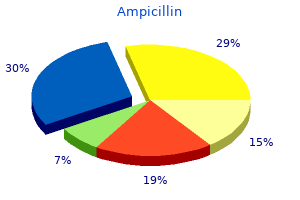
Ampicillin 250 mg generic without a prescription
They range in size and form in their natural state antibiotic erythromycin buy 250 mg ampicillin mastercard, chrysotile being smaller and curved in distinction to the more stable bigger fibres of the amphibole group can antibiotic resistance kill you ampicillin 500 mg low price. Fibres measuring up to 5 m are often cleared from the lungs without inflicting illness, whereas longer ones are phagocytosed by alveolar macrophages. They are then coated with protein and iron to produce inactivated fibres generally known as ferruginous or asbestos bodies. These buildings are as a lot as 200 m in size and are often dumbbell, beaded or drumstick in form, their golden brown coating targeting the pointed ends of the fibres. Similar deposits could type around other mineral fibres, hence the extra general time period ferruginous our bodies. This is adopted by the appearance of macrophages laden with brown haemosiderin pigment as the blood is broken down. Hyperplasia of bronchoalveolar epithelium is a notable characteristic, although of uncertain origin. The cells are rounded and swollen and present enlarged hyperchromatic nuclei with outstanding nucleoli. Clusters vary from three or 4 cells as a lot as much bigger collections by which cell particulars are troublesome to visualise. Attention to nuclear details and the presence of different features such as iron-laden macrophages will reduce the chance of this mistake. Carbon, in black or darkish brown granules, is the commonest pigment in respiratory samples, obscuring iron if deposition is heavy. Congestive cardiac failure Left ventricular failure from no matter cause subjects the lungs to congestion which if persistent results in microscopic haemorrhage in to alveoli. Degradation of the blood then occurs and is associated with accumulation of haemosiderin-laden macrophages in the alveoli. Sputum samples are typically submitted particularly requesting detection of such cells for affirmation of coronary heart failure as a cause of wheezing and shortness of breath, so-called cardiac asthma. Lipoid pneumonitis Inflammation of lung parenchyma because of the presence of lipid substances is mostly the outcomes of either native obstruction to a bronchus with accumulation of lipoidal tissue breakdown products distally, or to inhalation or aspiration of oily materials. Exogenous sources embody industrial oil inhalation and the chance of an iatrogenic origin from drugs such as nostril drops. The most typical cause of endogenous lipoid pneumonia Cytological findings: congestive cardiac failure Watery sputum, or tinged with blood Haemosiderin laden macrophages (heart failure cells). Their cytoplasmic vacuoles show appreciable variation in measurement and form and some multinucleation could be seen. The former error may be prevented by staining for fat, whereas the uncommon prevalence of liposarcoma in lung is associated with only few abnormal tumour cells and the cells present larger nuclear pleomorphism. Fat-laden macrophages could be found transiently in sputum in some conditions with out progressing to pneumonitis. An instance of that is seen with fat embolism after fractures or orthopaedic surgery, when fat is launched in to the venous circulation and thence deposited in the lungs. Sputum examination in such patients nearly invariably reveals the presence of free lipid or some fats in macrophages, which is of no consequence clinically until massive sufficient to induce pulmonary oedema or enable the passage of the fats in to the systemic circulation. Amiodarone toxicity is related to accumulation of phospholipids in lung and different tissues. The hallmark of lipoid pneumonitis, whatever the trigger, is the presence of lipid-laden macrophages and swimming pools of free lipid in the alveoli and interstitial tissues. Other inflammatory cells are almost at all times current, and the inflammation could become granulomatous. Cholesterol clefts from cell breakdown are seen when bronchial obstruction is current. Talc granuloma Foreign materials, corresponding to particles of talc, trapped in pulmonary vessels after intravenous injection of drugs blended with talc as a base, evoke a granulomatous inflammatory reaction within the lung parenchyma, resulting in diffuse or focal nodular radiological shadowing. The overseas materials itself can typically be recognized in the aspirated material with the assistance of polarising light. Other inflammatory cells could additionally be present, in varying numbers, and in instances due to an obstructing tumour malignant cells may be seen. Involvement of the respiratory tract may be tracheobronchial or parenchymal in distribution and at either site deposition can be localised, nodular, multifocal or diffuse. Other types of amorphous plaque similar to those because of alveolar proteinosis or Pneumocystis infection have to be thought-about. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis this rare illness was associated with recognized exposure to dusts in about half of the circumstances initially described by Rosen et al. This materials has been proven by electron microscopy to contain massive amounts of surfactant. Samples of this sputum or lavage fluid from a therapeutic lavage procedure may be obtained. Cytological findings: pulmonary amyloidosis Smooth amorphous eosinophilic plaques of amyloid. The affected person was a middle-aged man presenting with breathlessness and bilateral pulmonary infiltrates. The plaques differ in distribution, measurement and texture from those of Pneumocystis an infection or amyloidosis, however both of those should be considered in the differential diagnosis. The proteinaceous precipitate is eosinophilic and fills the alveolar areas in the lung section. Rounded fragments of amorphous material of variable measurement, with amphophilic or pale eosinophilic staining properties are seen on gentle microscopy. Thermal damage Severe burns from inhalation of smoke or hot gases result in partial or full necrosis of bronchial epithelium and the extent of injury may determine the overall prognosis. A combination of inflammatory cells together with plasma cells could be seen in a background of spindle cell connective tissue. The affected person was a male of 22, presenting with a lung mass 2 months after an ill-defined respiratory tract infection (H&E). A few plasma cells with eccentric nuclei can be made out, together with histiocytes, lymphocytes and occasional polymorphs. Destruction of cilia, the terminal plate and even whole epithelial cell teams could also be seen, but in less injured sufferers these damaged cells are mixed with exfoliated normal cells. Squamous cells could also be present in abundance and may be misshapen, with hyperchromatic nuclei and multinucleation. Cytological findings: plasma cell granuloma Mixed inflammatory image, together with plasma cells, polymorphs, eosinophils and mast cells Foamy histiocytes or giant cells Fibroblasts and collagen. However, a solitary nodule may probably characterize an early stage of lung most cancers or a metastasis. There is a background of collagen with spindle-shaped fibroblastic cells, which regularly have a storiform pattern of development. Xanthoma cells with finely vacuolated cytoplasm may be extra numerous than plasma cells.
