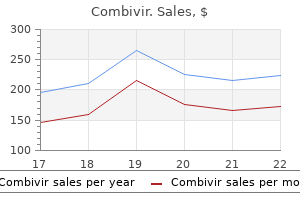
Combivir 300mg discount fast delivery
Also symptoms 12 dpo combivir 300mg order with visa, a method known as plasmapheresis could also be used to remove harmful antibodies from the blood plasma 897 treatment plant rd purchase 300mg combivir free shipping. Trust/Tony Stone Images/ Getty Images Muscles transfer and stabilize joints and produce stresses that affect ossification, bone remodeling, and the shapes of bones. Why train is followed by a protracted state of elevated oxygen consumption, and the name of that state 10. Differences between gradual oxidative and quick glycolytic muscle fibers; the respective advantages of each; how they relate to the ability and recruitment of motor items; and examples of muscle tissue by which every type predominates 11. Examples of resistance exercise and endurance exercise, and the results of each on muscle performance 11. Five physiological properties of all muscular tissue and their relevance to muscle function 2. Connective tissues related to a muscle fiber and their relationship to muscle�bone attachments eleven. Excitation of a muscle fiber; how a nerve sign leads to a traveling wave of electrical excitation in a muscle fiber 2. Excitation�contraction coupling; how electrical excitation of a muscle fiber results in publicity of the active sites on the actin of a thin myofilament three. The sliding filament mechanism of contraction; how publicity of the active sites leads to repetitive binding of myosin to actin and sliding of the skinny filaments over the thick filaments four. Muscle relaxation; how the cessation of the nerve sign leads to blockage of the lively websites so myosin can not bind to them and maintain muscle rigidity 5. The length�tension relationship in muscle; why muscle would contract weakly if it was overcontracted or overstretched just previous to stimulation; and the way this precept pertains to the perform of muscle tone eleven. The sarcolemma and sarcoplasm, and the roles of glycogen and myoglobin within the sarcoplasm 2. The function of myoblasts within the improvement of a muscle fiber, and how they provide rise to the multinuclear condition of the muscle fiber and to the satellite cells exterior to the fiber 3. Composition and molecular group of a thick myofilament, and the structure of a myosin molecule 6. Composition of a skinny myofilament; the organization of its actin, tropomyosin, and troponin; and the active websites of its actin monomers 7. Composition of elastic filaments and their relationship to the thick filaments and Z discs 8. Names of the striations of skeletal and cardiac muscle and the way they relate to the overlapping arrangement of thick and thin myofilaments 10. The autorhythmicity of the heart and its ability to contract without nervous stimulation four. The uncommon fatigue resistance of cardiac muscle; structural and biochemical properties that account for it 5. Functional differences between easy muscle and the 2 forms of striated muscle 6. The structure of smooth muscle myocytes and what takes the place of the absent Z discs and T tubules eleven. Differences between multiunit and singleunit easy muscle, and the nerve�muscle relationship of each 11. Terms for the minimum stimulus depth needed to make a muscle contract, and for the delay between stimulation and contraction 2. Differences between isometric and isotonic contraction, and between the concentric and eccentric types of isotonic contraction 11. Motor items; the meanings of enormous and small motor units; and the respective benefits of the 2 types 2. How excitation�contraction coupling in clean muscle differs from that in skeletal muscle; the roles of calmodulin and myosin light-chain kinase in smooth muscle contraction 14. Benefits of the stress�relaxation response of clean muscle, and of its absence of a length�tension relationship Testing Your Recall 1. To make a muscle contract extra strongly, the nervous system can activate more motor items. The useful unit of a muscle fiber is the, a segment from one Z disc to the following. In autonomic nerve fibers that stimulate single-unit easy muscle, the neurotransmitter is contained in swellings referred to as. For the primary 30 seconds of an intense exercise, muscle will get most of its power from lactate. Smooth muscle controls the curvature of the lens of the attention and the diameter of the pupil, but it would serve poorly for controlling eye actions as in tracking a flying chook or reading a page of print. Explain how this illustrates the complementarity of type and performance at a mobile and molecular level. As skeletal muscle contracts, a number of bands of the sarcomere become narrower and disappear, and one or more of them stay the same width. Spinal cord Nerves The nervous system is one of nice complexity and thriller, and can absorb our attention for the next 5 chapters. It profoundly intrigues biologists, physicians, psychologists, and even philosophers. Its scientific study, referred to as neurobiology, is regarded by many as the last word problem facing the behavioral and life sciences. We will begin on the simplest organizational level-the nerve cells (neurons) and cells referred to as neuroglia that assist their perform in varied methods. We will then progress to the organ level to look at the spinal wire (chapter 13), mind (chapter 14), autonomic nervous system (chapter 15), and sense organs (chapter 16). If each cell behaved with out regard to what others were doing, the outcome would be physiological chaos and demise. We have two organ systems dedicated to maintaining internal coordination- the endocrine system (see chapter 17), which communicates by the use of chemical messengers (hormones) secreted into the blood, and the nervous system (fig. There is solely one nervous system, and these subsystems are interconnected parts of the whole. A ganglion1 (plural, ganglia) is a knotlike swelling in a nerve where the cell bodies of peripheral neurons are concentrated. The peripheral nervous system is functionally divided into sensory and motor divisions, and every of those is further divided into somatic and visceral subdivisions. Distinguish between the central and peripheral nervous methods, and between visceral and somatic divisions of the sensory and motor systems. This produces voluntary muscle contractions in addition to involuntary somatic reflexes. Universal Properties the communicative function of the nervous system is carried out by nerve cells, or neurons.
