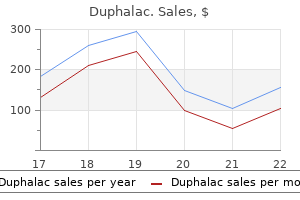
Duphalac 100 ml order
Like other important organs of the physique symptoms jock itch buy 100 ml duphalac amex, coronary circulation reveals welldeveloped phenomenon of autoregulation symptoms pink eye duphalac 100 ml generic amex. As described intimately on page 315, autoregulation refers to the flexibility of an organ/tissue to adjust its vascular resistance and maintain a comparatively constant blood move over a variety of arterial blood strain. However, this phenomenon of autoregulation of coronary blood move fails when blood strain falls under 70 mmHg and coronary perfusion is seriously compromised. Metabolic local elements are an important elements which regulate the coronary blood move and therefore, they even override the impact of nervous stimulation. Therefore, not much additional oxygen may be offered to myocardium unless the blood move will increase. Adenosine is considered the most important consider production of coronary vasodilation during hypoxic states. In myocardial ischaemia, either as a result of generalized hypoxia or as a end result of elevated myocardial metabolism the intracellular myocardial adenine nucleotides are degraded to adenosine. Role of endothelial cells � Endothelial cells launch a quantity of vasodilator autacoids that contribute to the physiologic regulation of coronary vasomotor tone. Nervous management mechanism Autonomic nerves control the coronary blood circulate instantly as well as not directly. Direct nervous management on coronary circulation is exerted via sympathetic and parasympathetic nerve provide to the coronary vessels. The transmitters released at their nerve endings are epinephrine and norepinephrine. Indirect management of nervous stimulation on coronary blood circulate is thru their motion on the guts. This oblique effect of sympathetic stimulation overrides the direct impact of sympathetic discharge on coronary vasculature. Thus, the general impact of sympathetic stimulation is coronary vasodilation and elevated coronary blood flow. But if pressure remains high for a long time, due to increased work load on the guts, heart will go into congestive heart failure. This effect is noticed secondary to the metabolic modifications in myocardium at a time when there happens vasoconstriction of splanchnic, renal and cutaneous vessels. Increased metabolism of the guts will increase O2 consumption resulting in relative hypoxia. It is a situation associated with development of atherosclerosis within the coronary arteries, which supply the center muscular tissues (myocardium). With atherosclerosis, the arterial wall is hardened and its lumen turns into narrow due to plaque formation which may include calcium deposits, fatty deposits, clean muscle proliferation and abnormal inflammatory cells. Angina pectoris refers to a transient form of myocardial ischaemia, particularly occurring during elevated oxygen demand. Superadded thrombus formation causing incomplete coronary occlusion leads to an unstable angina. Typically, the angina is described as a feeling of uncomfortable pressure, fullness, squeezing or pain in the substernal area, which can be localized or could additionally be referred to the inside border of left arm, neck or jaw. Pain happens because of accumulation of anoxic myocardial metabolites and factor P, which stimulates pain nerve endings. Laboratory testing embrace serum lipid ranges, Treatment � Nitroglycerine-sublingual nitroglycerine is the drug of selection. Nitrates lower arteriolar and venous tone, scale back preload and after load, and lower the oxygen demand. Nitrates also enhance myocardial blood circulate by dilating collaterals and within the presence of elevated vasomotor tone. This impact is completed by decreasing the heart price, myocardial contractility and blood stress. Commonly, Ml occurs when partially occluded coronary artery is constricted additional by vasospasm or plaque (most frequent cause), which triggers formation of thrombus and occludes coronary artery. Causes of myocardial infarction embrace: � Atherosclerosis of coronary arteries, � Thrombus formation, � Embolus coming from different areas and � Spasm of coronary vessels. Pain lasts for greater than 30 min and sometimes may radiate to left arm and left facet of neck. Silent Ml normally occurs in diabetics with related autonomic neuropathy in elderly and also in sufferers with coronary heart transplants. Certain enzymes and proteins known as as cardio-biomarkers leak into the circulation from the damaged myocardial cells. Homocysteine is transformed into nontoxic substance (methionine) by vitamin B12 and folic acid. For localization of the infarct and to determine additional management different investigations included are; � Echocardiography provides assessment of left ventricular and regional functioning, and can help in prognosis and management of infraction. Treatment In myocardial infarction, remedy must be began instantly to keep away from irreversible adjustments. General measures: Coronary care unit monitoring must be instituted as early as possible. Aspirin (for mechanism of motion see page 242) Analgesia: To relieve pain, sublingual nitroglycerine must be tried first, if no reduction than intravenous opioids provide efficient and fast analgesia. Surgical treatment contains: � Aortic coronary bypass surgery is performed to remove discrete points of blockage as a result of atherosclerosis. In this procedure, a section of subcutaneous vein both from arm or leg is eliminated and then grafting is done from root of aorta to the peripheral artery (beyond the blockage point). A small balloontipped catheter about 1 mm in diameter, is handed beneath radiographic steering into the coronary system and pushed through partially occluded vessel until balloon reaches to blocked level. Then, the balloon is inflated beneath pressure, which stretches the diseased artery. After the process, blood circulate increases by three- to fourfolds and 75% sufferers are relieved of ischemic signs. The endothelin normally grows over the stents and permits smooth blood circulate through the stent. Drug-eluting stents are usually preferred because these slowly release the drugs, which prevent the excessive progress of scar tissue and reduce the incidence of restenosis. The severity of myocardial dysfunction is proportionate to the extent of myocardial necrosis. Acute left coronary heart failure, hypotension and shock are frequent myocardial dysfunctions. This is an autoimmune phenomenon and presents as pericarditis, associated with fever, leucocytosis and pericardial/pleural effusion. Cerebral circulation Cerebral blood vessels Arteries of the brain � the arteries which supply the mind are derived from two inner carotid arteries and the basilar artery (formed by union of the proper and left vertebral arteries). Branches of the interior carotid arteries and of basilar artery anastomose on the inferior surface of the mind to type the circulus arteriosus (Circle of Willis). In this fashion, the circulus arteriosus permits blood that enters by both internal carotid or vertebral artery to be distributed to any part of both cerebral hemispheres. Venous drainage of the brain the cerebral hemisphere has two sets of veins: the superficial and deep.