Ampicillin 500 mg lowest price
Sputum can be processed in a variety of ways but all specimens should be regarded as potentially infective antibiotics quinolones discount ampicillin 500 mg on line. A number of other preparation and storage strategies for sputum have been tried and are nonetheless evolving virus on mac purchase ampicillin 500 mg without a prescription. Mechanical liquefaction and concentration in addition to cell block technique have been used successfully in some centres. Thin layer preparation methods yield well-preserved, clearly displayed cells without background particles, excellent for prognosis of malignancy. The pattern is positioned instantly in to a preservative answer obtainable commercially from the producers of the assorted processing gadgets now obtainable, as described in Chapters 1 and 36. These liquid-based samples have the added advantage of offering spare materials for special stains and different adjunctive methods, together with immunocytochemistry. Material from the brush can both be wiped on to microscope slides, then fastened in alcohol and stained by the Papanicolaou method or washed in to appropriate collection fluid for specimen preparation using thin layer strategies. Elucidation of pulmonary infiltrates and identification of opportunistic infections in immunocompromised patients are necessary functions of this process as described in Chapter sixteen. Thin layer strategies are less suitable as each organisms and inflammatory cells may be selectively lost in the preparation, a risk that can be circumvented by dividing the sample between the industrial cell fixative and saline. Induced sputum Where sputum manufacturing is poor, it could be elevated artificially by inhalation of an aerosolised irritant resolution. Induced sputum is a useful non-invasive method for the assessment of airway and parenchymal lung illnesses. The introduction of ultrasound guided imaging has improved the accuracy of sampling, while use of a fantastic gauge needle (19�22G) makes the process safe and well-tolerated. This is particularly useful within the transcarinal aspiration of mediastinal constructions but is of much less value for sure pulmonary lesions as a end result of intervening air throughout the lung tissue. Beneath the basement membrane of this epithelium lies a fibrocollagenous stroma containing blood vessels, lymphatics, nerves and seromucinous glands. Inflammatory cells of the immune system, primarily lymphocytes, plasma cells and macrophages, are also seen migrating in to the overlying epithelium. In strategic areas lymphoid cells mixture in to organised tissue lots forming the tonsils and adenoids. The bronchial tree and remainder of the higher airways are lined by specialised respiratory epithelium. This consists of a pseudostratified layer of ciliated tall columnar cells interspersed with mucin secreting goblet cells, which have microvilli on their luminal surfaces. Mucin from the goblet cells coats the airways with a sticky layer inside which inhaled particles, organisms and cell particles are trapped. The cilia have a metachronous beat which sweeps this materials upwards, to be expectorated or swallowed. General respiratory tract findings the respiratory system contains the nasal passages, sinuses and nasopharynx, the oropharynx and larynx, trachea, bronchi and bronchioles, and the air areas beyond. Gaseous change is carried out within the alveoli and other advanced activities take place in the lung parenchyma, together with further pulmonary defence mechanisms, some endocrine capabilities and upkeep of homeostasis. Not surprisingly, there are numerous variations in cell structure all through the respiratory system, and their delicate stability is frequently disturbed by disease. A complete knowledge of the normal findings is therefore essential to perceive the pathological changes encountered in cytological specimens. Normal histology of the respiratory tract Two several sorts of epithelium form the mucosa of the respiratory tract, their exact distribution various with age. Note the multilayered pseudostratified columnar epithelium composed primarily of ciliated cells with occasional goblet cells. A distinct single layer of reserve cells could be seen resting on the basement membrane. Deep to this the submucosa features a few capillaries, lymphatics and inflammatory cells (H&E). Small reserve cells relaxation on the basement membrane, forming an undifferentiated stem cell population from which regeneration of bronchial mucosa takes place after harm. Inconspicuous spherical cells with neuroendocrine properties are additionally found located towards the basement membrane. Bronchioles, the primary branches of bronchi without cartilaginous assist of their walls, are lined by a single layer of nonciliated columnar cells interspersed with a couple of goblet cells. Terminal bronchioles are lined by low columnar epithelium and are concerned solely in air conduction. They are steady with respiratory bronchioles, which mark the graduation of gaseous trade. Here the liner becomes cuboidal, merging with flattened epithelial cells within the alveolar ducts. The periphery of each sac is partitioned in to alveoli, the principle site of gaseous trade. In addition, there are many macrophages of bone marrow derivation, forming an essential element of cytology samples from the decrease airways. They adhere to the partitions of alveoli, ingesting cellular particles and overseas material, which is then transported to the bronchial tree or to lymphatic channels arising at the degree of the terminal bronchioles. It has been estimated that kind I pneumocytes cowl approximately 90% of the alveolar wall space, but form solely about 40% of the liner cell population. Their cytoplasm is thinly spread out to enable maximal exchange of gasoline between the alveolar house and the underlying capillaries. Their cytoplasm is dense, containing spherical laminated osmiophilic bodies when examined by electron microscopy, composed of the precursors of pulmonary surfactant. General cytological findings in respiratory samples Cell inhabitants Only a number of of the numerous completely different cells lining the respiratory tract are seen with any regularity in cytological preparations. The distribution of cells varies significantly with the nature of the pattern, however is of significance in assessing specimen adequacy. The appearances to be described for normal and irregular cells are those seen with Papanicolaou staining until in any other case specified. They have small central pyknotic or vesicular nuclei, as seen in squames from different websites Bronchial epithelial cells. Nuclei differ considerably in size and shape however are often basal and rounded or oval. Cilia are often preserved, arising from a darkish stained terminal bar at the broader end of the cell Goblet cells are inconspicuous in sputum except hyperplastic, but are very often seen in brushings and improve in number with persistent bronchial irritation. They are columnar but are distended centrally by globules of mucin, which overlie or displace the nucleus. These tall columnar cells present the tapering level of anchorage at one end and dark terminal bar, bearing pink cilia at the opposite finish of the cell.