Combivir 300mg discount free shipping
Hyperemia not solely ends in the more speedy supply of leukocytes medicine look up drugs buy generic combivir 300mg online, but in addition washes toxins and metabolic wastes from the tissue extra quickly medicine zithromax combivir 300 mg buy visa. In addition to dilating native blood vessels, the vasoactive chemical substances stimulate endothelial cells of the blood capillaries and venules to contract barely, widening the gaps between them and rising capillary permeability. This permits for the easier movement of fluid, leukocytes, and plasma proteins from the bloodstream into the encompassing tissue. Among the useful proteins filtering from the blood are complement, antibodies, and clotting elements, all of which help in combating pathogens. In the realm of harm, they produce cell-adhesion molecules called selectins, which make their membranes sticky, and snag leukocytes arriving within the bloodstream. Leukocytes adhere loosely to the selectins and slowly tumble along the endothelium, generally coating it so thickly they obstruct blood move. The leukocytes then crawl by way of the gaps between the endothelial cells- an action known as diapedesis 15 or emigration-and enter the tissue fluid of the damaged tissue (fig. Chemical messengers are launched by basophils, mast cells, blood plasma, and damaged tissue. These inflammatory chemicals stimulate leukocyte margination (adhesion to the blood vessel wall), diapedesis (crawling through gaps within the wall), chemotaxis (movement towards the source of the inflammatory chemicals), and phagocytosis (engulfing bacteria or other pathogens). Containment and Destruction of Pathogens One precedence in irritation is to stop pathogens from spreading by way of the physique. The fibrinogen that filters into the tissue fluid clots in areas adjoining to the damage, forming a sticky mesh that sequesters (walls off and isolates) bacteria and other microbes. Heparin, the anticoagulant, prevents clotting in the quick area of the damage, so bacteria or other pathogens are primarily trapped 15 16 dia = through; pedesis = stepping additional = outside; vas = vessel in a fluid pocket surrounded by a gelatinous capsule of clotted fluid. They are attacked by antibodies, phagocytes, and different defenses, while the surrounding areas of clotted tissue fluid prevent them from simply escaping this onslaught. The chief enemies of bacteria are neutrophils, which accumulate within the inflamed tissue within an hour. After emigrating from the bloodstream, they exhibit chemotaxis-attraction to chemical compounds (chemotactic factors) such as bradykinin and leukotrienes that information them to the site of injury or an infection. As they encounter bacteria, neutrophils avidly phagocytize and digest them, and destroy many more by the respiratory burst described earlier. Neutrophils additionally recruit macrophages and extra neutrophils by secreting cytokines, like shouting "Over here! Activated macrophages and T cells in the infected tissue secrete cytokines referred to as colony-stimulating elements, which promote the manufacturing of more leukocytes (leukopoiesis) by the pink bone marrow. In the case of allergy or parasitic infection, an elevated eosinophil count, or eosinophilia, may also happen. Tissue Cleanup and Repair Monocytes are main agents of tissue cleanup and restore. They arrive inside eight to 12 hours, to migrate from the bloodstream, and turn into macrophages. Macrophages engulf and destroy bacteria, damaged host cells, and dead and dying neutrophils. They additionally act as antigen-presenting cells, activating immune responses described later. The swelling compresses veins and reduces venous drainage, while it forces open the valves of lymphatic capillaries and promotes lymphatic drainage. The lymphatics can collect and take away bacteria, lifeless cells, proteins, and tissue debris higher than blood capillaries or venules can. These dead cells, different tissue particles, and tissue fluid kind a pool of yellowish fluid referred to as pus, which accumulates in a tissue cavity known as an abscess. Blood platelets and endothelial cells in an space of injury secrete platelet-derived growth issue, an agent that stimulates fibroblasts to multiply and synthesize collagen. At the identical time, hyperemia delivers oxygen, amino acids, and other necessities of protein synthesis, whereas the heat of infected tissue will increase metabolic price and the velocity of mitosis and tissue repair. It is an important alarm sign that calls our consideration to the harm and makes us restrict the use of a physique part so it has a chance to relaxation and heal. Earlier it was stated that innate immunity employs protecting proteins, protective cells, and protective processes. The remainder of this chapter is anxious with adaptive immunity (the third line of defense). Adaptive immunity is now defined by three characteristics that distinguish it from the three that were itemized earlier (local, nonspecific, and lacking memory) for innate immunity: 1. When an adaptive response is mounted towards a selected risk such as a bacterial an infection, it acts throughout the physique to defeat that pathogen wherever it might be found. The reaction time for inflammation and other innate defenses, in contrast, is simply as lengthy for later exposures as for the initial one. Forms of Adaptive Immunity In the late 1800s, it was discovered that immunity can be transferred from one animal to another by method of the blood serum. Thus, biologists got here to recognize two forms of adaptive immunity, called cellular and humoral immunity, though the two interact extensively and sometimes respond to the identical pathogen. Cellular (cell-mediated) immunity employs lymphocytes that instantly attack and destroy international cells or diseased host cells. Cellular immunity additionally acts in opposition to parasitic worms, most cancers cells, and cells of transplanted tissues and organs. The expression humoral refers to antibodies dissolved in the physique fluids ("humors"). Humoral immunity is efficient in opposition to extracellular viruses, micro organism, yeasts, protozoans, and molecular (noncellular) pathogens corresponding to toxins, venoms, and allergens. In the unnatural occasion of a mismatched blood transfusion, it also destroys international erythrocytes. Note that humoral immunity works mainly towards the extracellular levels of infectious microorganisms. However, the intracellular stages are nonetheless vulnerable to cellular immunity, which destroys them by killing the cells that harbor them. Furthermore, sure antibodies within the IgE class (explained later) bind to parasitic worms and aid of their destruction. Thus, humoral and cellular immunity generally attack the identical microorganism in several ways or at different factors in its life cycle. After our dialogue of the main points of the two processes, you can see mobile and humoral immunity summarized and in contrast in table 21. Other ways of classifying immunity are energetic versus passive and pure versus synthetic. Either type of immunity can happen naturally or, for therapy and prevention purposes, it can be induced artificially. A vaccine consists of either useless or attenuated (weakened) pathogens that can stimulate an immune response however cause little or no discomfort or disease. In some circumstances, periodic booster photographs are given to restimulate immune reminiscence and maintain a high degree of protection (tetanus boosters, for example).