Generic duphalac 100 ml amex
After reaching the cell bodies the neurotrophins foster the production of proteins associated with neuronal improvement medications not to take with grapefruit discount duphalac 100 ml without a prescription, progress and survival treatment norovirus discount 100 ml duphalac mastercard. It is produced by Schwann cells and astrocytes and performs a progress promoting function in lesioned and embryonic spinal cord neurons. It is believed that it might be of some worth in treating human ailments during which motor neurons degenerate. The nerve terminal or the so-called synaptic knob accommodates large variety of vesicles (about three lakh) containing acetylcholine. This refers to the axonal membrane lining the terminal buttons of the nerve endings. It is a 50�100 nm broad house between the presynaptic membrane and the postsynaptic membrane. This is the name given to the muscle fibre membrane (sarcolemma) in the area of neuromuscular junction. The muscle membrane on this area is thickened and depressed to type the synaptic trough during which the terminal button matches. Further, the postsynaptic membrane is thrown into large variety of folds known as subneural clefts or pallisades. The matrix of subneural cleft incorporates the enzyme cholinesterase which can degrade acetylcholine. Neuromuscular transmission the skeletal muscle is stimulated only via its nerve. The sequence of occasions which causes transmission of impulse via neuromuscular junction are: � Release of acetylcholine by the nerve terminals � Effect of acetylcholine on postsynaptic membrane � Development of finish plate potential � Miniature finish plate potential � Removal of acetylcholine by cholinesterase � Initiation of the action potential in muscle fibre. When the nerve impulse (action potential) travelling in the nerve fibre (axon) reaches the terminal buttons, the voltage-gated Ca2+ channels present on the presynaptic membrane open up rising its permeability to Ca2+ ions. The elevated Ca2+ ranges in the cytosol of terminal buttons bring a few fusion of vesicles (containing acetylcholine) with the presynaptic membrane and set off a marked enhance in exocytosis of vesicles releasing acetylcholine within the synaptic cleft. When two molecules of acetylcholine get attached to the binding web site of the receptors. In different phrases, conductance to Na+ and Ca2+ ions is increased at the motor finish plate. The resting membrane potential at the postsynaptic membrane is about -80 to -90 mV. When sodium ions enter inside carrying with them massive numbers of optimistic charges, there happens depolarization causing an area optimistic potential change inside the muscle fibre membrane referred to as the tip plate potential. The motion potentials are generated on both facet of the tip plate and are carried out away from the top plate in both the instructions along the muscle fibres thus inflicting muscle contraction. Even at relaxation, small quanta of acetylcholine are launched randomly from the nerve terminal. The dimension of the quanta of acetylcholine launched on this method varies immediately with the Ca2+ focus and inversely with the Mg2+ concentration on the finish plate. The miniature finish plate potential similar to that seen on the myoneural junction has been observed at different cholinergic synapses as properly. The acetylcholine is so potent that its stay in the synaptic house even for this brief period of 1 ms is enough to excite the muscle fibre. It is important to notice that the fast removing of acetylcholine prevents the repeated excitation of muscle fibre. Drugs affecting and problems of neuromuscular junction Drugs affecting neuromuscular junction Neuromuscular blockers. Neuromuscular blockers are the medication that block transmission on the neuromuscular junction. Some of the common neuromuscular blockers, that are generally used, in medical apply and in analysis are: 1. Curare or the energetic principle of D-tubocurarine prevents the neuromuscular transmission by combining with acetylcholine receptors. The curariform drugs are known as receptor blockers since they block the neuromuscular transmission by performing on acetylcholine receptors. Bungarotoxin discovered in the venom of deadly snakes additionally blocks neuromuscular transmission by binding with acetylcholine receptors. Succinylcholine and carbamylcholine act like acetylcholine and trigger depolarization of the postsynaptic membrane. Thus, these medication block the myoneural junction by maintaining the muscle in a depolarized state. It blocks the transmission across the myoneural junction by stopping the discharge of acetylcholine from the terminal buttons of the nerve endings. The drugs methacholine, carbachol and nicotine act like acetylcholine and produce end plate potential thrilling the muscle fibre. However, these medicine are either not destroyed or are destroyed very slowly by the enzyme acetylcholineesterase. So they cause repeated stimulation and steady action of muscle, thereby inflicting a state of muscle spasm. Myasthenia gravis is a dysfunction in which the myoneural junction is unable to transmit signals from the nerve fibre to muscle fibres, thereby causing paralysis of the involved muscular tissues. In this disease, antibodies are produced in opposition to the acetylcholine-gated channels (receptors) present on the motor end plate which destroy these channels. The major medical feature of the illness is muscle fatigue with sustained or repeated exercise. Studies show that the number of receptors on motor finish plates of affected muscle is reduced by 70�90%. If the disease is intense enough, the affected person dies of paralysis, significantly of respiratory muscle tissue. I n this disease, antibodies are produced against the calcium channels present on the presynaptic membrane, which destroy the channels. Consequently, Ca2+ influx into the nerve terminal is markedly decreased and thereby release of acetylcholine is also lowered. A similar sort of syndrome also can occur after the utilization of aminoglycoside antibiotics which impair the functioning of Ca2+ at nerve terminals. Further, the muscle is a contractile tissue with a chemically stored energy which may be reworked into mechanical power. There are three several types of muscles in the body: skeletal muscles, cardiac muscular tissues and smooth muscles. Based on sure distinctive features the muscular tissues could be grouped as: Striated versus nonstriated muscular tissues Striated muscle cells show large variety of cross striations at common intervals when seen under a light-weight microscope. Voluntary versus involuntary muscle tissue Voluntary muscular tissues can be made to contract underneath our will to carry out the movements we want. Skeletal muscular tissues the skeletal muscle tissue, because the name indicates, are attached with the bones of the physique skeleton and their contraction results in the body actions. Each fasciculus is surrounded by a stronger sheath of connective tissue referred to as perimysium. Structure of a muscle fibre Each muscle fibre is mainly an extended (1�4 cm), cylindrical (10�100 micron in diameter) multinucleated cell.
Syndromes
- Sip water or other clear fluids.
- Tumors
- Some types of epilepsy
- Irregular heartbeat
- Stomach
- The doctor makes a very small cut on your breast over the area that needs to be biopsied.
- Long-term need of a ventilator
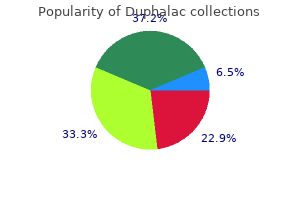
100 ml duphalac cheap with amex
However medicine 512 duphalac 100 ml buy cheap, a immediate improve in insulin secretion brings it back to baseline worth inside 2 h medicine 3d printing duphalac 100 ml overnight delivery. Normal body reserves of glucose Free glucose is carbohydrate currency of the physique. This amount is simply enough to meet the basal power requirements of the physique for 1 h. However, liver can also be capable of producing about 125�150 mg glucose/min or 180�220 g/2 h. The dietary carbohydrates are digested and absorbed as monosaccharides (glucose, fructose, galactose, and so on. The liver is able to converting fructose and galactose into glucose, which can readily enter the blood. Precursors for gluconeogenesis embody lactate, glycerol, propionate and some amino acids. Stored glycogen in liver is degraded to glucose, while muscle glycogen after degradation produces lactate which is used for gluconeogenesis as described above. Role of hormones in regulation of blood glucose Under normal circumstances, various hormones play a significant role in sustaining the blood glucose levels inside regular physiological range. This is accomplished by preventing the incidence of hyperglycaemia and hypoglycaemia. The prevalence of hyperglycaemia after a pure carbohydrate load or a combined meal in a wholesome individual is prevented by a manifold (4�5 times) improve in insulin secretion. Insulin normalizes the blood glucose levels by: � Increasing uptake and utilization as chief gas in the muscular tissues, � Promoting storage of glucose as glycogen in liver and as triglycerides in the adipose tissue and � Decreasing glucose manufacturing by inhibiting gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis (for particulars see actions of insulin on web page 775). Hypoglycaemia, which can happen due to fasting or extended train, is prevented in a healthy particular person by a number of hormones, which include glucagon, epinephrine, growth hormone and glucocorticoids. This could additionally be correlated with the truth that moderate and transient hyperglycaemia is innocent and occurs after every meal. The roles played by completely different hormones in stopping hypoglycaemia are described: 1. During normal sample of food consumption (consisting of 2�3 meals/day), in between the meals when glucose degree tends to lower, the insulin secretion stops and instead glucagon is poured into the bloodstream beneath these circumstances. When hunger interval additional will increase (say many hours), even within the presence of glucagon, blood glucose ranges begin to fall. The resulting hypoglycaemia stimulates the sympathetic nervous system through hypothalamus to promote the discharge of epinephrine from the adrenal medulla. When hunger is more prolonged (say for a few days), together with glucagon and epinephrine, secretion of progress hormone and glucocorticoids can additionally be elevated. These hormones, along with selling glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis and lipolysis, additionally decrease the peripheral utilization of glucose, thereby sparing glucose for nervous tissue, especially mind. Pancreatic somatostatin is a neuropeptide containing 14 