Ampicillin 250 mg with mastercard
Haematolymphoid disorders affecting the serous cavities could additionally be categorised in different ways antibiotic rash purchase 500 mg ampicillin amex. They may be divided primarily based on the predominant cells within the effusion � lymphocytic and non-lymphocytic effusions antibiotic drops for conjunctivitis ampicillin 500 mg purchase with visa. Reciprocally, well-differentiated and low-grade adenocarcinoma cells might resemble reactive mesothelial cells and result in false negative interpretation (Table 3. Radiotherapy effects embody weird cells in effusions with: cytomegaly, degenerative hyperchromasia and two-tone staining (cyanophilia � blue/green and acidophilia � pink). Vacuolation of cytoplasm because of degeneration may deform the nucleus, the chromatin is commonly smudgy and mitotic figures are current. They might lead to falsepositive interpretation, suggesting recurrence of the initial disease. Additional potential pitfalls include: poorly preserved, degenerate or scanty cells in improperly processed specimens. In such circumstances resubmission of a properly preserved effusion specimen with revaluation after optimum processing should be really helpful. Malignant effusions normally reaccumulate and include unequivocal most cancers cells, with improved morphology. Effusions with unfavorable cytology in circumstances with lymphoma/leukaemia could additionally be as a end result of blockage of lymphatic drainage or the presence of a concurrent unrelated condition causing effusion. It is associated with increased levels of triglyceride in effusion fluids: a stage over a hundred and ten mg/dL is highly suggestive of a chylous effusion. The haemopoietic cells present might comprise eosinophils, neutrophil polymorphs or histiocytes. Identifying the first of those non-epithelial malignancies primarily based on cytomorphology alone is tough, because they often exhibit variable morphological features in effusions completely different from the preliminary primary tumour. However, with proper scientific historical past, the diagnosis is usually simple and simple comparability of the tumour morphology in cell block sections of effusion preparations with the original main tumour may be adequate. However, depending on the medical scenario, ancillary studies may be performed to assist the interpretation. Most of these specimens are sparsely cellular with a couple of solitary cells or loose clusters. The sarcoma cells may present vague cytoplasmic borders with bipolar cytoplasmic processes. The neoplastic cells could also be binucleated or multinucleated with spherical, oval and generally fusiform or spindle-shaped nuclei. The nuclei usually show apparent options of malignancy with irregular outlines and frequent nuclear membrane infolding. Malignant effusions attributable to lymphomas, breast cancer, ovarian most cancers and small cell lung carcinoma could reply to systemic chemotherapy or hormonal remedy, as in contrast with effusions secondary to therapy-resistant cancers, such as non-small cell lung carcinoma, which are approached with palliative measures, such as pleurodesis or a pleuroperitoneal shunt. The cytomorphology of the malignant cells within the present fluid specimen should correspond to that of the primary neoplasm. Review of any prior surgical and/or cytological supplies might assist in some instances, but not all, due to effusion related secondary morphological alterations. Depending on the clinical scenario and the cytological image, clinical details can be deceptive, resulting in a false optimistic interpretation. However the availability of scientific historical past on the request kind plays a critical position in directing proper triaging and processing of effusion specimens, in order to keep away from suboptimal cytopathological interpretation. A clinical historical past of a previous malignancy is probably not available in all instances and in some sufferers a malignant effusion will be the preliminary presentation. Most of the cells are neoplastic cells (arrows) which are comparatively troublesome to distinguish from reactive mesothelial cells (not present on this field). Malignant effusions are relatively unusual in children and most are secondary to malignant lymphomas and leukaemias. Other primaries include the so-called small blue cell tumours of childhood similar to neuroblastoma, Wilms tumour, and rhabdomyosarcoma. Cytology4 Primary tumours from various sites normally have attribute cytomorphology, and often the cytomorphology of metastases resembles that of the primary tumour, however in the case of effusions, resemblance may be distant. However, some cytomorphological options should be applicable within the differential prognosis, at least in broad sense. It is necessary to recognise haematological malignancies for instituting effective administration. Lymphoma or leukaemia seldom current as an effusion and not using a known historical past,34 besides in circumstances with an preliminary effusion presentation of systemic illness or in circumstances of main effusion lymphoma. In Hodgkin lymphoma Reed�Sternberg cells may be seen in a background of blended lymphocytes, eosinophils and plasma cells. Although continual inflammation is polymorphic, florid processes similar to tuberculosis could additionally be troublesome to distinguish from lymphoma on morphology alone. Immunophenotyping with techniques corresponding to move cytometry is indicated to evaluate the reactive nature of the cells. Additionally flow cytometry can sub-classify non-Hodgkin lymphomas and leukaemias (see Ch. Singly scattered, quite a few, medium sized, pleomorphic carcinoma cells (arrows) show options overlapping with other anaplastic carcinomas. Squamous cell carcinomas can even shed single cells in to body cavity fluids and will resemble reactive mesothelial cells, probably a false unfavorable pitfall. With cytoplasmic melanin pigment, the prognosis is commonly easy, however, the vast majority of melanomas are amelanotic. Usually large enough to be seen at low energy and barely even to the bare eye the cohesive, tightly packed cells within the cell balls range from a quantity of to several hundred They are typically seen in carcinomas of breast and ovary and very large cell balls in elderly women favour the ductal variant of infiltrating mammary carcinoma. Larger mesothelial windows could additionally be misinterpreted as acini and artefactual clustering may entrap areas resembling acini. Papillary formation and psammoma our bodies Papillae are three-dimensional, cohesive constructions derived from papillary neoplasms. Individual cells within the clusters are often polarised with nuclei organized perpendicular to the lengthy axis or to the fibrovascular cores. Intranuclear cytoplasmic inclusions are seen in papillary carcinoma of the thyroid and bronchioloalveolar carcinoma. However, other non-papillary neoplasms with tendency for proliferation spheres may present papillary-like constructions and could additionally be misinterpreted as a papillary neoplasm (potential pitfall). Psammoma bodies are spherical to oval calcified buildings with concentric lamellations. Other malignancies related to psammoma bodies embody primary peritoneal serous tumour, papillary carcinoma of the thyroid, bronchogenic carcinoma, malignant mesothelioma and, less frequently, breast and gastric carcinomas. Caution must be exercised not to misinterpret psammoma our bodies and/or papillary formation in fluid specimens as unequivocal evidence of malignancy, especially in peritoneal fluid. Benign circumstances such as: ovarian cystadenoma/cystadenofibroma, papillary mesothelial hyperplasia, endosalpingiosis, endometriosis and different miscellaneous benign diagnoses could. Higher magnification of different subject (inset), highlights the options of malignancy in medium to large neoplastic cells.