Discount 300mg combivir with amex
Blood always passes by way of exactly one capillary bed from the time it leaves the guts to the time it returns to the guts medicine misuse definition generic combivir 300mg with amex. If the radius of a blood vessel doubles and all other factors stay the identical treatment 2014 combivir 300mg lowest price, blood flow by way of that vessel also doubles. The femoral triangle is bordered by the inguinal ligament, sartorius muscle, and rectus femoris muscle. The lungs receive blood completely from the pulmonary circuit of the circulatory system. In the baroreflex, a drop in arterial blood pressure triggers a corrective vasodilation of the systemic blood vessels. Aldosterone secreted by the adrenal gland should be delivered to the kidney immediately under. Trace the route that an aldosterone molecule must take from the adrenal gland to the kidney, naming all major blood vessels in the order traveled. People in shock generally exhibit paleness, cool skin, tachycardia, and a weak pulse. Brushing up on the that means of those terms and their structural relationships might assist you to better perceive anatomy of the lymphatic organs (see "Exocrine Gland Structure" in part 5. The mechanisms of lymph move are similar to those for the venous return of blood (see part 20. You can brush up on leukocyte varieties, appearances, and features most easily in table 18. The actions of immune cells against disease agents involve the processes of phagocytosis, receptor-mediated endocytosis, and exocytosis described beneath "Vesicular Transport" in part 3. Indeed, he shared the 1908 Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine with Paul Ehrlich (1854�1915), who had developed the idea of humoral immunity, a process also mentioned in this chapter. But immune cells are especially concentrated in a real organ system, the lymphatic system. This is a community of organs and veinlike vessels that recuperate tissue fluid, inspect it for illness brokers, activate immune responses, and return the fluid to the bloodstream. After all, human homeostasis works wonderfully not solely to sustain our lives, but also to provide a predictable, heat, moist, nutritious habitat for our internal friends. Many of these guest microbes are useful or even necessary to human health, however some have the potential to cause illness in the occasion that they get out of hand. One of those defenses was found in 1882 by a moody, intense, Russian zoologist, Elie Metchnikoff (1845�1916). When finding out the tiny transparent larvae of starfish, he noticed cell cells wandering throughout their our bodies. He thought at first that they have to be digestive cells, however when he noticed related cells in sea anemones ingest nonnutritive dye particles that he injected, he thought they need to play a defensive position. Metchnikoff knew that cellular cells additionally exist in human blood and pus and shortly surround a splinter introduced via the pores and skin, so he decided to experiment to see if the starfish cells would do the same. He impaled a starfish larva on a rose thorn, and the subsequent morning he found the thorn crawling with cells that seemed to be attempting to devour it. He later noticed comparable cells devouring and digesting infectious yeast in tiny clear crustaceans called water fleas. He coined the word phagocytosis for this reaction and named the wandering cells phagocytes-terms we still use at present. Metchnikoff showed that animals from easy sea anemones and starfish to people actively defend themselves against illness brokers. His observations marked the founding of mobile and comparative immunology, and won him the scientific respect the lymphatic system (fig. One task of the lymphatic system is to reabsorb this extra and return it to the blood. Even partial interference with lymphatic drainage can result in severe lymphedema (fig. As the lymphatic system recovers tissue fluid, it additionally picks up overseas cells and chemicals from the tissues. On its way back to the bloodstream, the fluid passes by way of lymph nodes, where immune cells stand guard against overseas matter. When they detect anything potentially dangerous, they activate a protective immune response. On the right is a 52-year-old lady with extreme lymphedema of the legs and toes; on the left, for comparability, is a 21-year-old woman without edema. Lymph and the Lymphatic Vessels Lymph is often a clear, colorless fluid, just like blood plasma however low in protein. After a meal, for instance, lymph draining from the small gut has a milky appearance because of its lipid content material. Lymph leaving the lymph nodes accommodates a giant quantity of lymphocytes-indeed, that is the main supply of lymphocytes to the bloodstream. Lymph may include macrophages, hormones, micro organism, viruses, cellular debris, or even touring cancer cells. Thus, the composition of lymph arriving at a lymph node is kind of a report on the state of the upstream tissues. The overlapping edges of the endothelial cells act as valves that can open and close. When tissue fluid strain is high, it pushes the flaps inward (open) and fluid flows into the capillary. When stress is greater within the lymphatic capillary than within the tissue fluid, the flaps are pressed outward (closed). Explain why their structural difference is said to their functional difference. Lymphatic Vessels Lymph flows through a system of lymphatic vessels (lymphatics) similar to blood vessels. These start with microscopic lymphatic capillaries (terminal lymphatics), which penetrate almost every tissue of the physique but are absent from cartilage, bone, bone marrow, and the cornea. A lymphatic capillary consists of a sac of skinny endothelial cells that loosely overlap one another like the shingles of a roof. The cells are tethered to surrounding tissue by protein filaments that stop the sac from collapsing. Their walls are thinner and their valves are nearer collectively than these of the veins. As the lymphatic vessels converge along their path, they become larger and larger vessels with changing names. The route from the tissue fluid again to the bloodstream is: lymphatic capillaries accumulating vessels six lymphatic trunks two collecting ducts subclavian veins. These usually travel alongside veins and arteries and share a standard connective tissue sheath with them. The lymph trickles slowly through every node, where micro organism are phagocytized and immune cells monitor the fluid for international antigens.