amino acids, synthesized by cells. It is also synthesized by intestinal cells and was initially discovered as a hypothalamic neuropeptide that inhibits development hormone secretion. Somatostatin secretion is increased after ingestion of food, as a end result of increased blood glucose, amino acids, fatty acids and gastrointestinal tract hormones stimulate its secretion. Glucagon, -adrenergic and cholinergic neurotransmitters also stimulate somatostatin secretion. In a nutshell, actions of somatostatin along with these of insulin and glucagon in all probability coordinate nutrient input with substrate disposal. I mportant N ote Somatostatin analogues are actually used therapeutically to alleviate diarrhoea attributable to unregulated gastrointestinal hormone secretion. They are additionally employed to inhibit unregulated launch of various peptides and protein hormones by neoplasms. Pancreatic polypeptide has 36 amino acids and belongs to a household of similar molecules together with neuropeptide Y in the hypothalamus and gastrointestinal polypeptide Y. Pancreatic polypeptide is secreted in response to food ingestion via gastrointestinal secretagogues and cholinergic stimulation. Its secretion is also stimulated by hypoglycaemia and inhibited by glucose administration. Its best known action is to inhibit exocrine pancreatic secretion and slows the absorption of meals in humans. Applied aspects Important utilized features of endocrine pancreas which want point out are: � Diabetes mellitus and � Hypoglycaemia Diabetes mellitus Diabetes mellitus, commonly referred to as just diabetes, refers to a scientific syndrome of hyperglycaemia occurring as a result of deficiency of insulin. Types and levels of diabetes mellitus Diabetes mellitus could be categorised into following sorts: 1. It is associated with sure pathological circumstances corresponding to pancreatitis, cystic fibrosis, acromegaly and Cushing syndrome. Stages within the development of diabetes mellitus embody: � Prediabetics or potential diabetics. These are the individuals with regular blood glucose stage however are potential candidates to develop diabetes due to strong genetic predispositions. These persons have normal fasting and postprandial blood glucose levels and regular glucose tolerance test. But their blood glucose becomes abnormally excessive during stress or after administration of glucocorticoids. Overeating coupled with underactivity resulting in weight problems acts as a diabetogenic factor in genetically predisposed individuals. It is supposed to occur because of decrease in insulin receptors on the insulinresponsive (target) cells. In some circumstances, the defects in individual genes have been recognized; these embrace defect in glucokinase (1%), insulin molecule (0. Obesity (the metabolic syndrome) the incidence of obesity is increasing; it pertains to the discrepancy between energy consumption and vitality expenditure. Metabolic syndrome is principally a glucose metabolism dysfunction; due to this fact, it has special relation with diabetes mellitus. The combination of these findings is commonly referred to as metabolic syndrome or syndrome X. Hyperglycaemia and its consequences Hyperglycaemia (elevation of blood glucose concentration) is the attribute feature of uncontrolled diabetes mellitus. It occurs because of lack of insulin leading to: � Decreased peripheral utilization of glucose. Consequences of hyperglycaemia are: � Glycosuria and its consequences, � Impaired phagocytic operate, � Hyperosmolar effects and � Glycosylation of haemoglobin. It is the outcome of osmotic diuresis brought on by renal excretion of osmotically lively glucose molecules.
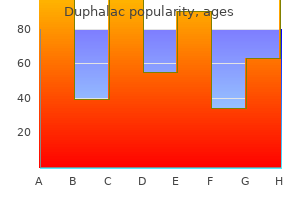
Duphalac 100 ml purchase with mastercard
These originate from the pars compacta medications for bipolar duphalac 100 ml buy cheap on line, a part of substantia nigra and terminate within the striatum symptoms ptsd order duphalac 100 ml with mastercard. Raphe striate fibres are serotoninergic fibres received by the striatum from raphe nuclei within the reticular formation of brainstem. Locus coeruleus striate fibres are noradrenergic fibres obtained by the striatum from the locus coeruleus. Striatum (caudate nucleus and putamen) which obtain a lot of the afferents offers robust projection to each segments of globus pallidus. Efferents or output from globus pallidus the pallidum (globus pallidus) is the output aspect of basal ganglia. These fibres take three routes: � Some reach the substantia nigra immediately, � Others go by way of subthalamic nucleus and � Still others via pedunculopontine nucleus. This pathway includes fibres from globus pallidus�red nucleus�rubrospinal tract pathway. Functional neuronal circuits or loops Physiologically, the connections of basal ganglia are best understood in term of useful circuits or loops. Cortex-basal ganglia-cortex neuronal circuit, offers a adverse suggestions loop to management the activity of motor cortex Parts. The major feedback loop (cortex-basal ganglia-cortex neuronal circuit) consists of two components, i. Caudate loop plays a job in cognitive management of motor exercise (thinking strategy of brain). Functions of basal ganglia Control of voluntary motor exercise Basal ganglia management the voluntary movements, which are initiated by the motor cortex. During lesions of basal ganglia, the controlling mechanism is lost and so movements turn out to be inaccurate and awkward. Role of basal ganglia in cost of voluntary motor exercise consists of: � Cognitive management of motor exercise, � Timing and scaling of intensity of actions and � Subconscious execution of some movements. Physiological research have proven that neural discharge in basal ganglia, like cerebellum, begins well before the movements start. The cognitive control of motor activity is executed by the basal ganglia by way of the feedback loops (functional neuronal circuit). As described on page 943, the caudate loop is primarily involved in the cognitive control of motor activity. Two necessary capabilities of mind in controlling the movements are: � Timing of the actions, i. In larger animals, the basal ganglia act as necessary co-ordinating centre of extrapyramidal system. In the absence of basal ganglia, the timing and scaling perform becomes very poor. Basal ganglia subconsciously execute some movements in the course of the performance of skilled motor activities, i. Examples of actions executed subconsciously at the stage of basal ganglia are: � Swinging of arm whereas walking, � Crude motion of facial expression that accompany feelings and � Movements of limbs whereas swimming. By subconscious control of activities, the basal ganglia relieve cortex from routine acts so that cortex can be free to plan its actions. As described on page 943, the putamen suggestions circuit is anxious with control of subconscious execution of some actions, through the efficiency of skilled motor activities as listed above. Control of reflex muscular exercise the basal ganglia exert inhibitory impact on spinal reflexes and regulate activity of muscle tissue, which maintain posture. The co-ordination and integration of impulses for these actions rely upon basal ganglia. Control of muscle tone Muscle spindles and the gamma motor neurons of spinal twine (which are liable for sustaining the tone of the muscles) are controlled by basal ganglia, particularly substantia nigra. Pathway contains projection from cortical inhibitory area-striatumpallidum-substantia nigra-reticular formation-spinal wire. Role in arousal mechanism Globus pallidus and purple nucleus are concerned within the arousal mechanism due to their connections with reticular formation. Extensive lesions in globus pallidus are associated with drowsiness, resulting in sleep. The term Parkinsonism nigra is used to denote such a situation, which may occur as a result of following causes: � Viral encephalitis, � Cerebral arteriosclerosis, � Complication of sure medication. The ensuing improve in inhibitory output to the exterior section of the globus pallidus decreases inhibitory output from the subthalamic nucleus, and this increases the excitatory output from this nucleus to the internal segment of globus pallidus. This in flip will increase the inhibitory output from this phase to the thalamus, causing a reduction in excitatory drive to the cerebral cortex. Number of plus (+) and minus (-) signs indicate relative enhance and reduce in excitation and inhibition of outputs. Its cardinal features are a triad of akinesia, rigidity and tremor; of which akinesia is a hypokinetic characteristic whereas rigidity and tremors are hyperkinetic options. The affected person is unable to provoke the voluntary actions (akinesia) or the voluntary actions are decreased (hypokinesia). Difficulty in initiating voluntary actions is because of hypertonictiy of the muscle tissue. Manifestations of akinesia or hypokinesia embrace: � Delayed motor initiative, as evidenced by extended response time. An elevated discharge of -efferents supplying the muscle spindle causes rigidity. This fact is confirmed by the observation that native injection of 1% procaine resolution into the affected muscles decreases rigidity by abolishing the -discharge. As described on page 942, the striatum (caudate nucleus and putamen) is under the influence of each excitatory (cholinergic) fibres and inhibitory (dopaminergic) fibres. Under normal circumstances, there exists a steadiness between the excitatory and inhibitory influences. The above information may be confirmed by the following observations: � Administration of physostigmine (which increases the action of acetylcholine) results in increase in rigidity and tremors. Lesion Rigidity Oc c urs in basal ganglia lesion, due to this fact, c alled the extrapyramidal rigidity 2. Musc les Both agonist and antagonist musc les are involved involved produc ing a uniform hypertonia typically resulting generally attitude of flexion of the limbs and trunk three. Spasticity Oc c urs in pyramidal trac t lesions, c ommonest website being inside c apsule One group of musc les either agonist or antagonist (usually antigravity musc les) are involved 3. The tremors are observed as rhythmic movements of pronation and supination in fingers, palms, lips or tongue. The tremors appear to happen as a result of pacemaker exercise in the nucleus ventralis intermedius of the thalamus. Thalamic neurons exhibit an intrinsic autorhythmicity, and probably it gets unmasked due to enhance in the inhibitory enter from the pallidum. The thalamic pacemaker exercise induces oscillation in the long-loop reflex pathways, which originate from muscle spindle.