Buy discount ampicillin 250 mg on line
This investigation will be centered on various organs relying on factors similar to age antibiotics classes ampicillin 500 mg generic on line, intercourse antibiotic resistance wastewater discount 250 mg ampicillin overnight delivery, scientific historical past, website of metastatic node and the cytological options. The search for a main tumour may be facilitated by immunological characterisation of the aspirated cells. Unfortunately, some metastases defy all diagnostic efforts and their origin remains obscure. The cytological presentation of different tumours is relatively impartial of metastatic website. Hence the following description of various metastases will give consideration to identification of tumour cell kind. The massive cell kind is characterised by pleomorphic tumour cells with multilobated, horseshoe- or ring-shaped nuclei. The cellular atypia can be minimal and in such circumstances the prognosis may rest on the knowledge that the cells had been aspirated from a lymph node. Some keratinising carcinomas present liquefaction and a yellow turbid thick materials is aspirated from metastatic nodes of this type. The smears consist largely of inflammatory cells and particles and malignant cells could also be sparse, requiring cautious search preferably in Papanicolaou stained smears. If such materials is aspirated from a neck tumour the risk of a branchial cleft cyst should be thought of. In an infected branchial cyst the epithelium can show a point of atypia and thus mimic squamous cell carcinoma. Occasional small keratinised cells can level toward a prognosis of squamous cell carcinoma however of their absence the cytological picture could also be that of an undifferentiated malignant tumour which defies further categorisation. In this process extra options could be helpful, for instance, mucin manufacturing is usually seen in gastrointestinal and lung carcinomas. Metastases of papillary carcinoma often have their origin in the ovary, thyroid, breast or lung. Psammoma bodies are most frequent in metastases originating from ovarian and thyroid carcinomas. Seropapillary ovarian carcinomas usually spread to lymph nodes in the groin, lower axilla and supraclavicular fossa. In contrast a papillary carcinoma of the thyroid seldom spreads exterior the regional nodes. Smears of aspirates from poorly differentiated adenocarcinomas could be impossible to differentiate from other poorly-differentiated tumours and subtyping can only be made after immunocytochemistry. Small cell carcinoma of undifferentiated kind Metastases from small cell carcinoma of the lung yield crowded clusters of tumour cells exhibiting moulding, with scanty cytoplasm, coarse chromatin, frequent mitoses and a background of necrosis. Immunocytochemistry Epithelial markers are readily detected and cytokeratin can be utilized to affirm the epithelial nature of the tumour deposits. The presence of the oestrogen or the progesterone receptor strongly favours metastatic breast carcinoma. Small cell undifferentiated carcinoma cells present optimistic staining with cytokeratin, albeit typically irregular or dot-like in distribution. The nuclei have giant nucleoli which occasionally could additionally be changed by cytoplasmic invaginations in to the nucleus. The cytology of metastatic melanoma can mimic either carcinoma or sarcoma, or even typically lymphoma. Knowledge in regards to the clinical history will permit an accurate identification of a metastasis. However, in cases without a previously identified sarcoma the exact subtyping of a lymph node metastasis could be troublesome even with using immunocytochemistry. In this case the aspirate consists of dissociated comparatively monotonous round cells. Immunocytochemistry Antibodies to epithelial, melanocytic and lymphoid cells give adverse staining reactions in sarcomatous metastases. Vimentin and markers for neural, vascular and myogenic differentiation will confirm the diagnosis of metastatic sarcoma. It is necessary, therefore, that cytologists are capable of attend the multidisciplinary conferences the place selections about further investigations and remedy are made, so as to clarify their findings to the clinicians and ensure full clinicopathological correlation and optimal patient end result (see Algorithm, p. Immunocytochemical evaluation and cytomorphologic prognosis on fine-needle aspirates of lymphoproliferative illness. The value of immunocytochemical staining of lymph node aspirates in diagnostic cytology. Fine-needle aspiration analysis of intraabdominal and retroperitoneal lymphomas by a morphologic and immunocytochemical approach. Accuracy of diagnosis of malignant lymphoma by combining fine-needle aspiration cytomorphology with immunocytochemistry and in selected circumstances. Ex vivo fine-needle aspiration cytology and move cytometric phenotyping within the prognosis of lymphoproliferative disorders: A proposed algorithm for maximum useful resource utilisation. Combining fineneedle aspiration and circulate cytometric immunophenotyping in analysis of nodal and extranodal sites for possible lymphoma: a retrospective review. Fineneedle aspiration with circulate cytometric immunophenotyping for main analysis of intra-abdominal lymphomas. Utilisation of fine needle aspiration cytology and move cytometry in the diagnosis and subclassification of primary and recurrent lymphoma. The value of fluorescence in situ hybridisation and polymerase chain reaction in the diagnosis of B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma by fineneedle aspiration. Fine-needle aspiration of lymph nodes in sufferers with acute infectious mononucleosis. Sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy (Rosai-Dorfman Disease): cytomorphologic evaluation on nice needle aspirates. Sinus histiocytosis with large lymphadenopathy (Rosai-Dorfman disease): report of two circumstances with fine-needle aspiration cytology. Lymphadenitis displaying focal reticulum cell hyperplasia with nuclear debris and phagocytosis. Histiocytic necrotising lymphadenitis (KikuchiFujimo to disease) diagnosed by fantastic needle aspiration biopsy. Polymerase chain reaction detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis from fine-needle aspirate for the prognosis of cervical tuberculous lymphadenitis. Fine needle aspiration cytology of talc granulomatosis in a peripheral lymph node in a case of suspected intravenous drug abuse. National Cancer Institute sponsored research of lymphomas: summary and description of a working formulation of medical usage. Diagnosis of lymphoma by fine-needle aspiration cytology utilizing the Revised European-American classification of lymphoid neoplasms. A potential comparison of fine-needle aspiration cytology and histopathology in the diagnosis and classification of lymphomas. Fine-needle aspiration cytology of Hodgkin disease: a study of 89 cases with emphasis on false-negative cases. Fine needle aspiration biopsy: functions in the analysis of lymphoproliferative diseases.