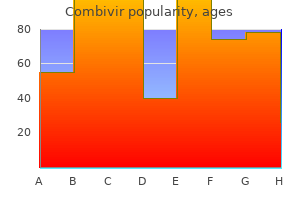
| Comparative prices of Combivir |
| # | Retailer | Average price |
| 1 | Rite Aid | 399 |
| 2 | PetSmart | 548 |
| 3 | Save Mart | 448 |
| 4 | Defense Commissary Agy. | 262 |
| 5 | Bon-Ton Stores | 867 |
| 6 | Meijer | 733 |
| 7 | Big Lots | 964 |
| 8 | J.C. Penney | 769 |
| 9 | Lowe's | 179 |
| 10 | Giant Eagle | 694 |
300 mg combivir buy visa
Passive immunity typically lasts for only 2 or 3 weeks treatment kitty colds buy generic combivir 300 mg line, till the acquired antibody is degraded medications by mail discount combivir 300mg amex. Some antigens are free molecules corresponding to venoms, toxins, and foodborne substances; others are parts of plasma membranes and bacterial cell walls. Most antigens have molecular weights over 10,000 amu and have sufficient structural complexity and variability to be unique to every particular person: proteins, polysaccharides, glycoproteins, and glycolipids. Their uniqueness enables the body to distinguish its own ("self") molecules from those of any other individual or organism ("nonself"). The immune system learns to distinguish self-antigens from nonself-antigens so that it usually assaults only nonself-antigens. Only sure areas of an antigen molecule, known as epitopes (antigenic determinants), stimulate immune responses. One antigen molecule usually has a number of totally different epitopes, however, that can stimulate the simultaneous manufacturing of various antibodies. After the first publicity, the hapten alone could stimulate an immune response while not having to bind to a bunch molecule. Many individuals are allergic to haptens in cosmetics, detergents, industrial chemical compounds, poison ivy, and animal dander. The most common drug allergy is to penicillin-a hapten that binds to host proteins in allergic individuals, creating a complex that binds to mast cells and triggers massive release of histamine and other inflammatory chemical compounds. Antibodies Antibodies (Abs), also known as immunoglobulins (Igs), are proteins in the gamma globulin class that play quite so much of roles in protection. Some of them are integral proteins in the plasma membranes of basophils and mast cells and thus perform in innate immunity. Others, with roles in adaptive immunity, are membrane proteins of B lymphocytes or are soluble antibodies dissolved in physique fluids corresponding to blood plasma, lymph, mucus, saliva, intestinal secretions, tears, and breast milk. The fundamental structural unit of an antibody, referred to as an antibody monomer, is composed of four polypeptides linked by disulfide (-S-S-) bonds (fig. These embody two heavy chains about four hundred amino acids lengthy and two mild chains about half that long. The V regions of each heavy and light chain pair combine to type an antigen-binding web site on every arm. The rest of each chain is a continuing (C) area, which has the same amino acid sequence, or nearly so, in all antibodies of a given class (within one person). As shown within the desk, IgD, IgE, and IgG are monomers; IgA has a monomer form as properly as a dimer composed of two cojoined monomers; and IgM is a pentamer composed of 5 monomers. IgG is particularly essential in the immunity of the new child because it crosses the placenta with relative ease. In addition, an toddler acquires some maternal IgA through breast milk and colostrum (the fluid secreted for the first 2 or three days of breast-feeding). The human immune system is believed able to producing a minimal of 10 billion and perhaps up to 1 trillion completely different antibodies. Any one person has a much smaller subset of those, but such an enormous potential helps to explain why we are able to deal with the large diversity of antigens that exist in our environment. These and other mechanisms explain how we will produce such a tremendous variety of antibodies with a restricted number of genes. A transmembrane protein of B cells; functions in activation of B cells by antigens. Stimulates them to launch histamine and other mediators of irritation and allergy; necessary in immediate hypersensitivity reactions and in attracting eosinophils to websites of parasitic an infection. IgG and IgM are the one antibodies with significant complement-fixation activity. Monomer is a transmembrane protein of B cells, where it functions as part of the antigen receptor. Here, we must take a better have a glance at T and B lymphocytes, the principal agents of adaptive immunity. T cells are produced in the pink bone marrow by the hemopoietic stem cells described in part 18. Newborn T cells enter the bloodstream and travel to the thymus-the "college" where they mature into fully practical T cells (fig. On arrival, T cells go first to the thymic cortex and cluster on the cortical epithelial cells (see fig. Within three or four days, these useless T cells die by apoptosis and the cortical macrophages phagocytize them. T cells that cross the test, demonstrating their capability to respond to antigens, are called immunocompetent. The cortical course of of selecting the few T cells that show their immunocompetence is recognized as positive selection. Humoral immunity is represented by the violet pathways and cellular immunity by the purple. This explains why the medulla of the thymus looks a lot lighter than the cortex in histological sections (see fig. But like graduate students, the T cells in the medulla face one more troublesome take a look at and even more of them are doomed to fail and presumably die. Unlike the cortical epithelial cells, these are derived from bone marrow and check the T cells differently. Owing to the imperfections of the immune system, this typically happens anyway, inflicting infamous autoimmune diseases described later in section 21. There is also proof, nonetheless, that the thymic corpuscles secrete a sign (cytokine) that renders these self-reactive T cells completely inactive (a state referred to as anergy20) or converts them to regulatory T cells that reasonable the exercise of the cytotoxic (killer) T cells that truly attack international cells (all explained later). Only about 2% of the T cells survive each optimistic and adverse choice; 98% are eliminated, especially by constructive selection. They are abundant in the lymphatic nodules of the lymph nodes and within the spleen, bone marrow, and mucous membranes. They act as "identification tags" that label each cell of your body as belonging to you. The key to a profitable protection is then to quickly mobilize immune cells in opposition to it. With this introduction to the main actors in immunity, we will now take a glance at the extra specific options of mobile and humoral immunity. Since the terminology of immune cells and chemicals is kind of complex, you could discover it helpful to refer often to desk 21. Describe the structure of an antibody monomer and state what a part of it binds to antigens. B Lymphocytes (B Cells) Less is known about B cell maturation than about T cells, but the B cell process happens totally within the purple bone marrow. Adults produce about 50 million B cells per day, however only 10% enter the general circulation. The different 90% are apparently destroyed in the midst of constructive and adverse selection within the bone marrow. Self-tolerant B cells that survive selection go on to multiply and generate immunocompetent B cell clones. Both mobile and humoral immunity occur in three phases that we are in a position to consider as recognition, attack, and memory (or "the three Rs of immunity"-recognize, react, and remember).