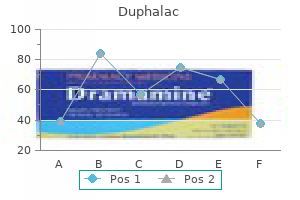
Duphalac 100 ml buy on-line
Constipation also happens due to symptoms week by week purchase duphalac 100 ml on-line imbalance between secretion and absorption in the colon symptoms white tongue buy 100 ml duphalac with mastercard. Persons affected by constipation may develop anorexia, nausea and belly distension and discomfort. Addition of dietary fibres (which are neither digested nor absorbed) in the meals, provides to the majority of faeces which helps in initiating the colonic peristalsis by distending the colon. It acts by enhancing chloride secretion and water into the colon, leading to increased fluidity of colonic contents. Diarrhoea Diarrhoea is a situation which is characterized by increased frequency of defaecation with elevated water content of the faeces. It could develop in number of bacterial, protozoal and viral infections of the intestinal tract, food poisoning, ulcerative colitis, and so on. Enteritis (inflammation of intestinal tract) is often brought on by viral or bacterial an infection. Cholera is a extreme secretory diarrhoea brought on by cholera bacillus which often occurs in epidemics. Thus, increase in intestinal water and electrolyte contents causes diarrhoea leading to about 20 L stool volume/day. Oral rehydration resolution (prepacked combination of sugar, salt) dissolved in water is effective to cut back mortality in epidemic of cholera. The irritation of the ulcerative colitis causes elevated motility which is so great that mass movements occur and colon secretions are tremendously increased. Psychogenic diarrhoea accompanies nervous tension and nervousness (such as during examination). This kind of diarrhoea, also called psychogenic diarrhoea, occurs as a end result of excessive stimulation of parasympathetic system inflicting increased motility and mucous secretion in distal colon. There might happen shock, cardiovascular collapse and even demise (especially in infants). These may be current in the following types: � Starch is the carbohydrate reserve of crops. In it, glucose molecules are principally lengthy chains (1:four linkages and 1:6 linkages) at branching factors. Undigested oligosaccharide incorporates 2�10 monosaccharide molecules that are liberated on hydrolysis. Based on the number of monosaccharide models current, oligosaccharides are additional subdivided into di-, tri-, tetra- and pentasaccharide. Disaccharides embody: � Sucrose (glucose + fructose) is also referred to as desk sugar (cane or beet sugar). Monosaccharides consumed mostly in human diet are hexoses such as: � Glucose (in fruits, vegetables and honey) and � Fructose in fruits. Other carbohydrates which could be current within the human food plan are alcohol, lactic acid, pyruvic acid, pectin, dextrin and minor portions of carbohydrate derivatives in the meat. Digestion of carbohydrates the digestion of carbohydrates begins in mouth, continues in stomach however happens primarily (almost all) within the small gut. Initial starch digestion begins in the mouth by the enzyme -amylase (ptyalin) current within the saliva. However, the position of salivary amylase within the digestion of carbohydrates is restricted by the short period of stay of the meals in the mouth. The optimum pH for the motion of salivary amylase is 6�7, and its exercise within the abdomen completely stops when pH falls beneath 4. Pancreatic -amylase is present within the pancreatic juice which is poured into the duodenum. It hydrolyses nearly all of the starch within 15�30 min of the entry of chyme into the duodenum. Pancreatic amylase acts in an alkaline medium and its digestive activity is elevated by the presence of bile salts. The carbohydrate-splitting brush border enzymes of small intestine include dextrinase, maltase, sucrase and lactase. It is believed that these brush border enzymes digest the oligosaccharides into monosaccharides on the surface of epithelial cells of villi as below: � -Limiting dextrinase. It also assaults 1,4 -glycoside linkages, resulting in sequential elimination of glucose monomers from the dextrins (the breakdown merchandise of starch by the enzyme amylase). Glucose represents 80% and galactose and fructose combinedly represent only 20% of the end products. The monosaccharides include those shaped on the brush border (described above) and in addition those ingested as such. Site of absorption Most of the monosaccharides are absorbed from the mucosal surface of jejunum and upper ileum. The absorption is nearly completed before the remains of a meal reach the terminal ileum. Mechanism of absorption Various monosaccharides are absorbed by following mechanisms: � Glucose and galactose are absorbed by a typical Na +-dependent active transport system. Fructose absorption occurs readily, because many of the fructose is rapidly transformed into glucose and lactic acid throughout the epithelial cells, thus sustaining a highconcentration gradient for diffusion. Glucose and galactose are absorbed into the epithelial cells (enterocytes) lining the mucous membrane of small intestine from their brush border floor (luminal surface) by an active transport mechanism-the sodium cotransport mechanism. The carrier protein (present within the cell membrane) has two binding sites, one for sodium and one other for glucose. The conformational change in the provider protein occurs solely when the binding websites are occupied by the sodium and glucose present within the intestine lumen forming the sodium�glucose�carrier complex. Because of the electrochemical gradient created, sodium strikes into the cell (downhill transport). The move of sodium ions down the gradient is so forceful that the glucose (or galactose) molecule hooked up to the provider protein additionally enters the cell, even towards concentration gradient for glucose (uphill movement). Because two Na+ are transported down their electrochemical gradient, a great amount of vitality is on the market for transport. Thus, almost all of the glucose and galactose current within the gut may be absorbed (against the concentration gradient). The energy so released is required for Na+�K+ pump exercise to maintain the sodium gradient. Due to widespread service protein, the entry of glucose/galactose into the epithelial cells is favoured by the presence of Na+ in the intestinal lumen (similarly, the presence of glucose and galactose within the lumen favours the absorption of Na+). Absorption of glucose is decreased in abnormal states of mucous membrane similar to in enteritis and coeliac illness. Duration of time during which the carbohydrate remains in contact with mucous membrane. Absorption of glucose is decreased because of intestinal hurry in conditions like diarrhoea, excision of small gut and gastrocolic fistula. Hyperpituitarism causes hyperthyroidism and thus increases the glucose absorption and vice versa. Rate of absorption of monosaccharides is variable, being: � Fastest with glucose and galactose, � Intermediate with fructose and � Slowest with mannose or pentoses. About 5% of the entire glucose absorbed is saved as glycogen in the liver and muscle tissue.