250 mg ampicillin purchase with amex
Loose aggregates and single histiocytes are often associated with shed endometrial cells and could additionally be confused with severely dyskaryotic cells if their reniform nuclei and delicate cytoplasm are overlooked xylitol antibiotics discount ampicillin 250 mg without a prescription. The mobile adjustments in endometrial cells in cervical smears in pathological states antibiotics for kitten uti order ampicillin 250 mg overnight delivery, similar to endometrial hyperplasia or neoplasia, are described in Chapter 26. This assortment includes several with bean-shaped nuclei and foamy cytoplasm, options typical of macrophages. Cell detail can be troublesome to make out at this stage and consciousness of the timing of smear assortment within the cycle is essential. They are additionally seen in granulomatous inflammation or repair and after radiotherapy. This crowded group of glandular cells includes a population of smaller darker nuclei, presumed to symbolize reserve cells. When reactive reserve cell hyperplasia has occurred the cells can generally be recognized as syncytial groups of small crowded cells with vague cell borders and spherical darkly stained nuclei which regularly overlap. They could also be distinguished from the cell groups of glandular dyskaryosis by the dearth of architectural abnormalities, the smaller dimension and uniform chromatin sample of their nuclei and by the presence of related naked nuclei and normal endocervical cells in standard smears. There may be problems within the interpretation of a sample if the epithelial cells are largely obscured by polymorphs. This drawback is overcome to a substantial extent by way of liquid-based strategies of preparation. Macrophages Macrophages are sometimes seen as a part of the inflammatory cell population, particularly following menstruation and in postmenopausal ladies. They are extremely variable in measurement and look, but can generally be distinguished from parabasal or columnar cells by their ill-defined foamy cytoplasm, their eccentric bean-shaped nuclei, and the presence of ingested particulate materials in some situations. It is helpful when in doubt to look at neighbouring cells as these frequently include different macrophages with extra typical options. Macrophages, although normally dissociated cells, may be loosely aggregated particularly in postmenstrual smears. They may turn out to be multinucleated and really large, forming giant cells, a phenomenon most frequently seen in postmenopausal women. They are present in larger numbers in follicular cervicitis, in affiliation with tingible-body macrophages. Cells other than inflammatory and epithelial cells Spermatozoa Spermatozoa are seen in postcoital smears, even a quantity of days after intercourse. Contaminants Cytological specimens may be contaminated at any stage in the assortment, transmission or laboratory preparation of the pattern. Liquid-based cytology preparations are less vulnerable to contamination from these sources. In addition, cervical samples could include extraneous materials from the vagina or vulva, even together with parasites or their ova from the digestive tract, particularly in those components of the world where parasitic infestations are common. The eggs are oval and are smaller than schistosome ova, with a clean doublewalled shell, usually with one facet flipped over. Descriptions of Ascaris lumbricoides, Taenia coli,5 Trichuris trichura, Hymenolepis nana6 and the microfilaria of Wuchereria bancrofti7,eight have been recorded. The first two are the frequent forms of schistosome ova present in cervical smears and are distinguished by the presence of either a terminal or lateral spine, respectively. Pediculus humanus, the body louse, and the pubic louse, Phthirus pubis, are seen sometimes in cervical smears. The louse may be broken during smear preparation, with fragmentation of the tail half from head and legs. Many external contaminants have been described, together with pollen and bugs as a end result of atmospheric contamination, and 564. Particulate materials from sources corresponding to tampons or glove powder is normally simply recognized. Note the dimensions of the ovum compared with the squamous cells, and the terminal spine. This is assumed to end result from the trapping of air on the floor of cells throughout mounting, particularly in thickly spread direct smears. Inadequate elimination of spray fixative containing Carbowax might trigger related problems. The artefact could additionally be so marked as to require an extra sample for correct evaluation. Lubricant contamination might often be seen with some liquid-based cytology preparations. The morphological appearances are variable and embody amorphous blue deposits and stringy eosinophilic background materials. Even without polarised gentle, the characteristic Maltese cross structure may be seen at the centre of a number of the starch particles. Assessment of high quality of smears the query of adequacy of cervical samples is central to the success of cervical screening in the prevention of cervical most cancers 566 dying (see Chs 22�24). In principle, the latter requirement can only be glad if squamous metaplastic cells, endocervical cells and mucus are present to indicate transformation zone origin and if the sample taker has visualised the cervix and sampled the entire circumference of the transformation zone at the exterior os. Formal coaching in cervical pattern taking is important if the take a look at is to be reliable and such coaching is more and more obtainable. As a high quality assurance measure, the proportion of insufficient or unsatisfactory cervical samples in relation to the complete sample workload of a laboratory provides a priceless indication of the standard of reporting and of the level of expertise of the pattern takers. These samples should be learn by two independent screeners � certainly one of whom will perform a full in-depth screen with overlapping fields of view and masking the complete sample. The second screener will perform a extra fast assessment 21 Vulva, vagina and cervix: normal cytology, hormonal and inflammatory situations of the pattern. These abbreviated quality assurance screening methods have been found to detect abnormalities missed on preliminary main screening. The smear taker has to be relied upon for confirming the thoroughness of the sampling process Squamous cells of cervical origin are normally distributed in loosely cohesive streaks alongside the traces of spread of the smear. This is helpful in trying to decide whether squamous cells are cervical or vaginal in origin, the latter usually lying in a flat dispersed pattern as a end result of the shortage of background mucus. However, postmenopausal smears with little or no mucus might, misleadingly, appear to be vaginal in origin Whether smears without any endocervical cells or recognisable metaplastic cells must be accepted as representative is debatable. The presence of these cells is set largely by the position of the squamocolumnar junction and the state of maturation of the transformation zone, components that are hormone dependent. Thus it may not be possible to embrace endocervical cells or determine metaplastic cells at all times. There are many reviews of comparative trials of the totally different smear taking instruments,18�22 the general conclusion being that devices with an extended arm give a more representative pattern and have a larger chance of together with abnormalities An excess of leucocytes obscuring epithelial cells. Recommendation to repeat the smear at midcycle often supplies a better sample than at different times of the cycle.