Combivir 300mg without prescription
The palate separates the nasal cavity from the oral cavity and permits you to symptoms 4 weeks 300 mg combivir buy overnight delivery breathe whereas chewing meals 97110 treatment code cheap 300 mg combivir mastercard. The paranasal sinuses and the nasolacrimal ducts of the orbits drain into the nasal cavity (see figs. The nasal cavity begins with a small dilated chamber referred to as the vestibule simply inside the nostril, bordered by the ala nasi. The narrowness of these passages and the turbulence caused by the conchae be sure that most air contacts the mucous membrane on its method through. As it does, most mud within the air sticks to the mucus and the air picks up moisture and heat from the mucosa. The conchae thus allow the nostril to cleanse, warm, and humidify the air more successfully than if the air had an unobstructed circulate by way of a cavernous area. Odors are detected by sensory cells in the olfactory epithelium, which covers a small space of the roof of the nasal fossa and adjoining elements of the septum and superior concha (see fig. The remainder of the nasal cavity, apart from the vestibule, is lined with respiratory epithelium. Both of those are ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelia, but in the olfactory epithelium, the cilia are immobile and serve to bind odor molecules. Its wineglass-shaped goblet cells secrete mucus, and its ciliated cells propel the mucus posteriorly towards the pharynx. The nasal mucosa additionally incorporates mucous glands, situated within the lamina propria (the connective tissue layer beneath the epithelium). The lamina propria can also be well populated by lymphocytes and plasma cells that mount immune defenses towards inhaled pathogens. The inferior concha has an especially intensive venous plexus known as the erectile tissue (swell body). Every 30 to 60 minutes, the erectile tissue on one facet swells with blood and restricts airflow through that fossa. Most air is then directed through the opposite nostril, permitting the engorged facet time to recuperate from drying. Thus, the preponderant circulate of air shifts between the best and left nostrils a few times each hour. If one nostril is blocked and the other nasal fossa is over-ventilated for several days, its pseudostratified columnar epithelium adjustments to stratified squamous, which higher resists drying. The nasopharynx is distal to the posterior nasal apertures and above the soft palate. It receives the auditory (eustachian) tubes from the middle ears and houses the pharyngeal tonsil. They collide with the wall of the nasopharynx and stick with the mucosa near the tonsil, which is well positioned to reply to airborne pathogens. The oropharynx is an area between the posterior margin of the taste bud and the epiglottis. The nasopharynx passes solely air and is lined by pseudostratified columnar epithelium, whereas the oropharynx and laryngopharynx move air, meals, and drink and are lined by stratified squamous epithelium. Its main function is to maintain food and drink out of the airway, however it developed the extra role of sound manufacturing (phonation) in many animals; hence, we colloquially consider it as the "voice field. During swallowing, nevertheless, extrinsic muscle tissue of the larynx pull the larynx upward towards the epiglottis, the tongue pushes the epiglottis downward to meet it, and the epiglottis closes the airway and directs food and drinks into the esophagus behind it. The vestibular folds of the larynx, mentioned shortly, play a higher position in keeping foods and drinks out of the airway, nevertheless. In infants, the larynx is relatively high within the throat and the epiglottis touches the taste bud. This creates a kind of steady airway from the nasal cavity to the larynx and permits an toddler to breathe frequently while swallowing. The epiglottis deflects milk away from the airstream, like rain working off a tent while it stays dry inside. By age 2, the root of the tongue becomes extra muscular and forces the larynx to descend to a decrease position. It then becomes unimaginable to breathe and swallow at the same time with out choking. Draw a line throughout part (a) of this determine to point out the boundary between the upper and lower respiratory tract. Testosterone stimulates the expansion of this prominence, which is subsequently bigger in males than in females. The thyroid and cricoid cartilages essentially represent the "field" of the voice box. The arytenoid and corniculate cartilages perform in speech, as defined shortly. A group of fibrous ligaments binds the cartilages of the larynx collectively and forms a suspension system for the upper airway. A broad sheet known as the thyrohyoid ligament suspends the larynx from the hyoid bone above, and under, the cricotracheal ligament suspends the trachea from the cricoid cartilage. These 5 6 thyr = shield; oid = resembling crico = ring; oid = resembling 7 aryten = ladle; oid = resembling eight corni = horn; cul = little; ate = possessing 9 cune = wedge; type = shape are collectively called the extrinsic ligaments as a result of they link the larynx to different organs. The intrinsic ligaments are contained totally inside the larynx and link its nine cartilages to one another; they embrace ligaments of the vocal cords and vestibular folds described subsequent. The inside wall of the larynx has two folds on each side that stretch from the thyroid cartilage in entrance to the arytenoid cartilages in back. The inferior vocal cords (vocal folds) produce sound when air passes between them. They contain the vocal ligaments and are lined with stratified squamous epithelium, finest suited to endure vibration and make contact with between the cords. The vocal cords and the opening between them are collectively known as the glottis (fig. The superficial extrinsic muscular tissues connect the larynx to the hyoid bone and elevate the larynx during swallowing. The deeper intrinsic muscular tissues control the vocal cords by pulling on the corniculate and arytenoid cartilages, inflicting the cartilages to pivot. Depending on their direction of rotation, the arytenoid cartilages abduct or adduct the vocal cords (fig. The crude sounds from the larynx are formed into words by actions of the pharynx, oral cavity, tongue, and lips. The trachea is called for the corrugated texture imparted by these rings10; you must be ready to palpate a few of these between your larynx and sternum. Like the wire spiral in a vacuum cleaner hose, the cartilage rings reinforce the trachea and maintain it from collapsing if you inhale. The hole in the C permits room for the esophagus to broaden as swallowed meals passes by. The inner lining of the trachea is a pseudostratified columnar epithelium composed primarily of mucus-secreting goblet cells, ciliated cells, and brief basal stem cells (figs.
