the tectum. These experiments again advised that topographic mapping within the tectum was not due to retinal axons firing in resonance with target cells, however was extra likely due to chemical cues current on the axons and target cells. For instance, research within the Seventies revealed that if half of the retina have been surgically eliminated and the animals got adequate time to recover, the remaining axons would finally grow over the entire tectum. This instructed that there was not a strict one-to-one matching of retinal axons and tectal cells or any inflexible boundaries to restrict where axons could grow. Those axons that may normally innervate the lacking portion of the tectum would now make connections with cells in the space of the tectum that remained, forming a "compressed" retinotectal map. For instance, temporal axons would converge on the remaining posterior tectum if the anterior portion were lacking. Several extra experiments had been carried out throughout the Nineteen Seventies and Nineteen Eighties, and from these studies scientists noted that there were often species variations in the capacity of retinal axons to map onto new tectal regions, as well as differences that trusted the age of the animal studied. Yet, by the l990s, the chemoaffinity speculation re-emerged as a viable mechanism for retinotectal mapping. A "stripe assay" reveals progress preferences for temporal retinal axons A main advance in understanding how retinal axons selectively grow to a given region of the tectum came from the lab of Friedrich Bonhoeffer in the 1980s. These scientists developed a novel cell culture methodology called a "stripe assay" to analyze the growth of chick retinal axons on cell membranes extracted from tectal cells. However, when the animals got a sufficient recovery time, the axons from nasal retinal ganglion cells expanded to contact cells in the obtainable anterior portion of the tectum. Scientists developed a cell (A) (B) channels tradition technique to produce precise lanes of anterior and posterior tectal cell membranes. The cell membranes from the anterior or posterior tectal cells were then added to a small silicon system with channels ninety microns in diameter and 90 microns aside.
Cheap 400 mg motrin with amex
Insulin is secreted into pancreatic venous blood and then delivered to the systemic circulation pain treatment west plains mo motrin 600 mg buy fast delivery. C peptide is secreted in equimolar quantities with insulin and is excreted unchanged in the urine pain treatment for osteoporosis motrin 600 mg buy otc. Therefore the excretion rate of C peptide can be utilized to assess and monitor endogenous cell perform. Recall from Chapter eight that oral glucose is a extra highly effective stimulant for insulin secretion than intravenous glucose. The subunits lie within the extracellular domain, and the subunits span the cell membrane. A disulfide bond connects the two subunits, and each subunit is connected to a subunit by a disulfide bond. Insulin binds to the subunits of the tetrameric insulin receptor, producing a conformational change in the receptor. Activated tyrosine kinase phosphorylates a quantity of other proteins or enzymes that are involved within the physiologic actions of insulin including protein kinases, phosphatases, phospholipases, and G proteins. Phosphorylation either prompts or inhibits these proteins to produce the various metabolic actions of insulin. The insulin receptor is either degraded by intracellular proteases, stored, or recycled to the cell membrane to be used once more. Insulin down-regulates its own receptor by reducing the rate of synthesis and rising the rate of degradation of the receptor. In addition to the beforehand described actions, insulin additionally binds to parts in the nucleus, the Golgi apparatus, and the endoplasmic reticulum. For example, the stimulatory results of amino acids and fatty acids on insulin secretion utilize metabolic pathways parallel to these utilized by glucose. Glucagon prompts a Gq protein coupled to phospholipase C, which results in an increase in intracellular Ca2+. When the availability of vitamins exceeds the calls for of the physique, insulin ensures that excess nutrients are saved as glycogen in the liver, as fat in adipose tissue, and as protein in muscle. These saved nutrients are then out there during subsequent durations of fasting to preserve glucose supply to the mind, muscle, and other organs. The effects of insulin on nutrient move and the resulting modifications in blood levels are summarized in Table 9. The two subunits are related by disulfide bonds; each subunit is related to a subunit by a disulfide bond. The total effect of insulin on fat metabolism is to inhibit the mobilization and oxidation of fatty acids and, concurrently, to enhance the storage of fatty acids. As a