Duphalac 100 ml for sale
The neutrophils contain a fever-producing substance called endogenous pyrogen medications on a plane proven 100 ml duphalac, which is an important mediator of febrile response to the bacterial pyrogens treatment 24 seven buy 100 ml duphalac with amex. Phagocytosis Phagocytosis (cell eating) refers to the process of engulfment and destruction of solid particulate material by the cells. In addition to neutrophils, the monocytes and fixed tissue macrophages also work as phagocytes. The margination is attributable to binding of the selectins (cell adhesion molecules) current on the endothelial cells with the carbohydrate molecules present on the surface of neutrophils. The marginated neutrophils are emigrated in a big quantity from the blood at the website of an infection attributable to the international microorganism. The diapedesis of neutrophils is led to by microtubules, microfilaments and interplay of actin with myosin-I on the internal side of the cell membrane. Chemotaxis refers to the method by which the neutrophils are attracted towards micro organism at the website of inflammation. The process of chemotaxis is mediated by the chemotactic brokers called chemokines, that are released on the infected space. Opsonization refers to the method of coating of bacteria by the opsonins by which micro organism turn into tasty to the phagocytes. The principal opsonins are naturally appearing factors in the serum and embody IgG opsonin and opsonin fragment of complement protein. This process triggers G protein-mediated responses, will increase motor activity of the cell, exocytosis and respiratory bursts. The increased motor exercise of neutrophils results in prompt ingestion of bacteria by endocytosis. There are giant variety of proteolytic enzymes, especially geared up for digesting the bacteria. In addition, lysosomes of macrophages also contain lipases which may digest the thick lipid membranes possessed by sure bacteria. The neutrophils and macrophages contain bactericidal brokers (defensins and), which might kill many of the micro organism even when lysosomal enzymes fail to digest them. The bactericidal substance accomplishes the killing process by the next mechanisms: � Oxygen-dependent bactericidal mechanism, which is mediated by oxidizing brokers (superoxides, H2O, and so on. O-2 and H2O2 (oxidants) both are bactericidal agents, but H2O2 is converted by the enzyme catalase into H2O and O2. These are referred to as pus cells and along with plasma leaked from the blood vessels, liquefied tissue cells and red blood cells escaped from the damaged capillaries represent the pus. Defective phagocytic features Defective phagocytic capabilities make the patients susceptible to recurrent infections. The following abnormalities could also be related to faulty phagocytic features. Defective chemotaxis occurs within the following conditions: � Lazy leucocyte syndrome, a uncommon congenital abnormality. Defective phagocytosis due to lack of opsonization happens in: � Hypogammaglobulinaemia, � Hypocomplementaemia, � After splenectomy and � In sickle cell illness. Defective killing by phagocytes occurs in: � Chronic granulomatous diseases of childhood. Therefore, due to its deficiency, microbial killing power is reduced but not absent, as a result of a lot of the oxygen-dependent bactericidal mechanism remain intact. Multiple infections occur in this condition due to defective killing of organisms. Inflammation Inflammation is a response or tissue change complicated led to by the substances launched from the injured tissue or in response to foreign substances such as bacteria. The substances launched from the injured tissues embrace histamine, serotonin, prostaglandins, lymphokines, response merchandise of complement and clotting system. In irritation, tissue macrophages are the first line of defence against infection. As identified earlier, macrophages can phagocytize about 5 occasions more bacteria and larger particles (including even neutrophil and necrotic tissue). Walling-off effect of inflammation is to wall off the world of injury from remaining tissue. This effect is led to by blockage of tissue areas and lymphatics by clotting of tissue fluid by fibrinogen. Variations in counts Neutrophilia Neutrophilia refers to increase within the circulating neutrophil counts (absolute depend > 10,000/mm3). Causes Physiological causes of neutrophilia are: � Newborn infants, � After train, � After meals, � Pregnancy, � Menstruation, � Parturition, � Lactation, � Mental stress and emotional stress and � After injection of epinephrine. Pathological causes of neutrophilia are: � Acute pyogenic bacterial infections, � Noninfective inflammatory conditions like gout and acute rheumatic fever, � Acute tissue destruction as in: � Burns, � Postoperatively and � Myocardial infarction. Neutropenia Decrease in neutrophil rely is named neutropenia (absolute depend < 2500/ mm3). Causes of neutropenia � Typhoid and paratyphoid fever, � Malaria, � Aplasia of bone marrow and � Bone marrow depression because of: � Drugs corresponding to chloromycetin and cytotoxic medicine used in malignant ailments, � Repeated exposure to X-rays and radiations and � Chemical poisons like arsenic. The neutrophils enter the bloodstream largely as bilobed cells, but the number of lobes will increase to 5 or extra by the end of their brief lifespan of 8�10 h. Thus, the presence of youthful cells (shift to the left) and more mature cells (shift to the right) within the blood can provide essential information about the rate of formation and release of neutrophils from the bone marrow. Variations in neutrophil morphology Some of the variations seen in morphology of neutrophils are: 1. Heavy, dark staining and coarse toxic granules are the traits of bacterial infections. Cytoplasmic vacuolation may develop in bacterial infections corresponding to in septicaemia. It is indicative of a hypoactive bone marrow, as seen in megaloblastic anaemia and uraemia. It is indicative of hyperactive bone marrow, as seen in extreme infections and leukaemias. It is an inherited disorder during which majority of the neutrophils have decreased number of nuclear segments (1�2) and coarsely staining chromatin. The two lobes are connected by the chromatin strands and thus look spectacle shaped. Like neutrophils, eosinophils are attracted in the direction of the endothelial cells by selectins and enter the tissue by diapedesis. They play an necessary position within the defence mechanism of body, especially in parasitic infestations. Because of this, eosinophils are able to harm the parasitic larvae, that are massive to be engulfed by phagocytosis. The eosinophils enhance in number in allergic situations like bronchial asthma and hay fever. The eosinophils are present in abundance within the mucosa of respiratory tract, gastrointestinal tract and urinary tract, the place they most likely provide mucosal immunity. Variation in counts Eosinophilia Eosinophilia refers to enhance in the eosinophil depend (absolute count > 500/mm3).
Huckleberry (Bilberry). Duphalac.
- Chest pain (angina), varicose veins, cataracts, hardening of the arteries (atherosclerosis), diabetes, arthritis (osteoarthritis), gout, skin problems, hemorrhoids, urinary tract problems, chronic fatigue syndrome, and other conditions.
- What is Bilberry?
- Dosing considerations for Bilberry.
- Improving night vision.
- Are there safety concerns?
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- How does Bilberry work?