Combivir 300mg buy discount online
Each zone of the skin is innervated by sensory branches of the spinal nerves indicated by the labels symptoms vaginitis combivir 300 mg on line. Most of us have had our reflexes examined with slightly rubber hammer; a faucet below the knee produces an uncontrollable jerk of the leg when administering medications 001mg is equal to best combivir 300mg, for example. It might come after the reflex action has been completed, and somatic reflexes can happen even when the spinal cord has been severed so that no stimuli reach the brain. Reflexes are stereotyped-they occur in basically the same means each time; the response may be very predictable, not like the variability of voluntary movement. Reflexes embrace glandular secretion and contractions of all three kinds of muscle. The reflexes of skeletal muscle are referred to as somatic reflexes, since they contain the somatic nervous system. Chapter 15 concerns the visceral reflexes of organs such as the center and intestines. A somatic reflex employs a reflex arc, by which signals journey alongside the following pathway (fig. Reflexes are quick-they generally involve only a few interneurons, or none, and minimum synaptic delay. Synaptic occasions in the integrating center decide whether the efferent neurons concern alerts to the muscles. The Muscle Spindle Many somatic reflexes involve stretch receptors called muscle spindles embedded within the muscle tissue. The function of muscle spindles is to inform the mind of muscle size and physique movements. Hand and foot muscle tissue have a hundred or more spindles per gram of muscle, whereas there are comparatively few in large muscles with coarse actions, and none in any respect in the middle-ear muscular tissues. A muscle spindle is a bundle of often seven or eight small, modified muscle fibers enclosed in an elongated fibrous capsule about 5 to 10 mm lengthy (fig. The modified muscle fibers within the spindle are known as intrafusal26 fibers, whereas people who make up the rest of the muscle and do its work are called extrafusal fibers. A gamma motor neuron of the spinal wire innervates each end and stimulates its contraction. This maintains rigidity and sensitivity of the intrafusal fiber, preventing it from going slack like an unstretched rubber band when a muscle shortens. Spinal motor neurons that provide the extrafusal muscle fibers are known as alpha motor neurons. Both of those sensory fiber types enter the posterior horn of the spinal cord, synapse on the alpha motor neurons and regulate their firing, and in addition send branches up the spinal cord to the mind. Through these fibers, the mind constantly however subconsciously displays the length and rigidity of nearly each skeletal muscle throughout the body. This enter is vital to the maintenance of posture, nice control of movements, and corrective reflexes. This stretches your calf muscle tissue and their muscle spindles, setting off sensory indicators to the spinal cord. The spindles within the calf muscle tissue at the moment are compressed and their signaling rate drops. At the same time, your backward tilt stretches spindles in your anterior leg and thigh muscle tissue, leading to their contraction and preventing you from falling over backward. You can properly think about the significance of those reflexes to the coordination of such common movements as walking and dancing. In more subtle methods, all day long, your brain screens input from the spindles of opposing muscular tissues and makes nice adjustments in muscle tension to maintain your posture and coordination. The Stretch Reflex When a muscle is abruptly stretched, it "fights again"-it contracts, increases tone, and feels stiffer than an unstretched muscle. This response, referred to as the stretch (myotatic27) reflex, helps to maintain equilibrium and posture, as we simply noticed in the rocking boat example. To take another case, if your head begins to tip forward, it stretches muscle tissue behind your neck. This stimulates their muscle spindles, which ship alerts to the cerebellum by way of the brainstem. The cerebellum integrates this data and relays it to the cerebral cortex, and the cortex sends indicators back, via the brainstem, to the muscles. Stretch reflexes often feed again not to a single muscle but to a set of synergists and antagonists. Since the contraction of a muscle on one side of a joint stretches the antagonist on the opposite side, the flexion of a joint creates a stretch reflex in the extensors, and extension creates a stretch reflex within the flexors. Stretch reflexes are particularly essential in coordinating vigorous and exact actions such as dance. The spinal component may be more pronounced if a muscle is stretched very suddenly. This happens within the reflexive contraction of a muscle when its tendon is tapped, as in the acquainted patellar (knee-jerk) reflex. Tapping the patellar ligament with a reflex hammer abruptly stretches the quadriceps femoris muscle of the thigh (fig. This stimulates quite a few muscle spindles in the quadriceps and sends an intense volley of signals to the spinal wire, mainly by means of primary afferent fibers. In the spinal cord, these fibers synapse instantly with the alpha motor neurons that return to the muscle, thus forming monosynaptic reflex arcs. The alpha motor neurons excite the quadriceps, making it contract and creating the knee jerk. A faucet on the calcaneal tendon causes plantar flexion of the foot, a tap on the triceps brachii tendon causes extension of the elbow, and a faucet on the masseter causes clenching of the jaw. Testing somatic reflexes is effective in diagnosing many ailments that cause exaggeration, inhibition, or absence of reflexes-for instance, neurosyphilis and other infectious illnesses, diabetes mellitus, a quantity of sclerosis, alcoholism, hormone and electrolyte imbalances, and lesions of the nervous system. Stretch reflexes and different muscle contractions usually rely upon reciprocal inhibition, a reflex that forestalls muscular tissues from working against each other by inhibiting antagonists. Some branches of the sensory fibers from the quadriceps muscle spindles stimulate spinal interneurons that, in turn, inhibit the alpha motor neurons of the hamstrings (fig. The Flexor (Withdrawal) Reflex A flexor reflex is the short contraction of flexor muscle tissue resulting in the withdrawal of a limb from an injurious stimulus. This motion entails contraction of the flexors and leisure of the extensors in that limb; the latter is one other case of reciprocal inhibition. The protecting operate of this reflex requires more than a fast jerk like a tendon reflex, so it involves more advanced neural pathways. Sustained contraction of the flexors is produced by a parallel after-discharge circuit in the spinal cord (see fig. This circuit is part of a polysynaptic reflex arc-a pathway during which signals journey over many synapses on their means again to the muscle. Some alerts follow routes with only some synapses and return to the flexor muscle tissue quickly. Others observe routes with extra synapses, and therefore extra delay, in order that they reach the flexor muscular tissues somewhat later. Consequently, the flexor muscles receive prolonged output from the spinal twine and not just one sudden stimulus as in a stretch reflex.