Ampicillin 250 mg buy fast delivery
Simultaneously presenting head and neck and lung cancer: a diagnostic and therapy dilemma infection bio war buy 250 mg ampicillin with amex. The cytologic analysis of occult small-cell undifferentiated carcinoma of the lung infection nosocomial ampicillin 250 mg buy low price. The potential usefulness of monoclonal antibodies in the willpower of histologic kinds of lung cancer in cytologic preparations. The use of a panel of monoclonal antibodies in ultrastructurally characterised small cell carcinomas of the lung. Paranuclear blue inclusions in small cell undifferentiated carcinoma: a diagnostically useful finding demonstrated in fine-needle aspiration biopsy smears. Primary cytodiagnosis of dually differentiated lung most cancers by transthoracic nice needle aspiration. Metastatic laryngeal basaloid squamous cell carcinoma simulating main small cell carcinoma of the lung on nice needle aspiration lung biopsy. Typical and atypical pulmonary carcinoid tumors overdiagnosed as small-cell carcinoma on biopsy specimens: a significant pitfall in the management of lung cancer patients. Utility of cytokeratin 7 and 20 subset evaluation as an help within the identification of main web site of origin of malignancy in cytologic specimens. Expression of thyroid transcription factor-1 in pulmonary and extrapulmonary small cell carcinomas and different neuroendocrine carcinomas of varied main sites. Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma of the lung; correlation of intraoperative cytology with histology. Morphologic and immunocytochemical studies of bronchiolo-alveolar carcinoma at Duke University Medical Centre 1968�1986. Value of sputum cytology in the differential prognosis of alveolar cell carcinoma from bronchogenic carcinoma. Cytologic differential prognosis of bronchioloalveolar carcinoma and bronchogenic adenocarcinoma. Cytopathology of granulocyte colonystimulating factor-producing lung adenocarcinoma. Histopathologic classification of small cell lung most cancers: changing ideas and terminology. Cytologic prognosis of bronchioloalveolar carcinoma by fine needle aspiration biopsy. Diagnosis by fantastic needle aspiration biopsy with histologic and ultrastructural confirmation. A problemorientated method regarding the fantastic needle aspiration cytologic prognosis of bronchioloalveolar carcinoma of the lung: a comparison of diagnostic standards with benign lesions mimicking carcinoma. Differentiating cytological features of bronchioloalveolar carcinoma from adenocarcinoma of the lung in fine-needle aspirations: a statistical evaluation of 27 instances. Light and electron microscopic evaluation of intranuclear inclusions in papillary adenocarcinoma of the lung. Psammoma our bodies in nice needle aspiration cytology of papillary adenocarcinoma of the lung. Giant cell carcinoma of the lung: cytologic study of the exfoliated cells in sputa and bronchial washings. Cytomorphologic changes in cut up course radiation handled bronchogenic carcinomas. A review of cytologic findings in neuroendocrine carcinomas together with carcinoid tumors with histologic correlation. Carcinoid tumours of the lung: cytologic differential diagnosis in fine-needle aspirates. Carcinoids, atypical carcinoids and small cell carcinoma of the lung: differential prognosis of fantastic needle aspiration biopsy specimens. Typical and atypical pulmonary carcinoid tumor overdiagnosed as small-cell carcinoma on biopsy specimens: a serious pitfall in the management of lung cancer sufferers. Peripheral low grade mucoepidermoid carcinoma of the lung � needle aspiration cytodiagnosis and histology. Cytologic diagnosis of bronchial mucoepidermoid carcinoma by fine needle aspiration biopsy. Pulmonary cytology in the post-therapeutic monitoring of sufferers with bronchogenic carcinoma. Bronchoscopic cytology of metastatic breast carcinoma with osteoclast like big cells. Metaplastic breast carcinoma metastatic to the lung mimicking a major chondroid lesion: report of a case with cytohistologic correlation. Choriocarcinoma metastatic to the lung: a cytologic study with identification of human choriogonadotrophin with an immunoperoxidase method. Pulmonary metastases from intracranial meningioma recognized by aspiration biopsy cytology. Metastatic medullary carcinoma of the thyroid in sputum � a light-weight and electron microscopic research. Cytologic options of pulmonary metastasis from a granulosa cell tumor recognized by fine-needle aspiration: a case report. Metastatic pulmonary leiomyosarcoma: cytopathologic analysis on sputum examination. Cytological appearances of a solitary squamous cell papilloma with related mucous cell adenoma in the lung. Pulmonary oncocytoma: report of a case with cytologic, histologic and electron microscopic examine. Cartilaginous hamartoma of the lung: a possible pitfall in pulmonary fantastic needle aspiration. Fine needle aspiration cytology of sclerosing haemangioma of the lung, a mimicker of bronchioloalveolar carcinoma. Fine needle aspiration cytology of sclerosing haemangioma of the lung: case report with immunohistochemical study. Endobronchial granular cell tumour: cytology of a brand new case and evaluate of the literature. Fine needle aspiration cytology of a mediastinal granular cell tumor with histologic confirmation and ancillary studies. Bronchial granular cell tumour � report of a case with preoperative cytologic diagnosis on bronchial brushings and immunohistochemical studies. The pathology of malignant mesothelioma, including immunohistology and ultrastructure. Well differentiated papillary mesothelioma of the peritoneum: a borderline mesothelioma. Primary Chest wall and pleura, malignant pleural tumors (mesotheliomas) presenting as localised plenty.