- Lesions in the eye (retina) in people with diabetes or high blood pressure.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96235
Buy duphalac 100 ml lowest price
The glucose-1-phosphate launched as a end result of glycogen phosphorylase activation is prevented from present process resynthesis to glycogen by simultaneous inhibition of glycogen synthase medications side effects duphalac 100 ml buy visa. After the glycogen in liver is exhausted symptoms knee sprain safe 100 ml duphalac, glucagon increases the speed of gluconeogenesis, i. Gluconeogenesis causes a sluggish but more sustained rise in blood glucose which lasts for hours and days. Glucagon activates multiple enzymes concerned in gluconeogenesis, particularly the enzyme system changing pyruvate to phosphopyruvate (rate-limiting step in gluconeogenesis). It additionally increases the entry of amino acids from blood to liver cells and makes them available for gluconeogenesis. Glucagon will increase the amino acid uptake of liver, which in turn promotes gluconeogeneis. Other miscellaneous actions of glucagon embody: � Inhibition of renal tubular sodium reabsorption, resulting in natriuresis. Therefore, the ratio of their concentrations could additionally be more crucial than their actual focus. In addition, they co-ordinate the efficient disposition of the nutrients input from the meals. Under basal situations, the standard molar ratio of insulin to glucagon in plasma is about 2. Under circumstances that require mobilization and increased use of endogenous substrate such as fasting and extended train, the insulin� glucagon ratio drops to 0. This decreased insulin�glucagon ratio outcomes from each the decreased insulin secretion and increased glucagon secretion. Under circumstances in which substrate storage is advantageous, such as after a pure carbohydrate load or a combined meal, the insulin�glucagon ratio rises to 10 or extra. This high insulin:glucagon ratio helps in storage of substrate by: � Increasing glucose uptake, oxidation and conversion to liver and muscle glycogen. After a pure protein meal, interestingly, solely a small change in insulin� glucagon ratio occurs; nevertheless, secretion of insulin in addition to that of glucagon is increased. The situation is attributable to: � Excess circulating antibodies in opposition to insulin within the fetus, resulting in pancreatic islet stimulation by raised blood glucose stage and raised amino acids in the diabetic mom. Normally, free insulin in the maternal blood is destroyed by protease within the placenta, but antibody-bound insulin is protected and reaches the fetal blood. Glucagon stimulates production and release of glucose, free fatty acids and ketoacids, which in turn suppress glucagon secretion, and glucagon in turn stimulates the conversion of amino acids to glucose. The most necessary precept is the upkeep of normoglycaemia within the face of elevated nutrients in the management of glucagon discussed briefly, governing glucagon secretion tissue calls for. Blood glucose level Low blood glucose focus is essentially the most potent stimulus for secretion of glucagon. Glucagon secretion by cells will increase even when blood sugar falls to just below 70 mg% (normal vary 70�110 mg%). Glucagon secretion is stimulated rather more by low glucose ranges if insulin is absent. The presence of insulin significantly potentiates the suppressive effect of excessive glucose ranges on cells. Secretory sample of glucagon in response to blood glucose ranges is simply reverse to insulin. Therefore, during starvation, glucagon secretion increases whereas that of insulin decreases, and conversely, after a carbohydrate-rich meal, glucagon secretion decreases while that of insulin increases. Secretion of glucagon is elevated by a protein-rich meal and, most effectively, by amino acids similar to arginine and alanine. Since the amino acids improve insulin secretion also, the simultaneous launch of glucagon along with insulin prevents the chance of hypoglycaemia, which otherwise would occur after a high protein meal. This accounts for the improved glucagon response to orally ingested nutrients versus the responses to intravenously delivered vitamins. Role of nervous system Sympathetic nerve stimulation to pancreas will increase glucagon secretion. Various stresses, fasting, exercise and an infection increase the glucagon secretion in part by their stimulatory impact on sympathetic nervous system and partly by release of glucocorticoids. A wholesome particular person is able to maintaining the blood glucose degree within a narrow vary. High glucose concentration will increase osmotic stress of extracellular fluid and osmotic switch of water from cells to extracellular fluid resulting in dehydration of cells. In addition to it, osmotic diuresis causes elevated loss of water from the physique thereby reducing extracellular fluid quantity which also causes compensatory dehydration of cells. Since lack of body weight occurs regardless of extreme meals consumption, diabetes known as a condition of starvation in the midst of a lot. Because of impaired phagocytic operate, diabetics are extra vulnerable to infections in contrast with the nondiabetics. Osmolarity of the blood goes on rising with the rising blood sugar levels. With the passage of time, a stage could come when glucose manufacturing is elevated and urinary excretion is decreased, and the plasma glucose stage could enhance up to 1000 mg%. Such a excessive hyperosmolality may trigger dehydration in central nervous system resulting in impairment of cerebral functions. Ultimately, a situation known as nonketotic hyperosmolar coma may outcome, which may be even deadly. Glycosylation of proteins refers to post-translation, nonenzymatic addition of sugar residues to amino acids of proteins. Glycosylated haemoglobin refers to the glucose-derived merchandise of normal haemoglobin (HbA). Among the glycosylated haemoglobins, probably the most plentiful type is HbA1C, which is produced by condensation of glucose with N-terminal valine of every chain of haemoglobin A (HbA). Glycosylation of tissue proteins happens when the blood glucose levels remain elevated for a protracted duration (years). Glycosylation leads to irreversible adjustments within the chemical construction of tissue proteins. These chemical adjustments have been implicated in producing long-term problems of diabetes mellitus, corresponding to: � Diabetic nephropathy, � Diabetic retinopathy, � Diabetic neuropathy and so on. Ketosis, hypertriglyceridaemia and their consequences Since because of insulin deficiency the utilization of glucose is poor, the body turns to fats for acquiring energy by lipolysis. Utilization of fats beyond a sure point within the face of impaired carbohydrate utilization results in formation of ketone our bodies in excess. If production of ketone our bodies is greater than their destruction, there occurs ketosis or ketonaemia. Ketone our bodies being hyperosmolar remove water from the cells producing mobile dehydration. Depression of consciousness to the level of coma may ultimately guarantee owing to marked acidosis and dehydration which can finally result in demise. Therefore, in diabetes, because of insulin deficiency, the protein anabolism is suppressed and catabolism is elevated. The amino acids released so are: � Used in massive quantities for vitality manufacturing and � Act as substrate for enhanced gluconeogenesis in liver promoted by insulin deficiency.