Order 300 mg combivir overnight delivery
A thoracic (respiratory) pump promotes the flow of lymph from the stomach to the thoracic cavity as one inhales medications education plans generic combivir 300 mg visa, simply because it does in venous return symptoms 9f anxiety buy cheap combivir 300mg online. Finally, at the point where the collecting ducts empty into the subclavian veins, the quickly flowing bloodstream draws the lymph into it. Considering these mechanisms of lymph flow, it ought to be apparent that physical train considerably increases the rate of lymphatic return. Subclavian vein Collecting vessels Superior vena cava Blood circulate Lymph move Systemic circuit Lymphatic capillaries Lymphatic Cells Another element of the lymphatic system is lymphatic tissue, which ranges from loosely scattered cells in the mucous membranes of the respiratory, digestive, urinary, and reproductive tracts to compact cell populations encapsulated in lymphatic organs. These tissues are composed of a selection of lymphocytes and different cells with varied roles in protection and immunity: 1. T lymphocytes (T cells) are lymphocytes that mature in the thymus and later depend upon thymic hormones; the T stands for thymus-dependent. B lymphocytes (B cells) are lymphocytes that differentiate into plasma cells-connective tissue cells that secrete antibodies. They are named for an organ in chickens (the bursa of Fabricius1) in which they had been first found. However, you may find it extra useful to consider B for bone marrow, the site the place these cells mature in people. The lymphatic system picks up extra tissue fluid and returns it to the bloodstream. It begins just under the diaphragm anterior to the vertebral column at the stage of the second lumbar vertebra. The thoracic duct then passes through the diaphragm with the aorta and ascends the mediastinum adjacent to the vertebral column. As it passes via the thorax, it receives additional lymph from the left bronchomediastinal, left subclavian, and left jugular trunks, then empties into the left subclavian vein. Why are the axillary lymph nodes often biopsied in instances of suspected breast most cancers They phagocytize tissue debris, useless neutrophils, micro organism, and other overseas matter (fig. They also course of international matter and display antigenic fragments of it to certain T cells, thus alerting the immune system to the presence of an enemy. They play an essential position in alerting the immune system to pathogens that have breached the body surfaces. They engulf foreign matter by receptor-mediated endocytosis somewhat than phagocytosis, but in any other case operate like macrophages. After internalizing an antigen, they migrate to a nearby lymph node and activate an immune response to it. In some places, lymphocytes and macrophages congregate in dense plenty known as lymphatic nodules (follicles) (fig. Abundant lymphatic nodules are, nonetheless, a relatively fixed characteristic of the lymph nodes (see fig. In the ileum, the distal portion of the small gut, they form clusters called Peyer patches or aggregated lymphoid nodules. Lymphatic Organs In contrast to the diffuse lymphatic tissue, lymphatic (lymphoid) organs have well-defined anatomical sites and at least a partial connective tissue capsule that separates the lymphatic tissue from neighboring tissues. These organs embody the purple bone marrow, thymus, lymph nodes, tonsils, and spleen. The lymph nodes, tonsils, and spleen are called secondary lymphatic organs because immunocompetent lymphocytes migrate to these organs solely after they mature in the main lymphatic organs. Lymphatic Tissues Lymphatic (lymphoid) tissues are aggregations of lymphocytes within the connective tissues of mucous membranes and numerous organs. The easiest type is diffuse lymphatic tissue, by which the lymphocytes are scattered quite than densely clustered. It is especially prevalent in physique passages which might be open to the exterior-the respiratory, digestive, urinary, and Red Bone Marrow Red bone marrow could not seem to be an organ; when aspirated from the bones for the purpose of biopsy or transfusion, it merely looks like extra-thick blood. Yet a cautious microscopic examination of much less disturbed marrow shows that it has a surprising diploma of construction and consists of a quantity of tissues, meeting the criteria of an organ, even if a very soft one. Yellow bone marrow is adipose tissue and can be disregarded for present purposes, however purple bone marrow is concerned in hemopoiesis (blood formation) and immunity. Red bone marrow is a delicate, loosely organized, extremely vascular material, separated from osseous tissue by the endosteum of the bone. It produces all lessons of shaped elements of the blood; its pink colour comes from the abundance of erythrocytes. Numerous small arteries enter nutrient foramina on the bone surface, penetrate the bone, and empty into large sinusoids (45 to 80 �m wide) within the marrow (fig. The sinusoids drain into a central longitudinal vein that exits the bone by way of the identical route that the arteries entered. The sinusoids are lined by endothelial cells, like other blood vessels, and are surrounded by reticular cells and reticular fibers. The reticular cells secrete colony-stimulating factors that induce the formation of assorted leukocyte types. In the long bones of the limbs, getting older reticular cells accumulate fats and transform into adipose cells, finally changing red bone marrow with yellow bone marrow. The areas between the sinusoids are occupied by islands (cords) of hemopoietic tissue, composed of macrophages and blood cells in all levels of improvement. The macrophages destroy malformed blood cells and the nuclei discarded by developing erythrocytes. As blood cells mature, they push their means through the reticular and endothelial cells to enter the sinusoid and flow away in the bloodstream. It homes creating lymphocytes and secretes hormones that regulate their later activity. It is a bilobed organ located between the sternum and aortic arch in the superior mediastinum. The thymus shows a exceptional diploma of degeneration (involution) with age, as described and illustrated earlier (see fig. The fibrous capsule of the thymus offers off trabeculae (septa) that divide the gland into a quantity of angular lobules. Each lobule has a light-weight central medulla populated by T lymphocytes, surrounded by a dense, darker cortex (fig. After growing in the cortex, T cells migrate to the medulla, where they spend one other three weeks. Epithelial cells of the thymus secrete several signaling molecules that promote the event and motion of T cells both domestically (as paracrines) and systemically (as hormones); these include thymosin, thymopoietin, thymulin, interleukins, and interferon. If the thymus is faraway from new child mammals, they waste away and by no means develop immunity. Other lymphatic organs also appear to depend upon thymosins or T cells and develop poorly in thymectomized animals.