Order 250 mg ampicillin with mastercard
In situ hybridization for affirmation of herpes simplex virus in bronchoalveolar smears antibiotic strep throat order ampicillin 250 mg free shipping. Anal intraepithelial neoplasia and different neoplastic precursor lesions of the anal canal and perianal region antibiotic use in livestock quality ampicillin 500 mg. Treatment of lung illness in sufferers with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. A comparability of induced and expectorated sputum for the prognosis of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Bronchoalveolar lavage and transbronchial biopsy for the prognosis of pulmonary infections in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Value of bronchoalveolar lavage within the analysis of pulmonary infection in acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Bronchoalveolar lavage as the unique diagnostic modality for Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Percutaneous needle lung aspiration for diagnosing pneumonitis in sufferers with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Atypical pathologic manifestation of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia within the required immune deficiency syndrome. Application in cardiac transplantation for the prognosis of pulmonary aspergillosis. Pulmonary mycetomas in immunocompetent sufferers: prognosis by fine needle aspiration. Diagnosis of histoplasmosis in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid by intracytoplasmic localization of silverpositive yeast. A evaluation of fine-needle aspiration cytology findings in human immunodeficiency virus an infection. Demonstration of parasites in toxoplasma lymphadenitis by fine-needle aspiration cytology: report of two cases. Review of central nervous system cytopathology in human immunodeficiency virus an infection. Alimentary tract cytopathology in human immunodeficiency virus an infection: a review of expertise in Los Angeles. Increased frequency of post-transplant lymphomas in patients treated with cyclosporine, azathioprine, and prednisone. Post-transplant lymphoproliferative problems; a morphologic, phenotypic and genotypic spectrum of disease. Utility of bronchoalveolar lavage within the prognosis of drug-induced pulmonary toxicity. Secretion of thyroid hormones takes place Superior thyroid artery Superior thyroid vein Internal jugular vein Isthmus of thyroid gland Inferior thyroid vein Thyroid gland left lobe Common carotid artery Sternum Arch of aorta Internal mammary vein Anatomy and physiology the thyroid is a bilobed endocrine organ located on either side of the trachea and oesophagus. Each lobe is about 5 cm in size and extends from the oblique line of the thyroid cartilage to the sixth tracheal ring. It is invested by the pretracheal fascia, which is firmly hooked up posteriorly to the second to fourth tracheal rings. For this cause, the gland and tumours arising from it characteristically move with the larynx on swallowing. The thyroid is derived embryologically as a downgrowth from the bottom of the tongue. A tubular evagination of endodermally derived cells, the thyroglossal duct, extends inferiorly in front of the laryngeal cartilage and the trachea. The distal finish proliferates, forming the thyroid lobes and the trail of descent ought to be obliterated. The calcitonin secreting cells are thought to come up as a separate contribution to the embryonic thyroid gland from the fourth and fifth pharyngeal pouches (ultimobranchial body). The follicles are spheroidal structures lined by a single layer of cuboidal follicular cells. The cells have microvillous processes embedded in the central store of Superior parathyroid gland Right lobe of thyroid gland Inferior parathyroid gland Trachea Inferior thyroid artery Recurrent laryngeal nerve. Longstanding saved thyroglobulin may accumulate calcium oxalate crystals and ageing follicular cells accumulate lipofuscin. This hormone has a hypocalcaemic motion but its physiological significance in man is unclear. These cells are extraordinarily tough to distinguish from follicular cells using standard histological stains. The cells are slightly larger, paler and spindle or polyhedral in shape with a faintly granular cytoplasm. They are preferentially localised within the thyroid to the central areas of the lateral lobes and are particularly seen in proximity to strong cell nests, which are thought to be ultimobranchial physique remnants. Core biopsy was related to an elevated danger of affected person discomfort and problems with little difference in diagnostic worth. Prior to consideration of needle aspiration, the history, examination, biochemical and imaging findings must be considered. Findings of significance for possible thyroid malignancy embody a household history of thyroid most cancers or adrenal phaeochromocytoma, earlier head and neck irradiation, fast progress, hardness or adherence of the lump to surrounding buildings and the presence of associated lymphadenopathy. Serological info and thyroid autoantibody levels can be useful in some circumstances. These options embody microcalcifications, the irregularity of the nodule margin and intra-lesional vascularity. Some of these lesions could additionally be microcarcinomas of uncertain medical significance but diagnosis and surgical elimination is appropriate as a minority behave aggressively. It is especially applicable to bigger discrete nodules that are clearly inside the thyroid. The ultrasonic features of these lesions give useful info as to their nature and permit evaluation of the remainder of the thyroid and native lymph nodes. The procedure ought to be preceded by scientific examination of the neck from the entrance and behind the seated affected person. The risk of a non-contributory, false adverse or false positive outcome must be talked about. This enables the head to fall again in a relaxed place, which separates the sternomastoid muscles, uncovering more of the lateral lobes of the thyroid. Patients will want reassurance as needle aspiration of the neck is amongst the more alarming websites for aspiration cytology. They should also be asked to not communicate or swallow through the procedure to keep away from movement of the gland. When aspiration is carried out in kids topical anaesthetic cream is efficacious however its use requires forethought, as the cream have to be utilized underneath an occlusive dressing for at least an hour to ensure anaesthesia. The vascularity of the thyroid implies that a 23, 25 or 27 gauge bevelled needle must be used. For the majority of thyroid lesions at most only three passes of the needle in a single plane must be carried out; persisting beyond this leads to blood contamination of the sample and the dilution or lack of diagnostic options.