Duphalac 100 ml effective
The right ventricular outflow is to the aorta treatment action group 100 ml duphalac order otc, while left ventricular outflow is to the pulmonary artery medicine x protein powder duphalac 100 ml buy generic on line. In the normal heart, the left coronary arises from the left/anterior sinus of Valsalva and the right coronary artery arises from the right/anterior sinus of Valsalva. There are quite a few different branching patterns that can be seen as properly as single coronary artery. The aorta and pulmonary artery are transected and moved to their respective ventricle. The coronary arteries are removed in buttons from the rightsided aortic root, mobilized, after which transferred to the left-sided pulmonary root (which becomes the neoaortic root). Significant stenosis of either outflow tract might preclude the switch operation and require an alternate surgical strategy with a Nikaidoh or Rastelli kind repair. Deep hypothermia may be especially useful with multidose cardioplegia protocols as temperature alone can have an arresting effect and direct redosing of cardioplegia in neonates is tough. The perfusionist ought to have extra cardioplegia ready in case an additional period of myocardial arrest is required. The pulmonary valve in tricuspid atresia can be atretic, dysplastic, or unrestrictive. If the proper coronary heart is unable to present pulmonary blood circulate, the affected person is often led down the pathway of staged procedures toward a Fontan circulation. Case notes: � Target temperature is 28�34 �C. Repair of the valve could embody placing an annuloplasty ring which helps management the annulus measurement and supply for improved leaflet coaptation. The perfusionist should prepare the cardioplegia as quickly as bypass parameters are deemed acceptable. They could current as a singular small hole centrally positioned in the septum requiring solely main closure or current as multiple holes in numerous elements of the septum, which can be troublesome for the surgeon to visualize and handle. Membranous septum this interventricular communication is commonly necessary for the systemic ventricular outflow tract. Alpha-stat blood gas administration is carried out for adults and sufferers with suspected vascular disease. Case notes: Chapter 7 Notes on select issues during bypass Blood pressure greater than expected �Is the value correct Significant collateral/shunt circulate to the left coronary heart within the presence of restrictive or absent septal defects could result in continued ejection. Otherconsiderations: Perfusion for Congenital Heart Surgery: Notes on Cardiopulmonary Bypass for a Complex Patient Population, First Edition. If the bypass circuit strain is unchanged or as expected with a displayed low patient pressure, the issue is extra likely to be with the patient arterial linesystemitself. Physicalobstructiontoflow Check for kinked tubing within the arterial circuit, especially where the tubing enters and exits the roller head. A reservoir lamp or flashlight may be useful with peering into the tubing guides to checkthis. The use of a move probe can quickly diagnose whether or not calculated move and delivered circulate are disparate. There is the possibility that when the arterial head tubing changestemperature through the case (warming with constant flow, cooling with low flow hypothermic bypass), the occlusion could change. Otherconsiderations: Notes on choose issues during bypass 151 Bypass circuit stress larger than anticipated �Isthevalueaccurate Otherconsiderations: 152 Chapter 7 Bypass circuit pressure decrease than expected �Isthevalueaccurate You can even briefly attach the bypass circuit pressure dometoadifferenttransducer(i. Some aortopulmonary collaterals will not be accessible and so elevated pump flows will be required throughout the bypass run. Thisisnotalwayspossibleandso aggressive subject suction (and venting) could also be neededtocompensate. There is the likelihood that once the arterial head tubing changes temperature in the course of the case (warmingwithconstantflow,coolingwithlowflow hypothermic bypass), the occlusion might change. Otherconsiderations: 154 Chapter 7 heat trade problem (slow cooling or warming) �Whatisthepumpflowrate Heat exchange performance is partially driven by the counter circulate precept (water and blood flows are opposing to maximize thermal transfer) and by absolutely the water flow by way of the system. Externalshunts Are there any inadvertently open circuit shunts (oxygenatorprime/purgeline) If isoflurane is integral with the circuit, is there a chanceofmalignanthyperthermia Areservoirlamporflashlightcan be useful with peering into the tubing guides to checkthis. Isthereachanceofaslowwater-to-bloodleakcausing metabolic acidosis and a concomitant want for bicarbonateadministration Isthelactatelevel elevated with rising patient temperature and a low venoussaturation(atleastlowerthanexpectedgiven the pump parameters) Otherconsiderations: 160 Chapter 7 paO2 lower than anticipated �Whatisthevenoussaturation Or, has the unit been in use for a time approaching the producer really helpful restrict Maximumgasflowvalues and deadlines for such are usually specified by the manufacturer. Switchtoastandalone100%oxygen tank with its personal move meter whereas verifying the problem and evaluating the general delivery system. Chapter eight Notes on select emergency procedures throughout bypass A perfusionist is confronted with nearly countless potentialities for failure or different points with the hardware and disposables used for cardiopulmonary bypass. Issues before or after bypass can usually be dealt with in a peaceful and managed manner. Four lifethreatening points that the perfusionist have to be prepared to cope with on bypass are arterial pump head failure, oxygenator failure, large air embolization, and acute aortic dissection on the initiation of bypass. Chapter 7 reviewed some issues that are extra widespread to be seen by the perfusionist. Here, high-risk/ low-frequency bypass emergencies that put the patient at considerable risk are discussed. Perfusion for Congenital Heart Surgery: Notes on Cardiopulmonary Bypass for a Complex Patient Population, First Edition. Regardless of the cause, the preliminary response by the perfusionist is to quickly assess the trigger. Then, with the whole staff being aware of the pump emergency, further personnel can assist the perfusionist by either hand cranking, retrieving provides, or helping diagnose and proper the problem.
Duphalac 100 ml discount with amex
Bone remodelling refers to a means of bone resorption followed by bone formation which retains on occurring all through life in a cyclic method symptoms of 100 ml duphalac discount with mastercard. The bone remodelling seems to be the outcome of co-ordinated activity of groups of interacting osteoclast and osteoblast cells which make up the bone remodelling unit medicine 513 duphalac 100 ml cheap visa. About 5% of the bone mass is being remodelled by about 2 million bone remodelling models within the human skeleton at anybody time. The elimination rate for bone is about 4% per yr for compact bone and 20% per 12 months for trabecular bone. A bone remodelling cycle takes about one hundred days and consists of two phases: the resorption part and the succeeding formation section. In this part, mineralized bone is reabsorbed by osteoclasts releasing calcium and phosphate. Formation part lasts for subsequent ninety days and is characterized by reformation of bone by osteoblasts (assimilating calcium and phosphate). Remodelling happens in areas of bone which have been structurally weakened by fatigue, by having uncommon mechanical stress placed on them or by disease. The osteocytes embedded deep inside mineralized bone act as mechanoreceptors that decide up mechanical signals transmitted by way of interstitial fluid and respond by increasing phospholipase-C, Ca2+ and protein kinase C exercise. The lining cells then provoke recruitment differentiation of osteoclast cells via communication with stromal precursors within the bone marrow. The paired activity of osteoclast and osteoblast cells in bone remodelling is properly regulated. All features of the remodelling cycle are influenced by a giant number of hormones and development elements, in addition to cytokines from immune cells Table eight. The process of bone remodelling is one example of coordinated perform of the endocrine and immune systems. For example, in athletes, soldiers and others in whom the bone stress is more, the bones turn into heavy and powerful. Each gland is slightly oval in shape and is in regards to the measurement of a cut up pea, measuring 6 � four � 2 mm. Normally, there are four parathyroid glands, but rarely they may be more (6 or even 8). Histological structure the parenchyma of the parathyroid gland is made up of cells that are arranged in cords. The cells of the parathyroid glands are of two major types: chief cells and oxyphil cells. Chief cells, also called as principal cells, are much more numerous than the oxyphil cells. These are small round cells having clear (agranular) cytoplasm and vesicular nuclei. Oxyphil cells, in distinction to chief cells, are much bigger and contain granules that stain strongly with acidic dyes. It additionally inhibits proliferation of parathyroid cells and upregulates the Ca2+ receptors in parathyroid cells. In this course of, the calcium is transferred from the bone canalicular fluid into osteocytes and then into the extracellular fluid. This paradoxical impact could be defined by the truth that in hyperparathyroidism, hypercalcaemia produces such a large load of filtered calcium in glomerular filtrate that regardless of increased distal tubular calcium reabsorption, the net excretion of urinary calcium is elevated. Actions on intestines Parathormone greatly enhances both calcium and phosphate absorption from intestine not directly by rising synthesis of 1,25dihydroxycholecalciferol in the kidney. Vitamin D the term vitamin D refers to group of carefully related steroids produced by the motion of ultraviolet light on certain provitamins. Because of its fats solubility, vitamin D absorption from the intestine is mediated by the bile salts. Besides dietary consumption, cutaneous synthesis is the opposite more important source of vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) within the physique. Vitamin D3 is synthesized primarily in the specialised pores and skin cells, called keratinocytes, which are located within the inside layers of epidermis. In the kidneys, the much less active metabolite 24,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol can be fashioned. The concentrations, approximate half-lives and estimated daily production charges for the three key vitamin D metabolites in humans are shown in Table 8. Recently, it has been seen that a mice poor in klotho protein shows accelerated aging, decreased bone density, mineral density and calcification, hypocalcemia and hyperphosphotaemia. It regulates the plasma ranges of calcium and phosphate by performing at three totally different websites: gut, bone and kidney. In human intestinal epithelium, two forms of calbindins are induced (calbindin-Dqk and calbindin 28k). These molecules could carry calcium throughout the intestinal cell or they might be essential for maintaining focus of free intracellular calcium low (when calcium is being absorbed from the food). The fee of calcium absorption throughout the duodenum is proportional to the cell content of calbindin. The formation of receptor� calcitriol complicated on osteoblasts originates cytokine signal that stimulates recruitment, differentiation and fusion of precursors into osteoclasts. Calcitriol maintains levels of calcium and phosphate, and calcium phosphate ion product within the regular vary by causing bone resorption (as above). It also causes direct effect on bone formation by increasing osteoblastic proliferation, alkaline phosphatase secretion and osteoclastin synthesis. Lack of vitamin D is related to defective mineralization of cartilage in addition to bones. Calcitriol will increase renal reabsorption of calcium and phosphate by growing the variety of calcium pump. About 98�99% of filtered calcium is absorbed (60% in the proximal tubule and rest in ascending limb of loop of Henle and distal tubule). Other actions of calcitriol Besides the above well-known websites of motion (intestine, bone and kidney) of vitamin D, the calcitriol receptors have additionally been found on the cells in numerous tissues. Therefore, vitamin D deficiency can end result in muscle weak point and cardiac dysfunction. Stimulation of differentiation of keratinocytes and inhibition of their proliferation is believed to be attributable to calcitriol by its paracrine and autocrine operate. Thus, formation of the outer cornified layer of the epidermis, with its applicable content of enzymes and structural proteins, is regulated by vitamin D. Probably, because of this motion, calcitriol has proven promise in the therapy of psoriasis. Therefore, an increased incidence of infections is famous in patients with deficiency of vitamin D. Calcitriol appears to be involved in regulation of development and production of development elements as the vitamin D receptors are found additionally in pancreatic islets, anterior pituitary, hypothalamus, placenta, ovary, aortic endothelium and pores and skin fibroblasts. Calcitonin is synthesized within the C-cells or parafollicular cells of the thyroid gland.