300 mg combivir order amex
Ordinarily medicine 035 combivir 300mg discount otc, however medicine 8 soundcloud 300mg combivir generic, the sympathetic division has more delicate results that we discover barely, if at all. The parasympathetic division, by comparability, has a calming impact on many physique capabilities. It is associated with lowered vitality expenditure and normal bodily maintenance, together with such features as digestion and waste elimination. Parasympathetic tone, for instance, maintains smooth muscle tone in the intestines and holds the resting coronary heart fee down to about 70 to 80 beats/min. If the parasympathetic vagus nerves to the guts are minimize, the heart beats at its own intrinsic price of about one hundred beats/min. Sympathetic tone keeps most blood vessels partially constricted and thus maintains blood stress. A loss of sympathetic tone could cause such a rapid drop in blood stress that an individual goes into shock and will faint. The sympathetic division, for instance, excites the guts however inhibits digestive and urinary features, whereas the parasympathetic division has the alternative effects. We will later examine how variations in neurotransmitters and receptors account for these differences of effect. This pathway produces the baroreflex, which compensates for blood strain fluctuations in arteries above the heart. The medulla integrates this with different info and transmits signals back to the heart by method of the vagus nerves. The vagus nerves slow down the heart and cut back blood strain, thus finishing a homeostatic negative feedback loop. A separate autonomic reflex accelerates the center when blood strain drops under normal-for example, when we move from a reclining to a standing place and gravity draws blood away from the higher physique (see fig. The autonomic motor pathway to a target organ differs considerably from somatic motor pathways. In somatic pathways, a motor neuron within the brainstem or spinal wire issues a myelinated axon that reaches all the means in which to a skeletal muscle. In autonomic pathways, the sign must journey across two nerve fibers to get to the goal organ, and it must cross a synapse where these two neurons meet in an autonomic ganglion (fig. The first fiber, called the preganglionic fiber, is myelinated and leads from a soma within the brainstem or spinal cord to the autonomic ganglion. In summary, the autonomic nervous system is a division of the nervous system answerable for homeostasis, appearing by way of principally unconscious and involuntary management of glands, smooth muscle, and cardiac muscle. Its goal organs are mainly thoracic and abdominopelvic viscera, but also embrace some cutaneous and different effectors. Both divisions have excitatory effects on some goal cells and inhibitory effects on others. These and different differences between the somatic and autonomic nervous techniques are summarized in desk 15. How does the autonomic nervous system differ functionally and anatomically from the somatic motor system How do the overall effects of the sympathetic division differ from those of the parasympathetic division The Sympathetic Division All nerve fibers of the sympathetic division arise from the thoracic and lumbar regions of the spinal wire; therefore, this technique can also be known as the thoracolumbar division. Their axons exit the twine by the use of spinal nerves T1 to L2 and lead to the nearby sympathetic chain of ganglia (paravertebral4 ganglia). The sympathetic chain is a longitudinal series of ganglia that lie adjacent to either side of the vertebral column from the cervical to the coccygeal degree. Thoracic ganglion Communicating ramus Sympathetic chain Bronchi Superior vena cava Rib Splanchnic n. Sympathetic fibers can follow any of the three numbered routes: (1) the spinal nerve route, (2) the sympathetic nerve route, or (3) the splanchnic nerve route. Name the elements of the spinal cord the place the somas of the sympathetic and somatic efferent neurons are located. It could seem odd that sympathetic ganglia exist within the cervical, sacral, and coccygeal areas considering that sympathetic fibers arise only from the thoracic and lumbar regions of the spinal wire (levels T1 to L2). Consequently, sympathetic nerve fibers are distributed to each level of the body. As a basic rule, the top receives sympathetic output arising from spinal twine phase T1, the neck from T2, the thorax and upper limbs from T3 to T6, the stomach from T7 to T11, and the decrease limbs from T12 to L2. In the thoracolumbar area, each paravertebral ganglion is connected to a spinal nerve by two branches referred to as speaking rami (fig. The preganglionic fibers are small myelinated fibers that journey from the spinal nerve to the ganglion by way of the white speaking ramus,5 which will get its shade and name from the myelin. Unmyelinated postganglionic fibers leave the ganglion by way of the gray communicating ramus, named for its lack of myelin and duller colour, and by other routes. Postganglionic fibers, longer than the preganglionics, prolong the relaxation of the way to the target organ. They are the only route by which ganglia at the cervical, sacral, and coccygeal ranges receive enter. Some postganglionic fibers exit a ganglion by means of the grey ramus, return to the spinal nerve or its subdivisions, and travel the relaxation of the means in which to the target organ. This is the route to most sweat glands, piloerector muscle tissue, and blood vessels of the skin and skeletal muscles. Other postganglionic fibers leave by means of sympathetic nerves that stretch to the guts, lungs, esophagus, and thoracic blood vessels. These nerves kind a carotid plexus around every carotid artery of the neck and problem fibers from there to effectors within the head- together with sweat, salivary, and nasal glands; piloerector muscle tissue; blood vessels; and dilators of the iris. Some fibers from the superior and center cervical ganglia type the cardiac nerves to the guts. Some of the fibers that come up from spinal nerves T5 to T12 cross through the sympathetic ganglia with out synapsing. Beyond the ganglia, they proceed as splanchnic nerves, which result in a second set of ganglia called collateral ganglia. The postganglionic fibers accompany these arteries and their branches to the target organs. The time period solar plexus is utilized by some authorities as a collective name for the celiac and superior mesenteric ganglia, and by others as a synonym for the celiac ganglion solely. In summary, effectors within the muscles and body wall are innervated mainly by sympathetic fibers within the spinal nerves, effectors within the head and thoracic cavity by sympathetic nerves, and effectors in the abdominopelvic cavity by splanchnic nerves. For one factor, each postganglionic neuron could receive synapses from multiple preganglionic fibers, thus exhibiting the principle of neural convergence. Furthermore, every preganglionic fiber branches out to multiple postganglionic neurons, thus exhibiting neural divergence. Therefore, when one preganglionic neuron fires, it could excite multiple postganglionic fibers resulting in different target organs. The sympathetic division thus tends to have relatively widespread effects-as advised by the name sympathetic. Each adrenal is actually two glands with different capabilities and embryonic origins.