Ampicillin 250 mg purchase amex
Functional impairment because of antibiotic resistance due to overuse of antibiotics 250 mg ampicillin buy with mastercard edema may happen bacteria die off symptoms cheap ampicillin 500 mg without prescription, for example, when it restricts vary of movement of joints. Edema or accumulated fluid across the coronary heart or lungs impairs the movement and function of these organs. Pain may happen if edema exerts stress on the nerves domestically, as with the headache that develops in sufferers with cerebral edema. If cerebral edema becomes extreme, the strain can impair mind function because of ischemia and can trigger demise. When viscera such as the kidney or liver are edematous, the capsule is stretched, causing ache. The increased interstitial pressure may restrict arterial blood move in to the realm, stopping the fluid shift that carries vitamins in to the cells. This can prevent normal cell operate and replica and eventually ends in tissue necrosis or the event of ulcers. This situation is obvious in people with extreme varicose veins within the legs-large, dilated veins which have a high hydrostatic pressure. Varicose veins can lead to fatigue, pores and skin breakdown, and varicose ulcers (see chapter 18). Edematous tissue within the pores and skin could be very vulnerable to tissue breakdown from pressure, abrasion, and external chemical substances. Explain briefly why an toddler is extra weak than a younger adult to fluid loss. If more sodium is lost from the extracellular compartment than water, how will fluid move between the cell and the interstitial compartment For instance, if fluid is misplaced from the digestive tract because of vomiting, water shifts from the vascular compartment in to the digestive tract to exchange the misplaced secretions. If the deficit continues, eventually fluid is misplaced from the cells, impairing cell perform. Fluid loss is commonly measured by a change in physique weight; understanding the usual body weight of a person could be very helpful in assessment of the extent of loss. As a basic guide to extracellular fluid loss, a gentle deficit is defined as a lower of 2% in body weight, a moderate deficit as a 5% weight loss, and extreme dehydration as a decrease of 8%. Dehydration is a extra significant issue for infants and elderly individuals, who lack vital fluid reserves in addition to the flexibility to preserve fluid quickly. Infants also expertise not solely higher insensible water losses through their proportionately larger body surface area but in addition an increased want for water owing to their higher metabolic price. The vascular compartment is rapidly depleted in an infant (hypovolemia), affecting the center, brain, and kidneys. This is indicated by decreased urine output (number of moist diapers), elevated lethargy, and dry mucosal membranes. Water loss is usually accompanied by a loss of electrolytes and typically of proteins, relying on the particular cause of the loss. Electrolyte losses can influence water steadiness considerably as a result of electrolyte modifications lead to osmotic pressure change between compartments. Isotonic dehydration refers to a proportionate loss of fluid and electrolytes, hypotonic dehydration to a lack of more electrolytes than water, and hypertonic dehydration to a lack of extra fluid than electrolytes. The latter two forms of dehydration cause indicators of electrolyte imbalance and affect the motion of water between the intracellular and extracellular compartments (see the following part of this chapter, Electrolyte Imbalances). Vomiting and diarrhea, both of which lead to loss of quite a few electrolytes and vitamins corresponding to glucose, as well as water; drainage or suction of any portion of the digestive system can also end in deficits 2. Diabetic ketoacidosis with lack of fluid, electrolytes, and glucose within the urine four. Use of a concentrated formula in an attempt to present extra nutrition to an infant Effects of Dehydration Initially, dehydration includes a decrease in interstitial and intravascular fluids. Examples include peritonitis, the irritation and an infection of the peritoneal membranes, and burns. The result of this shift is a fluid deficit in the vascular compartment (hypovolemia) and a fluid excess within the interstitial space. Laboratory checks corresponding to hematocrit and electrolyte concentrations will indicate third spacing. In the case of burns, the third spacing is obvious as edema in the area of the injuries. The focus of electrolytes in plasma varies barely from that in the interstitial fluid or different kinds of extracellular fluids. The number of anions, together with these present in small quantities, is equivalent to the focus of cations within the intracellular compartment (or the plasma) so as to keep electrical neutrality (equal adverse and constructive charges) in any compartment. Sodium transport across the cell membrane is controlled by the sodium-potassium pump or lively transport leading to sodium ranges which might be high within the extracellular fluids and low inside the cell. It exists in the body primarily within the type of the salts sodium chloride and sodium bicarbonate. It is ingested in meals and beverages, usually in additional than sufficient quantities, and is misplaced from the body in perspiration, urine, and feces. Sodium ranges in the body are primarily managed by the kidneys via the action of aldosterone. Sodium is essential for the maintenance of extracellular fluid volume through its impact on osmotic pressure because it makes up roughly 90% of the solute in extracellular fluid. For example, extreme sweating could end in a low serum sodium degree if proportionately more sodium is misplaced than water or if only water is used to replace the loss. If an individual loses more water than sodium in perspiration, the serum sodium degree may be excessive. Causes of hyponatremia A sodium deficit may result from direct lack of sodium from the body or from an extra of water within the extracellular compartment, leading to dilution of sodium. A excessive fever is more doubtless to cause deep, rapid respirations, excessive perspiration, and better metabolic fee. List several reasons why consuming a fluid containing water, glucose, and electrolytes would be higher than drinking faucet water after vomiting. Effects of hyponatremia Low sodium ranges impair nerve conduction and lead to fluid imbalances in the compartments. Manifestations embody fatigue, muscle cramps, and belly discomfort or cramps with nausea and vomiting (Table 6-5). Water shifts out of blood Na+ K+ K+ High osmotic strain in cell K+ K+ K+ K+ K+ 2. List the signs and symptoms common to both hyponatremia and hypernatremia and in addition any indicators that differentiate the 2 states. More K+ diffuse in to blood K+ K+ K+ extra K+ H+ K+ H+ H+ H+ K+ K+ H+ K+ Cell H+ H+ 3. Potassium is ingested in foods and is excreted primarily in the urine beneath the affect of the hormone aldosterone. Foods high in potassium include bananas, citrus fruits, tomatoes, and lentils; potassium chloride tablets could additionally be taken as a supplement. The hormone insulin also promotes motion of potassium in to cells (see chapter 25). Potassium ranges are additionally influenced by the acid-base balance within the physique; acidosis tends to shift potassium ions out of the cells in to the extracellular fluids, and alkalosis tends to move extra potassium in to the cells. With acidosis, many hydrogen ions diffuse from the blood in to the interstitial fluid due to the high hydrogen ion concentration within the blood.