Generic duphalac 100 ml visa
A load that begins acting on a muscle earlier than it begins to contract is known as freeload (or preload) medicine reminder alarm 100 ml duphalac for sale. Example of a free-load on the muscles in an intact body is filling water from a faucet by holding a bucket in the hand medicine for vertigo buy generic duphalac 100 ml. The free-load increases the force of contraction and work efficiency of the muscle. The freeload stretches the muscle passively producing a passive pressure throughout the muscle. This passive tension increases the drive of muscle contraction in two methods: � By increasing the preliminary size of the muscle to its resting size at which most force is generated, and � By including an elastic recoil force to the muscle during its contraction. Therefore, up to physiological limits, the greater the initial length, greater is the pressure of contraction. When a muscle is faraway from the physique, it shortens because muscle tissue within the physique are in a state of slight stretch. The length�tension relationship graph can be plotted by measuring isometric pressure at completely different muscle lengths in an isolated muscle preparation. The size of the muscle is diversified by changing the distance between its two attachments and the recording is made as: � First, at every length, the passive rigidity is measured. During isometric contraction, the stress developed within the muscle is proportional to the cross-bridges shaped between actin and myosin filaments. After-load refers to the load which acts on the muscle after the start of muscular contraction. The work done in an after-loaded muscle is lower than that of a free-loaded muscle. The load acts on the muscle tissue of arm solely after lifting the item off the bottom, i. Experimentally, the impact of after-load can be studied by subjecting the muscle to after-load preparation; when a muscle contracts against a load it exhibits three phases: i. In this phase of muscular contraction, as the name indicates, there occurs no shortening of the muscle. Intermediate isotonic contraction section starts when the muscle rigidity exceeds the load and load starts moving. After the muscle becomes shorter than the resting size, any further shortening is associated with a decrease within the rigidity. And, when the stress generated equals the load, the muscle as soon as once more begins contracting isometrically. It shows that: � As the load will increase, the latent interval increases as a end result of lever inertia. Following inferences could be drawn from the force�velocity curve: � When load is zero, the muscle contracts rapidly and the rate of muscle shortening is maximum (Vmax). With further improve within the load, a stage comes when the muscle is unable to raise the load. Calculations � Actual peak (h) is calculated bearing in mind the magnification factor (which is the identical as L/l): Work carried out is then calculated as: Work carried out W = w (weight in g) � h (actual top in cm) � To categorical the work accomplished in ergs, the above reading is multiplied by 981. Effect of temperature the contractile response is altered as a result of the effect of temperature. At moderately high temperature (say 40�C), there happens: � Faster diffusion of Ca2+ ions from sarcoplasmic reticulum to sarcoplasm resulting in: � An enhance within the muscle excitability, � Acceleration of the chemical processes concerned in muscle contraction and � A decrease in muscle viscosity. At high temperature (above 50�60�C), there occurs coagulation of the muscle proteins resulting in stiffness and shortening of the muscle fibres. Some other forms of rigors (other than the warmth rigor) are additionally described here due to the same changes: � Cold rigor. Some traits of the skeletal muscles within the intact body � Muscle tone � Nature of muscle contraction within the intact body � Gradation of muscular exercise � Muscle fatigue � Mechanics of muscle tissue Muscle tone Muscle tone is the state of slight contraction with certain diploma of vigour and rigidity. Muscle tone is a state of partial tetanus of the muscle maintained by asynchronous discharge of impulses from gamma motor neurons within the anterior grey horn of the spinal cord involved with the motor nerve provide of the muscle tissue. The gamma motor neurons in turn are managed by some greater centres in the mind (see page 1063). Abnormalities of the muscle tone embrace: � Hypertonic state or the spastic paralysis of the skeletal muscular tissues that happens in upper motor neuron lesions. Spasticity results because of exaggerated exercise of lower motor neurons following or loss of inhibitional exercise of higher motor neurons. The tone of the affected muscular tissues is decreased or totally misplaced and finally the muscle tissue bear wasting. Weak contractions outcome from low frequency of firing (5�10/s) of the motor models. The anticipated jerkiness and the drawback of incomplete tetanus are overcome by the asynchronous discharge (out of step firing) of groups of motor items. Algebraic summation happens, the individual variations are evened out and a easy contraction outcomes. The diploma to which the motor neuron discharge is asynchronous is related both to the drive and duration of contraction. With rising firing charges and, of course, with more recruitment of motor models, contractions turn into stronger till, at and beyond the tetanizing fee, sustained and powerful contractions end result. Gradation of pressure of muscle contraction within the intact physique For performing totally different sorts of labor. Gradation of muscle power in muscle tissue is made attainable by certain elements which have an effect on the force of contraction. The drive of contraction produced in a muscle relies upon upon the variety of motor units recruited. With rising effort, more and more motor units from the motor neuron pool of a muscle are recruited into activity. The motor management system within the brain can range the drive of contraction by varying the frequency of nerve impulses stimulating the muscle. As the impulse frequency will increase, its effects are summated (wave summation) and the muscle tension will increase.
[newline]With growing synchronization of the motor items, the force of contraction increases. Warming up is the term used within the parlour of sports persons for the workouts carried out before really participating in any sport event. Muscle fatigue Failure of a muscle to maintain rigidity on account of earlier contractile activity is called muscle fatigue. If the muscle is allowed to rest after the onset of fatigue it recovers its capability to contract. Muscle fatigue is discussed underneath two separate situations: � Fatigue in an isolated muscle, and � General fatigue. The web site of fatigue, when the muscle has undergone fatigue by way of stimulation of its nerve, is neuromuscular junction, as a outcome of the muscle responds briskly on direct stimulation. The repeated stimulation of muscle itself leads to precise muscle fatigue and is because of depletion of muscle glycogen. General fatigue General fatigue refers to the fatigue of a lot of the muscle tissue that develops after prolonged common train corresponding to marathon running and aggressive soccer match enjoying. Onset and recovery of fatigue is determined by: � Intensity and period of train, and � Type of muscle fibres. In the human body, the sites of fatigue are within the following order: � Fatigue of synapses of central nervous system because of slight hypoxia occurs to begin with.