result, insulin decreases the circulating ranges of fatty acids and ketoacids. Simultaneously, insulin inhibits ketoacid (-hydroxybutyric acid and acetoacetic acid) formation in liver as a end result of decreased fatty acid degradation signifies that less acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl CoA) substrate will be obtainable for the formation of ketoacids. Insulin increases amino acid and protein uptake by tissues, thereby decreasing blood ranges of amino acids. In addition to main actions on carbohydrate, fats, and protein metabolism, insulin has several additional effects. This motion of insulin could be viewed as "defending" towards an increase in serum K+ focus. When K+ is ingested in the diet, insulin ensures that ingested K+ might be taken into the cells with glucose and other vitamins. Insulin Decreases blood [amino acid] Decreases blood [fatty acid] Decreases blood [ketoacid] Decreases blood [K+] Insulin has the following actions on liver, muscle, and adipose tissue: Decreases blood glucose focus. The hypoglycemic motion of insulin may be described in two methods: Insulin causes a frank lower in blood glucose focus, and insulin limits the rise in blood glucose that occurs after ingestion of carbohydrates. Solid arrows indicate that the step is stimulated; dashed arrows point out that the step is inhibited. Pathophysiology of Insulin the most important dysfunction involving insulin is diabetes mellitus. Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, or type I diabetes mellitus, is brought on by destruction of cells, often as a result of an autoimmune process. Type I diabetes mellitus is characterised by the next changes: elevated blood glucose focus from decreased uptake of glucose into cells, decreased glucose utilization, and increased gluconeogenesis; elevated blood fatty acid and ketoacid focus from elevated lipolysis of fats, elevated conversion of fatty acids to ketoacids, and decreased utilization of ketoacids by tissues; and elevated blood amino acid concentration from elevated breakdown of protein to amino acids. Disturbances of fluid and electrolyte stability are present in type I diabetes mellitus. The increased blood glucose concentration leads to an elevated filtered load of glucose, which exceeds the reabsorptive capability of the proximal tubule. The nonreabsorbed glucose then acts as an osmotic solute in urine, producing an osmotic diuresis, polyuria, and thirst. Lack of insulin also causes a shift of K+ out of cells (recall that insulin promotes K+ uptake), leading to hyperkalemia. Treatment of sort I diabetes mellitus consists of insulin alternative therapy, which restores the 446 � Physiology capability of the physique to store carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins and returns the blood values of nutrients and electrolytes to normal. It displays some, but not all, of the metabolic derangements seen in type I diabetes mellitus. Typically, the blood glucose concentration is elevated in each fasting and postprandial (after eating) states. Glucagon Glucagon is synthesized and secreted by the cells of the islets of Langerhans. Thus while insulin is the hormone of "abundance," glucagon is the hormone of "hunger. Regulation of Glucagon Secretion the main factor stimulating the secretion of glucagon is decreased blood glucose concentration. Coordinating with this stimulatory effect of low blood glucose is a separate inhibitory action of insulin. Thus the presence of insulin reduces or modulates the effect of low blood glucose focus to stimulate glucagon secretion. Glucagon secretion also is stimulated by the ingestion of protein, particularly by the amino acids arginine and alanine. The response of the cells to amino acids is blunted if glucose is administered simultaneously (partially mediated by the inhibitory effect of insulin on glucagon secretion). Thus glucose and amino acids have offsetting or reverse results on glucagon secretion (in contrast to their effects on insulin secretion, that are complementary). Some of the stimulatory effects on glucagon secretion are mediated by activation of sympathetic -adrenergic receptors. Actions of Glucagon the actions of glucagon are coordinated to enhance and keep the blood glucose concentration. Thus the factors that cause stimulation of glucagon secretion are people who inform the cells that a lower in blood glucose has occurred (Table 9. The mechanism of action of glucagon on its target cells begins with hormone binding to a cell membrane receptor, which is coupled to adenylyl cyclase through a Gs protein. As the hormone of hunger, glucagon promotes mobilization and utilization of stored nutrients to keep the blood glucose concentration within the fasting state. The major actions of glucagon are on the liver (in contrast to insulin, which acts on liver, adipose, and muscle tissue).